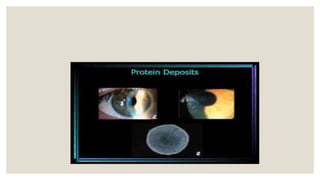
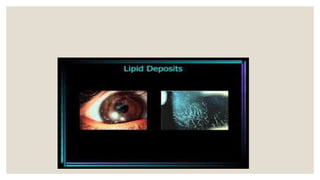
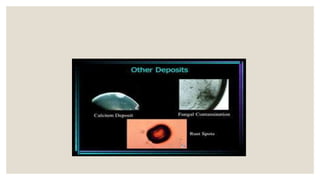
This document discusses contact lens deposits. It defines deposits as any surface coating or matrix that does not rinse off during blinking. Deposits are categorized by position (external or internal) and nature (organic or inorganic). Organic deposits include proteins and lipids from tears. Inorganic deposits include calcium salts and pigments. Environmental deposits come from sources like tap water or cosmetics. The document outlines how deposits form and their effects like discomfort, blurred vision, and increased risk of infection. It also describes different methods for removing protein, lipid, and other types of deposits from contact lenses.