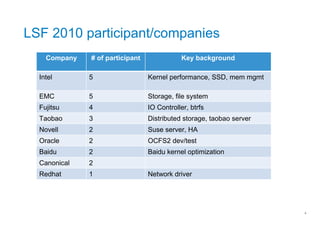
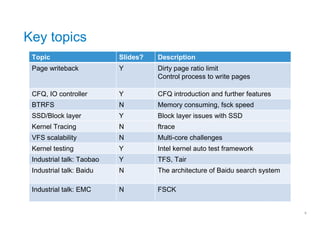
The document summarizes key topics and industry talks from the China Linux Summit Forum (CLSF) 2010 conference in Shanghai. It discusses presentations on writeback optimization, the BTRFS file system, SSD challenges, VFS scalability, kernel testing frameworks, and talks from companies like Intel, EMC, Taobao, and Baidu on their storage architectures and solutions. Attendees included representatives from Intel, EMC, Fujitsu, Taobao, Novell, Oracle, Baidu, and Canonical discussing topics around file systems, storage, and kernel optimizations.