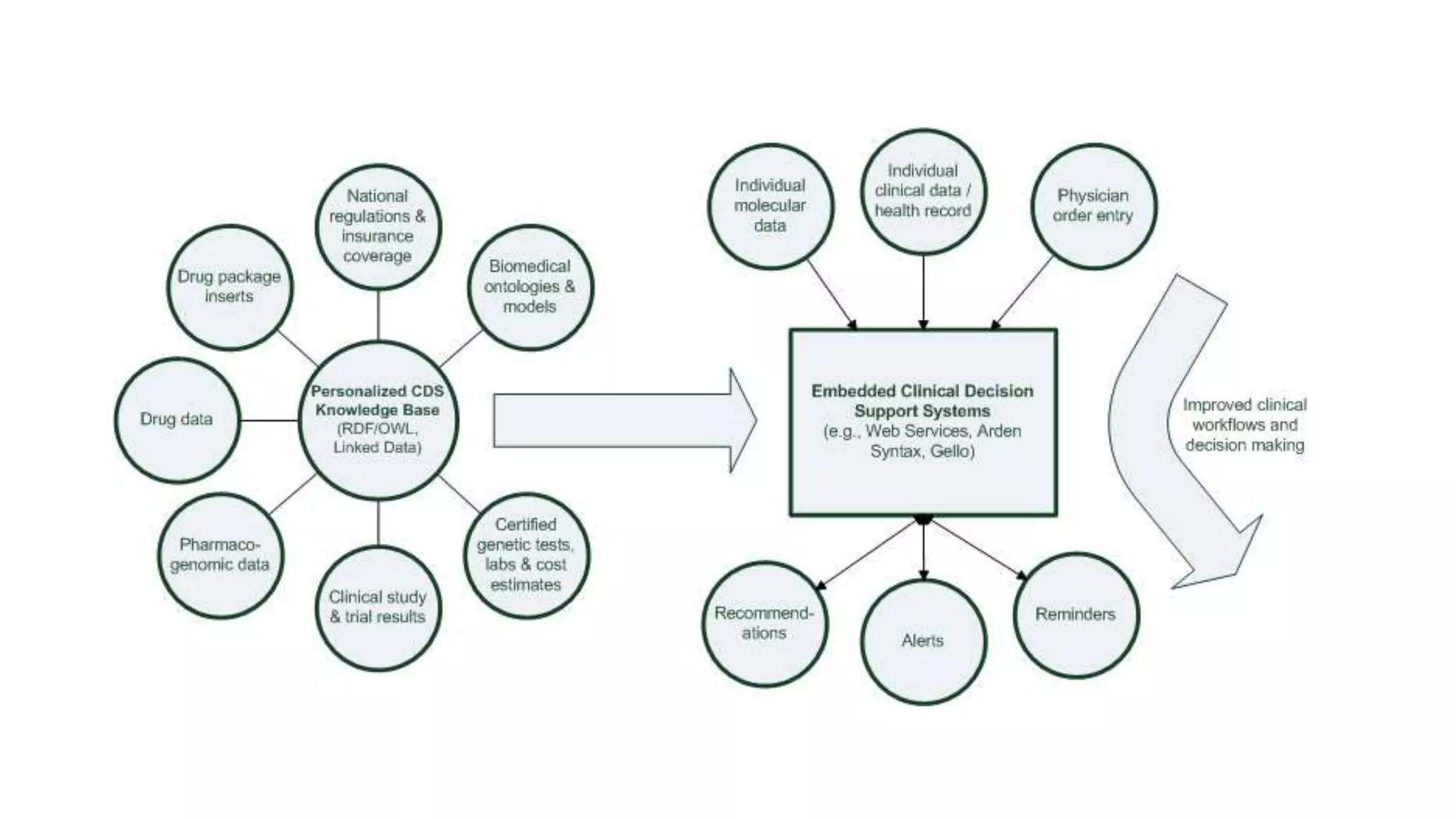
A clinical decision support system (CDSS) is an interactive computer program that uses patient data to generate advice to help clinicians make decisions. A CDSS uses a dynamic knowledge base and rules derived from experts to make suggestions, which clinicians can then use along with their own expertise to determine diagnoses and treatments. CDSS systems are used at the point of care to assist clinicians before, during, and after making diagnoses. They work by taking in patient data, applying medical knowledge, and providing recommendations to aid clinical decision making.