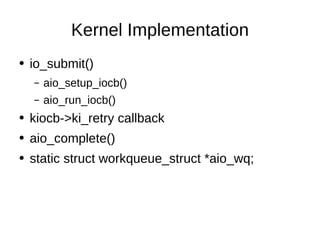
The document discusses two approaches to asynchronous I/O in Linux: POSIX AIO and Linux native AIO. POSIX AIO is implemented in userspace using pthreads, supports common operations like read and write, and queues requests to a thread pool for processing. Linux native AIO runs in the kernel, only supports direct I/O, and uses workqueues to handle requests asynchronously without threads. It provides syscalls like io_setup() and io_submit() as well as libaio wrappers for submitting and getting results of asynchronous I/O operations.
![Linux AIO [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linux-aio-111209112815-phpapp01/75/Linux-aio-1-2048.jpg)



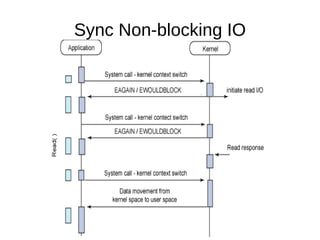
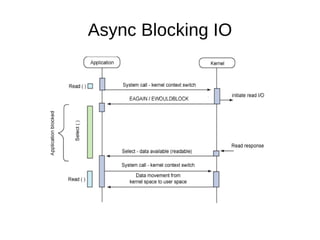
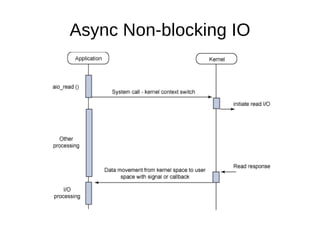








![Syscall APIs int io_setup(int maxevents, io_context_t *ctxp); int io_destroy(io_context_t ctx); int io_submit(io_context_t ctx, long nr, struct iocb *ios[]); int io_cancel(io_context_t ctx, struct iocb *iocb, struct io_event *evt); int io_getevents(io_context_t ctx_id, long min_nr, long nr, struct io_event *events, struct timespec *timeout);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linux-aio-111209112815-phpapp01/85/Linux-aio-16-320.jpg)