This document provides an overview of chronic liver disease (CLD) including:
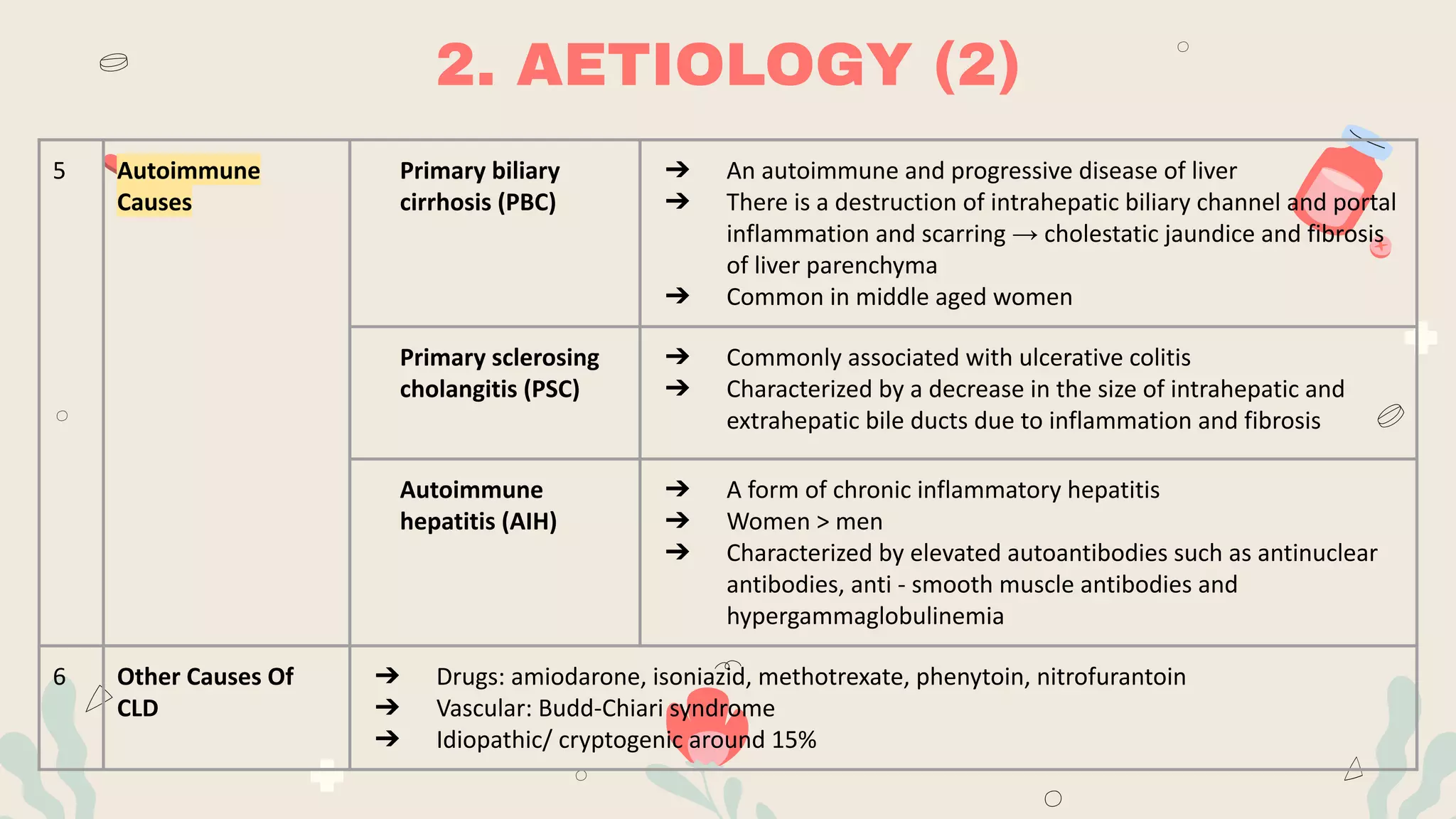
- CLD results from long-term inflammation and damage to the liver that can progress to cirrhosis over 6 months. Common causes include alcohol, viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, and genetic/autoimmune conditions.
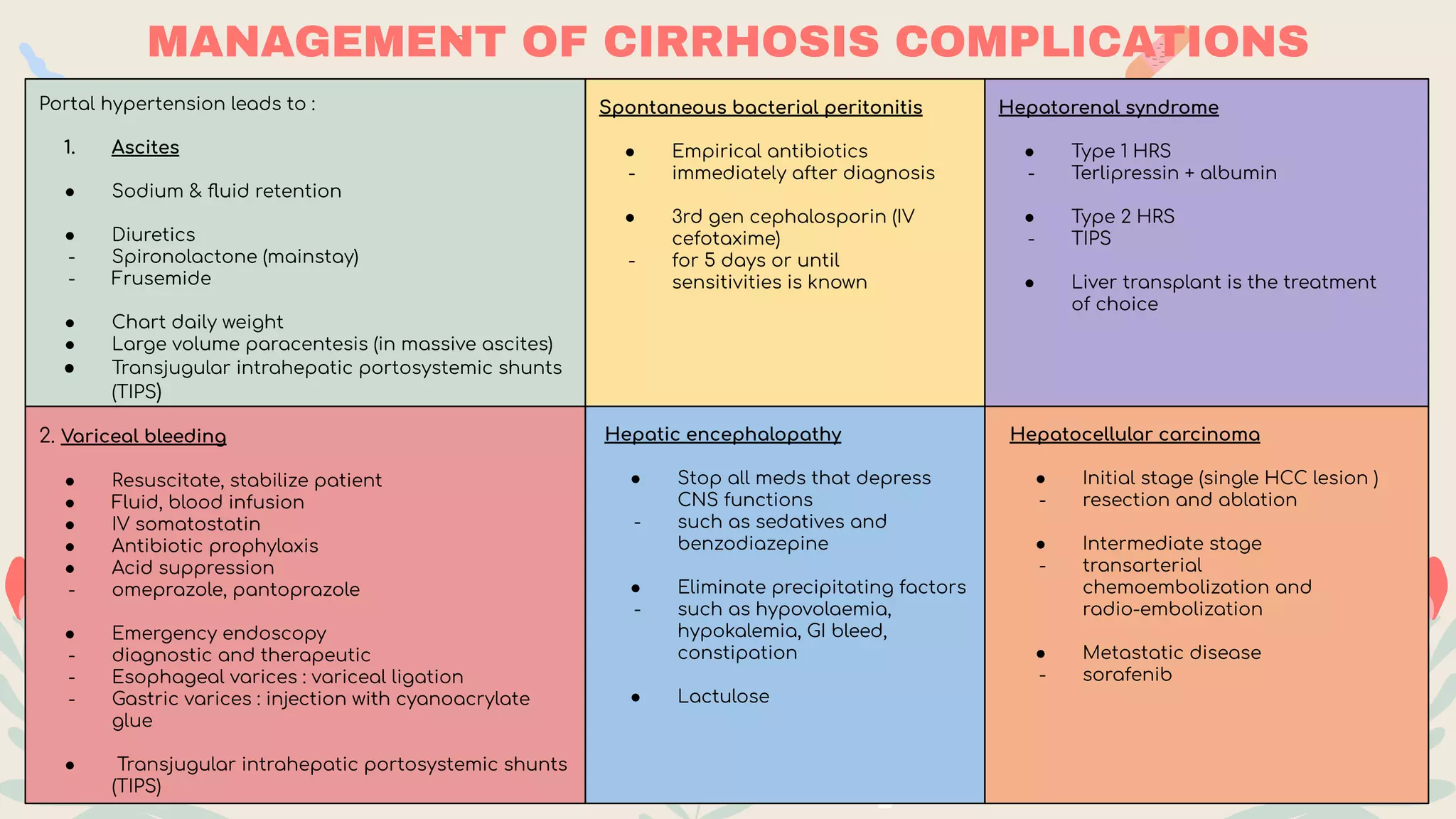
- Clinical manifestations range from asymptomatic to jaundice, abdominal pain/swelling, bleeding, confusion and liver failure. Complications include portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy and liver cancer.
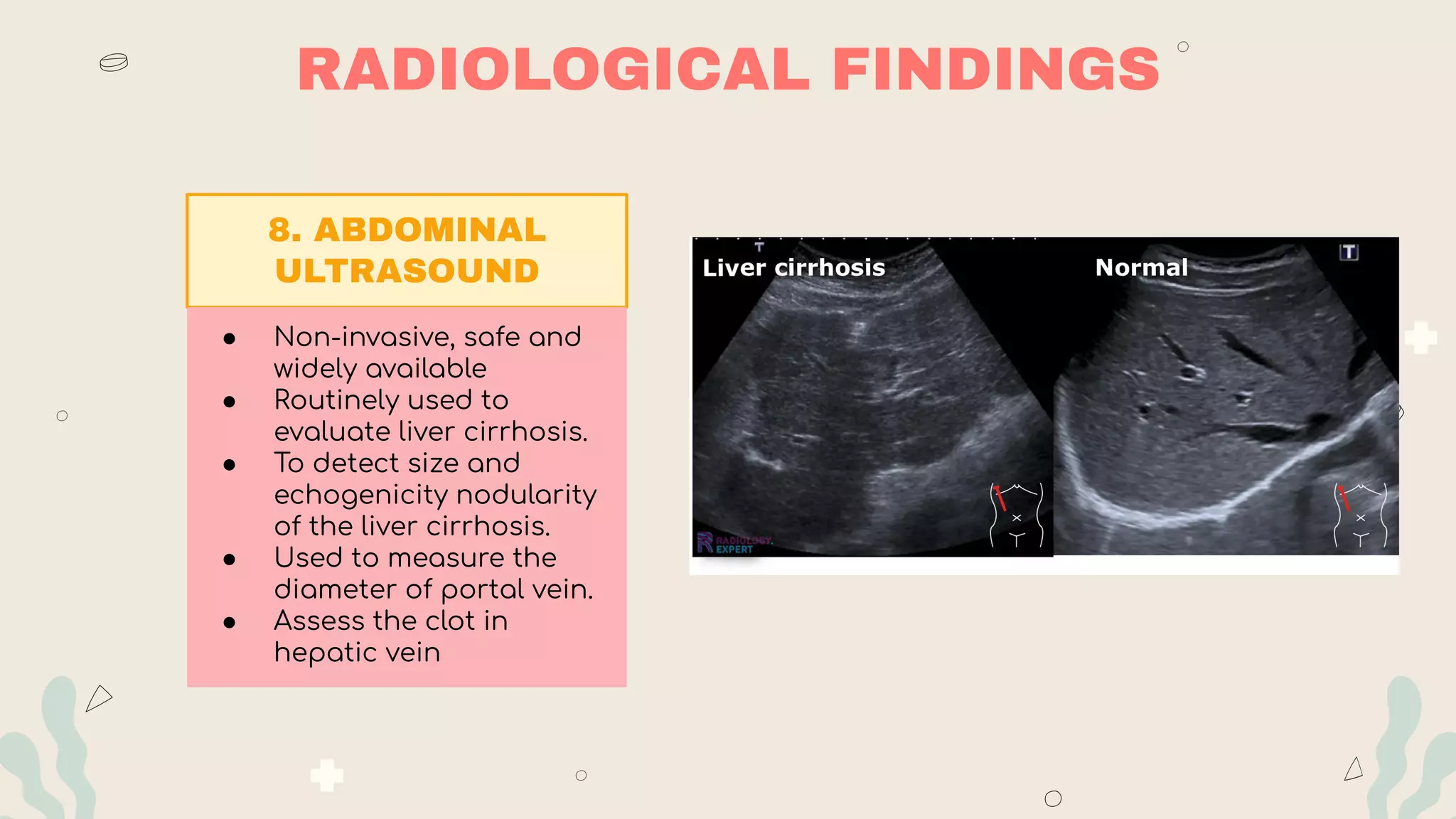
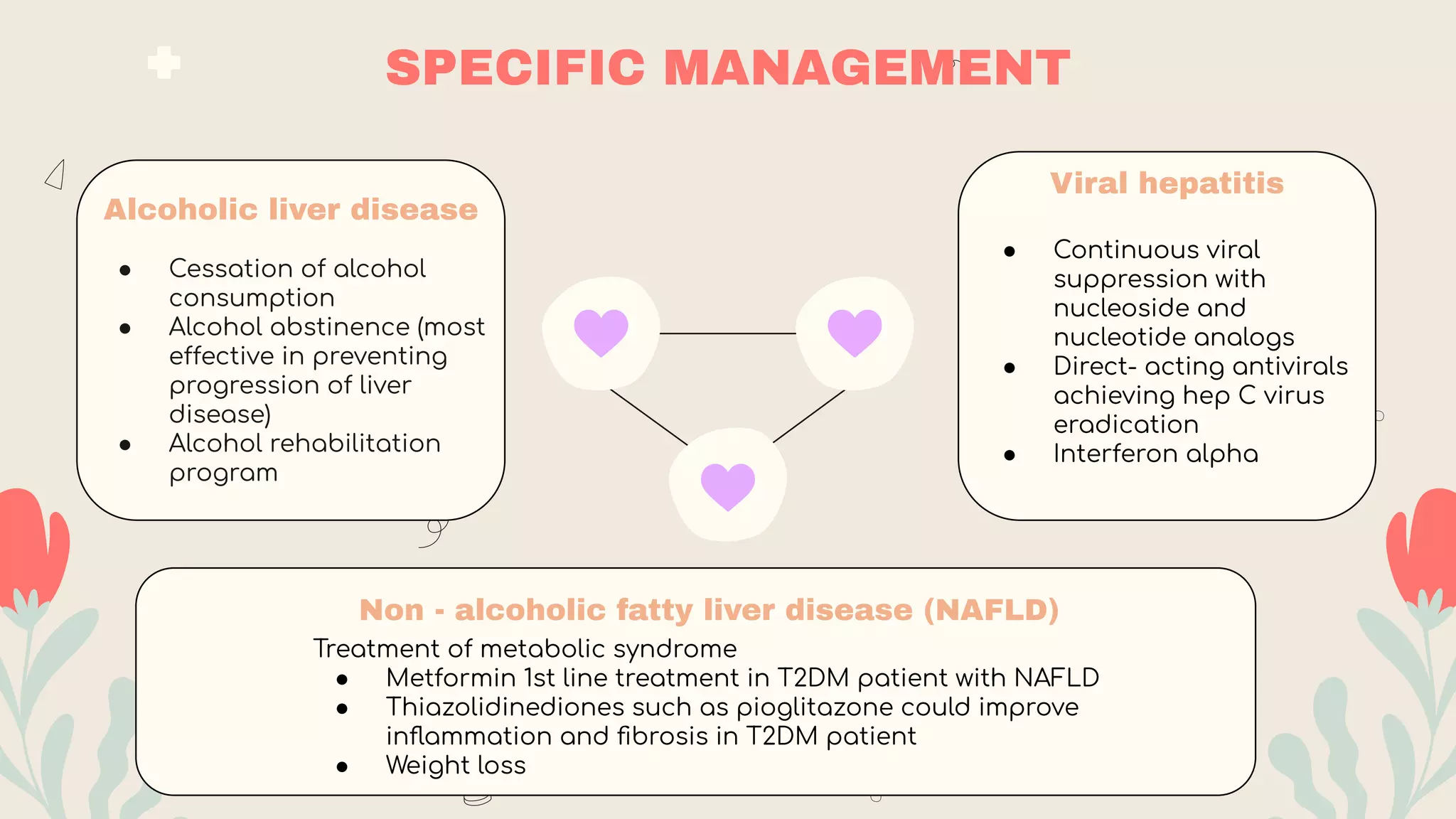
- Investigations include blood tests of liver function and damage, imaging like ultrasound/CT, and biopsy. Prognosis is assessed using Child-Pugh or MELD scores. Management focuses on treating the underlying


















![MELD SCORE (MODIFICATION OF
END STAGE LIVER DISEASE)
To convert:
• bilirubin from umol/L to mg/dL divide by 17
• creatinine from umol/L to mg/dL divide by 88.4
[ 3.8 x LN (bilirubin in mg/dL)] + [ 9.6 x LN
(creatinine in mg/dL) ] + [ 11.2 x LN (INR) ] + 6.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronicliverdisease1-230723175649-f09030e8/75/Chronic-Liver-Disease-1-pdf-23-2048.jpg)