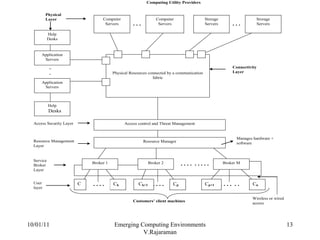
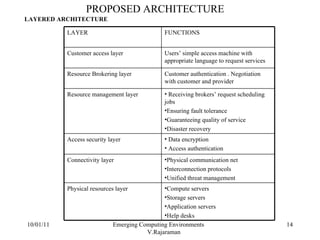
The document discusses emerging computing environments like grid computing, cloud computing, and computing utilities. It explains that these environments allow distributed computing resources to be accessed remotely over the internet on a pay-per-use basis. This helps organizations avoid the high costs of maintaining their own computing infrastructure and gives them flexible access to advanced software and applications. The document also outlines some of the key characteristics and components of these emerging environments.