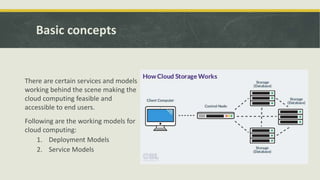
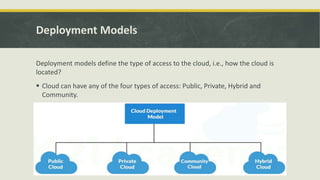
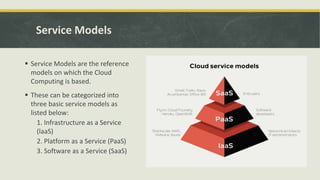
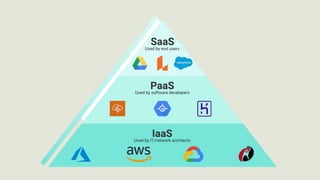
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Key features of cloud computing include on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. Common types of cloud computing include public, private, hybrid and community clouds. Common cloud service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).