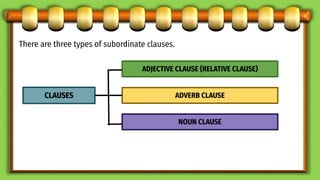
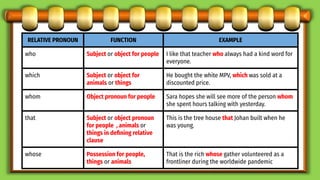
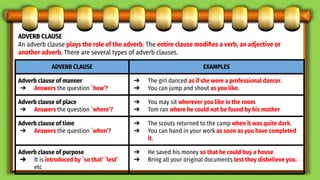
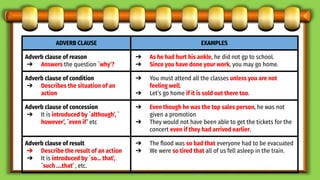
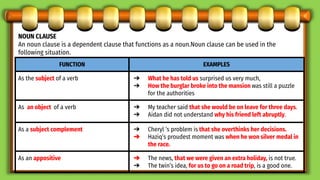
This document discusses different types of subordinate clauses in grammar. It defines a subordinate clause as a clause that cannot stand alone as a complete sentence and provides supporting information to the main clause. There are three main types of subordinate clauses: adjective clauses, adverb clauses, and noun clauses. Adjective clauses modify nouns and are introduced by relative pronouns. Adverb clauses modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs and describe manner, place, time, purpose, reason, condition, concession, or result. Noun clauses function as nouns and can be subjects, objects, subject complements, or appositives. Examples of each type of clause are provided.