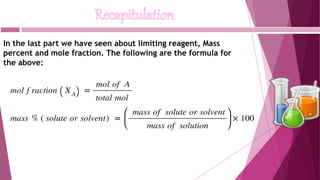
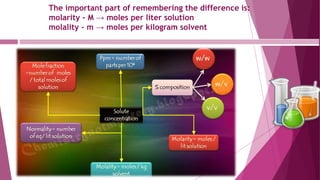
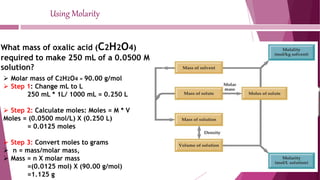
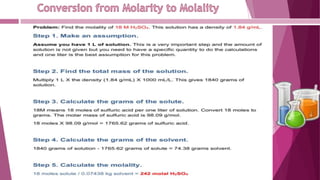
This document discusses stoichiometry calculations involving molarity and molality. It provides examples of calculating molarity, molality, mass percent, and mole fraction for various solutions. Molarity is moles per liter of solution, while molality is moles per kilogram of solvent. Examples include calculating the molality of NaCl in water, the molarity of HCl in a solution, and the molality, molarity, and mass of various solutes needed to make solutions of specific concentrations.















![ 7.45 g of potassium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water. What will be the
molality of the solution?
1.11 g of urea was dissolved in 100 g of water. Calculate the molality of
solution. (N=14, H=1. C=12, O=16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class11sbccpartxi30thapril-200722072010/85/Class-11-sbcc-part-XI-21-320.jpg)
