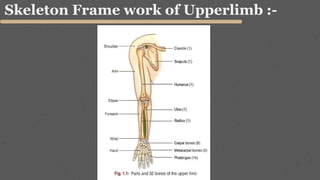
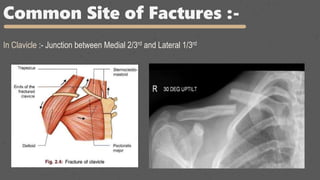
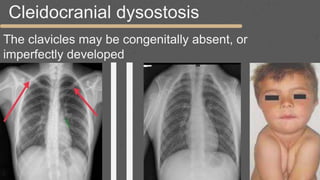
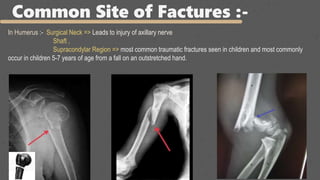
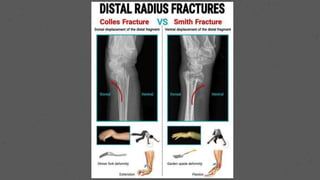
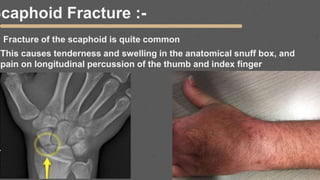
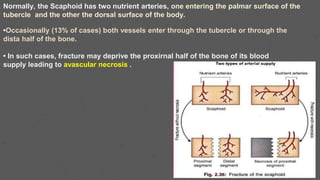
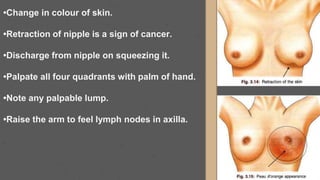
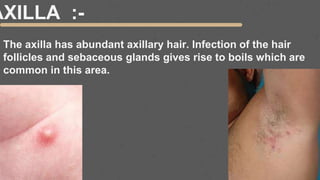
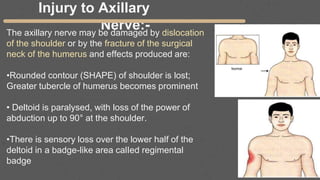
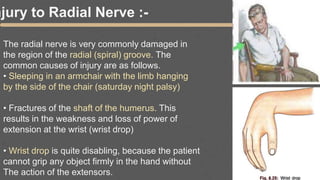
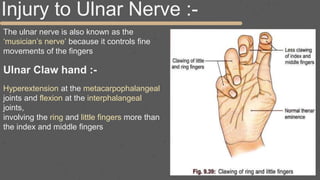
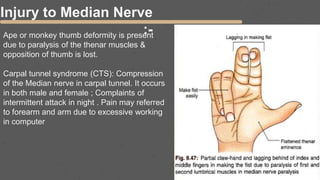
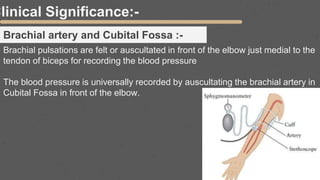
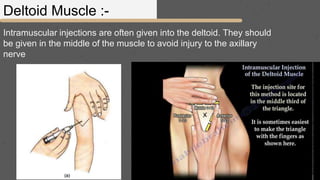
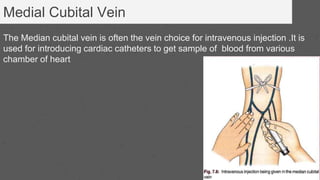
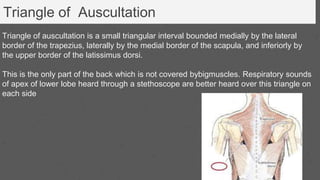
This document provides an overview of the clinical anatomy of the upper limb, including common sites of fractures and injuries. It discusses the skeleton framework, clavicle fractures, cleidocranial dysplasia, scapula winging, humerus fractures at the surgical neck and supracondylar region, radius fractures including Colles' and Smith's, ulna fractures of the shaft and olecranon, scaphoid fractures and avascular necrosis, injuries to nerves including the axillary, radial, ulnar and median nerves, and the clinical significance of the brachial artery, cubital fossa, deltoid muscle, median cubital vein, and triangle of auscultation.