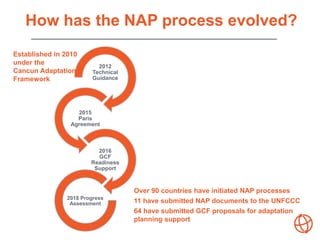
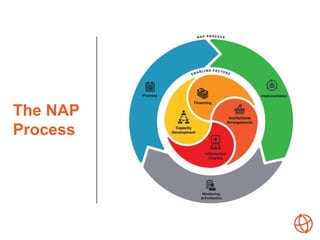
This document provides an overview of the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) process, which aims to integrate climate change adaptation into development planning at the national, sectoral, and local levels. Over 90 countries have initiated NAP processes to assess climate risks, identify adaptation priorities, and enhance coordination on adaptation actions. The NAP process is intended to be strategic, coordinated, iterative, country-driven, and participatory to effectively reduce vulnerability to climate impacts over the medium and long term.