This document discusses the factors affecting India's climate and the seasonal patterns of weather in India. It describes:
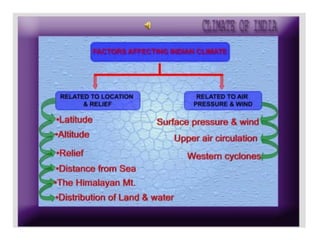
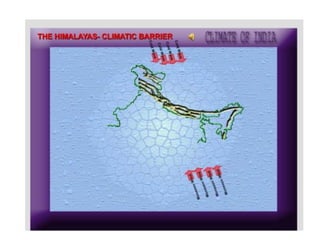
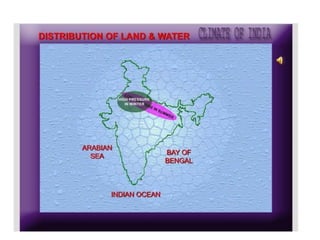
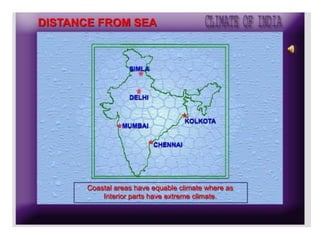
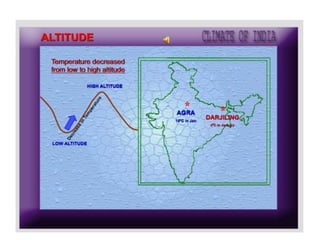
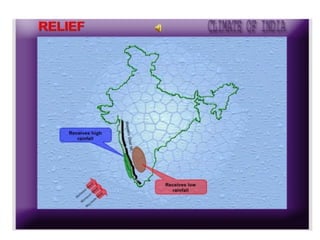
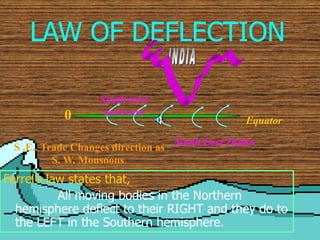
1) The key geographic factors that influence India's climate, including its location, latitude, relief features like the Himalayas and Western Ghats, surface winds, air currents, and ocean patterns.
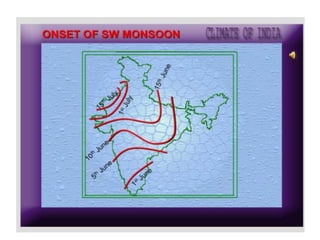
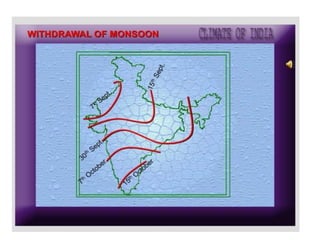
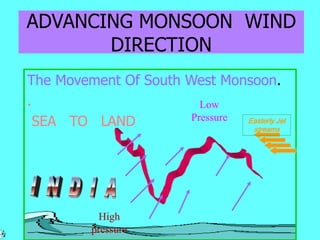
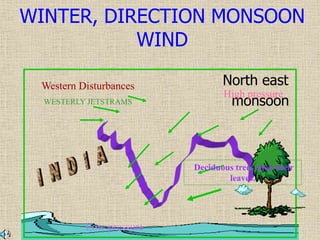
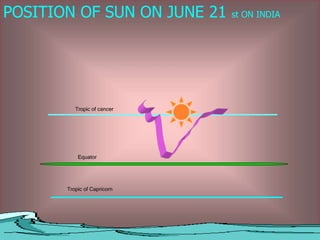
2) The seasonal patterns of weather in India - the hot weather season from March to May, the advancing monsoon from June to September, the retreating monsoon from October to November, and the cold weather season from December to February.
3) The characteristic weather features of each season, including monsoon winds, rainfall distribution, temperature variations in different regions, and seasonal precipitation patterns across India