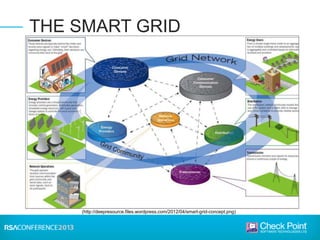
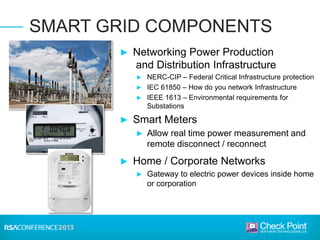
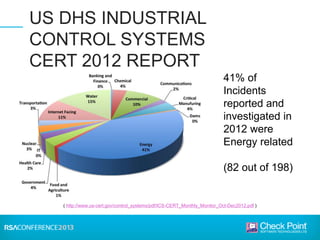
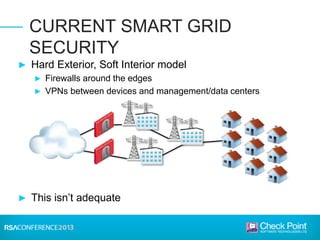
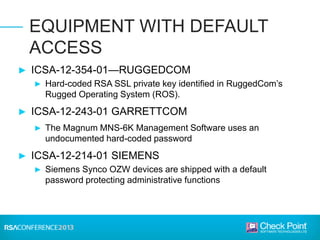
This document discusses the security challenges facing the smart grid. It notes that the smart grid involves networking power infrastructure like substations, distribution networks, and smart meters. However, energy companies building these systems lack security expertise. Attacks on power infrastructure could have serious consequences by disrupting power or killing people. The document outlines challenges like default passwords on equipment and USB attacks. It argues that a "hard exterior/soft interior" security model is not enough, and recommends measures like malware detection, control protocol inspection, and frequent software updates to help secure the smart grid.