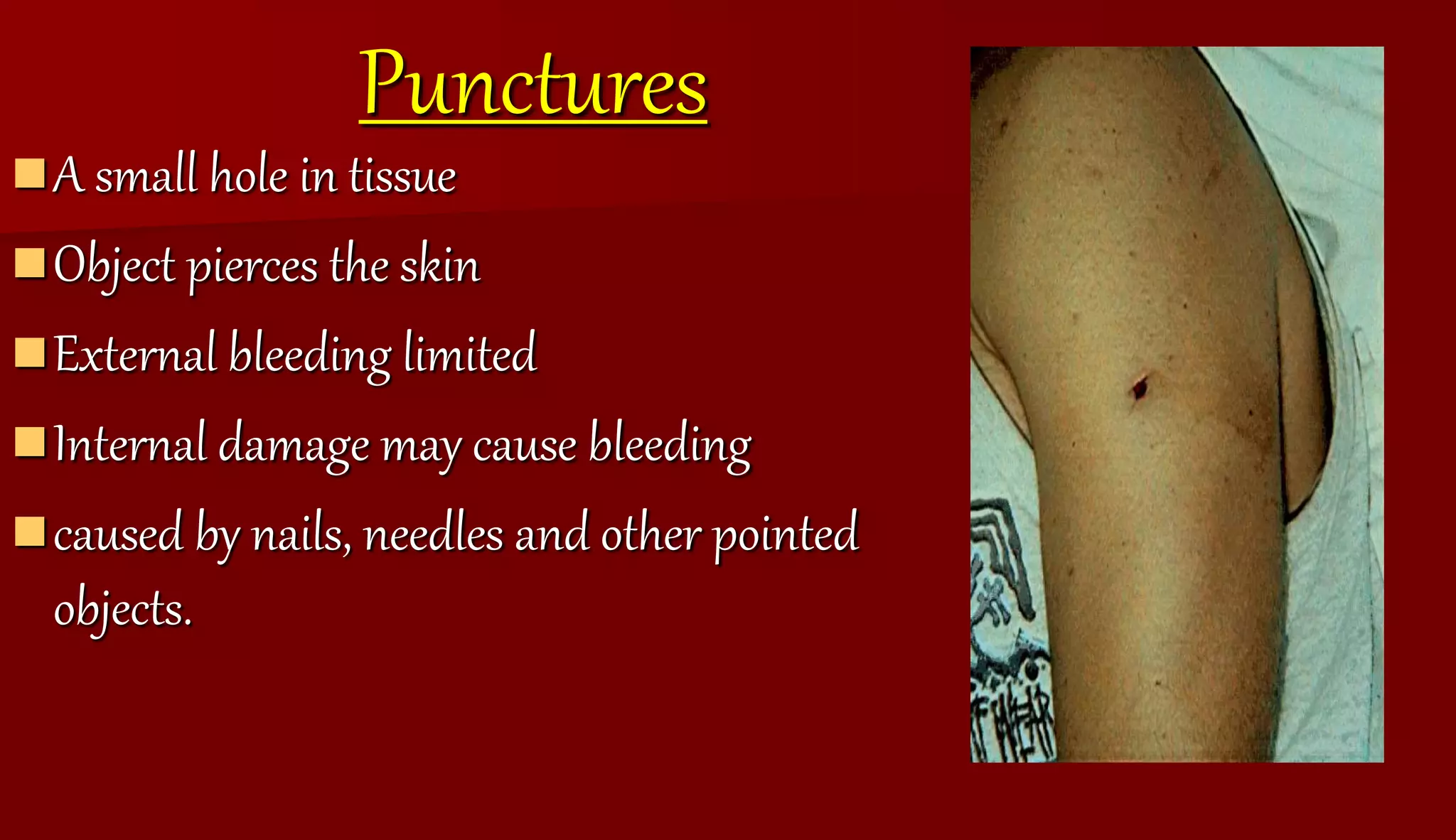
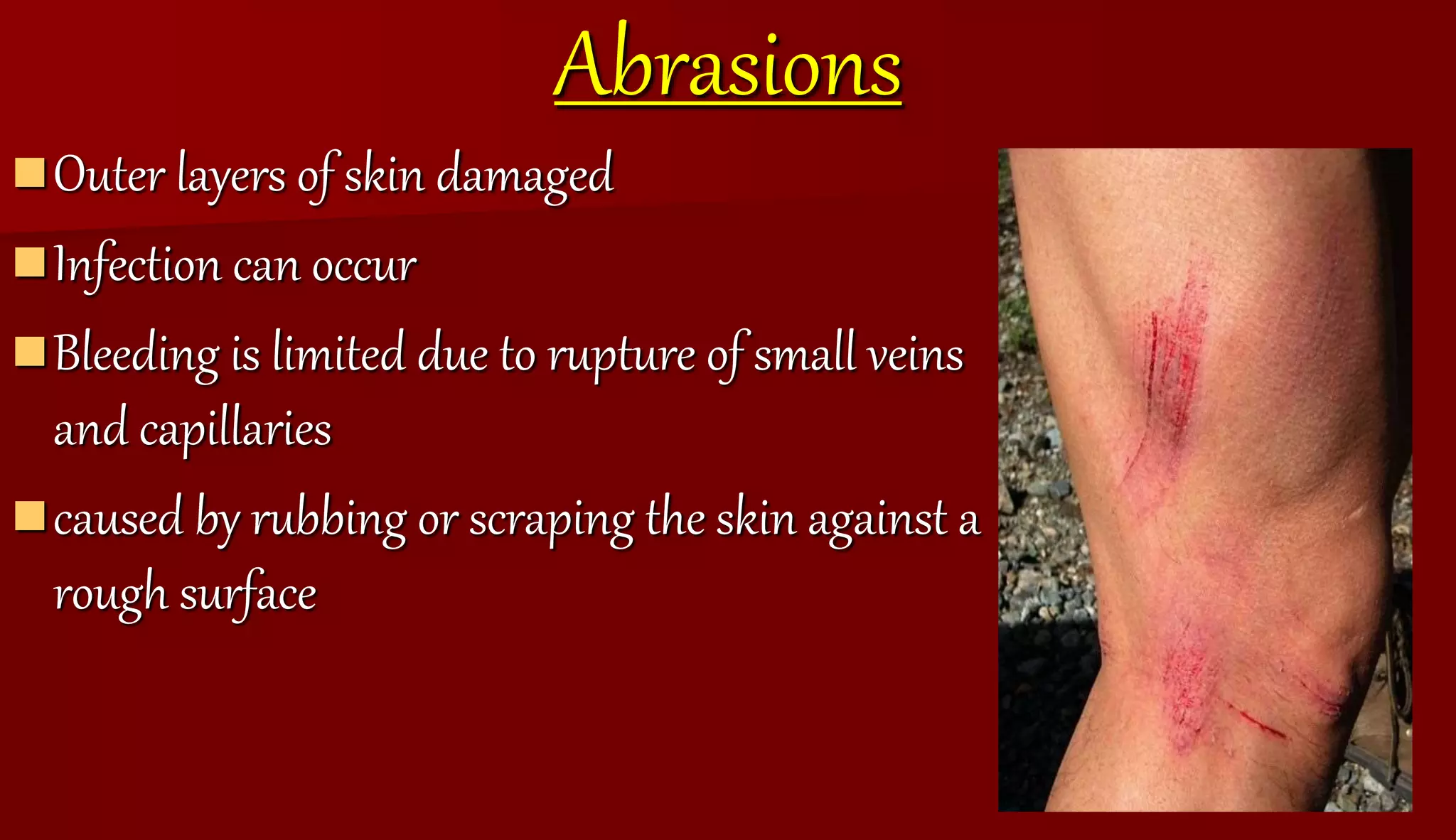
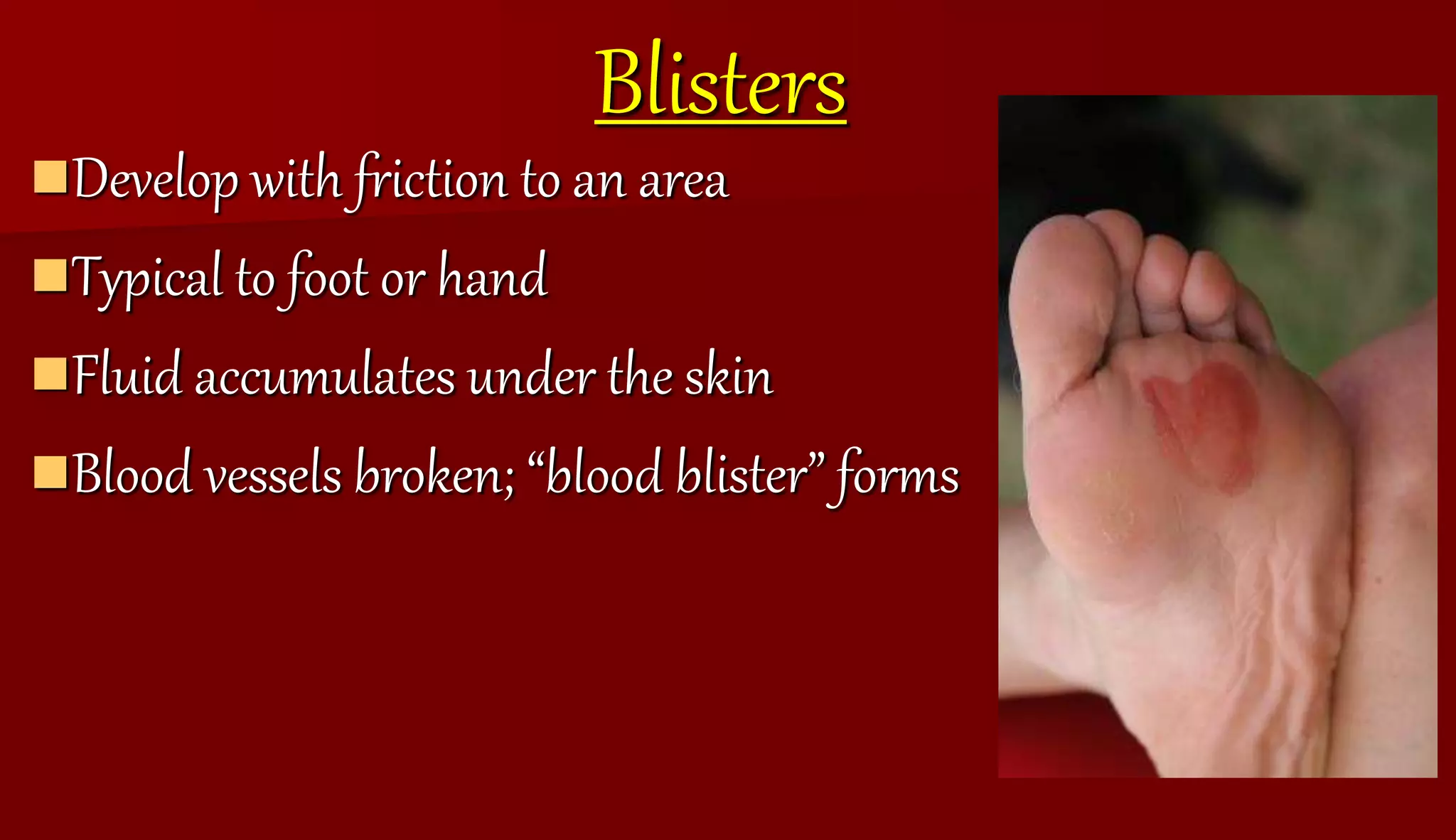
The document defines and describes different types of wounds including incisions, punctures, calluses, lacerations, avulsions, and abrasions. It also outlines signs of infection in wounds such as pain, swelling, redness, heat, loss of function, and fever. The document provides treatment advice for wounds with severe bleeding and blisters.