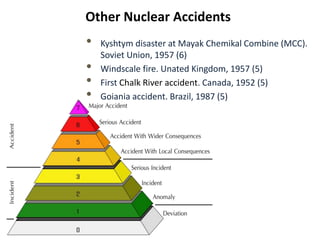
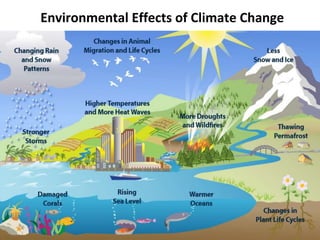
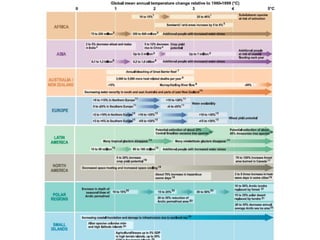
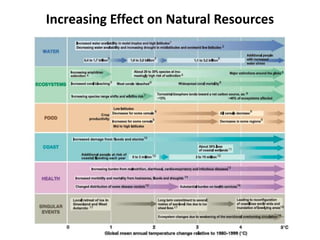
The document discusses the risks of climate change and strategies to address it. It provides context on climate change including that it is caused by global warming due to human greenhouse gas emissions. Examples are given of how climate change is impacting different regions of the world through increased temperatures, changes in weather patterns, rising sea levels, and more frequent extreme weather events. The document also examines past nuclear disasters and how nuclear winter could potentially impact the climate. It outlines goals to limit global warming and strategies companies and governments are implementing to increase energy efficiency, transition to renewable resources, and develop new technologies and policies to mitigate climate change.