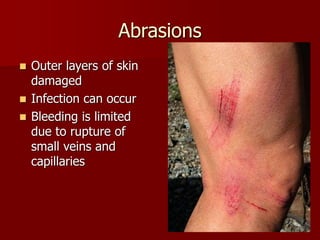
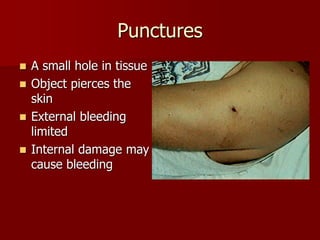
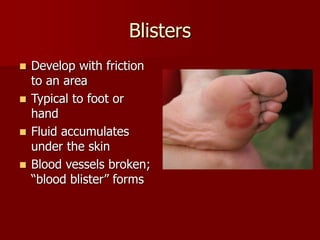
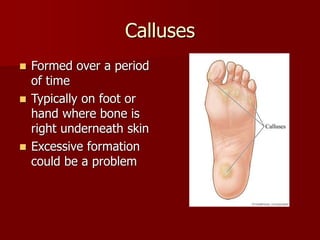
This document categorizes and describes different types of wounds: abrasions involve damage to the outer skin layers and limited bleeding; lacerations are jagged tears of soft tissue; and punctures are small holes caused by piercing objects. It also covers treatments for blisters, calluses, and wound management, noting that immediate treatment should involve cleaning and monitoring for signs of infection such as pain, swelling, and pus formation.