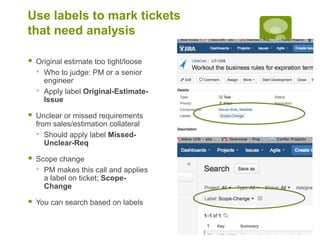
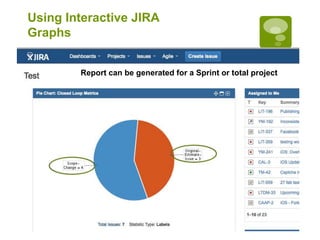
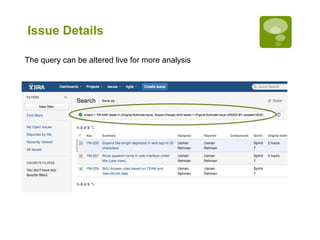
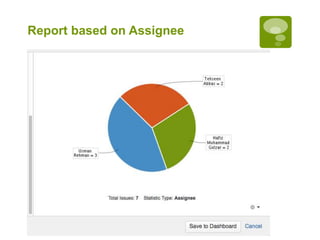
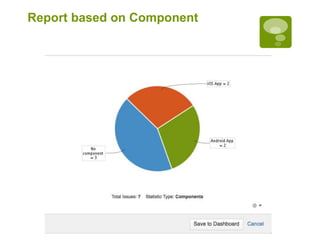
This document discusses a closed loop process for project estimation and delivery. The process involves:
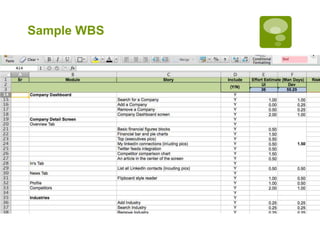
1. Creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) by defining project modules, user stories, and tasks.
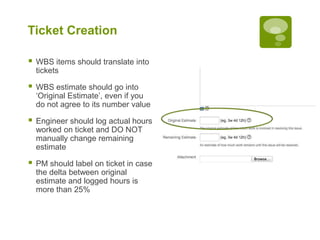
2. Estimating the effort for each WBS item.
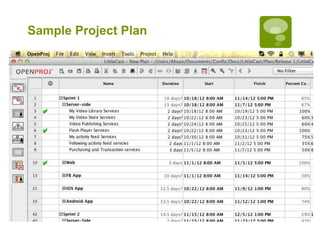
3. Creating a project plan.
4. Having a project kick-off meeting.
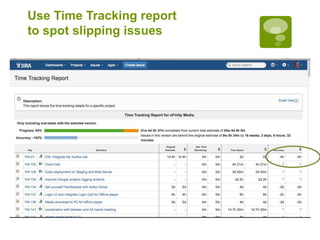
5. Executing sprints, logging hours against tickets, and gathering metrics on estimates versus actuals.
6. Analyzing variance data to improve future estimations and catch issues.