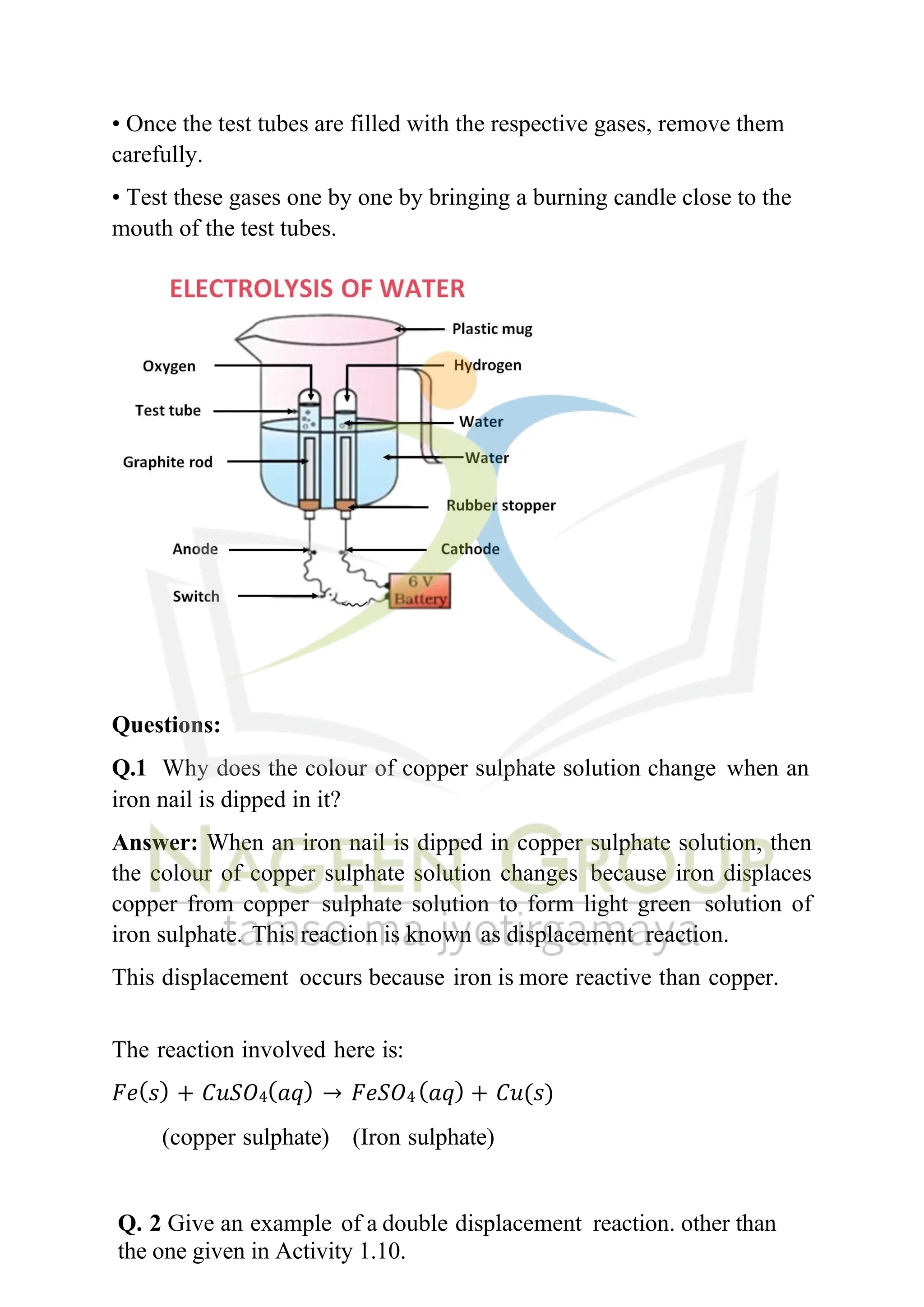
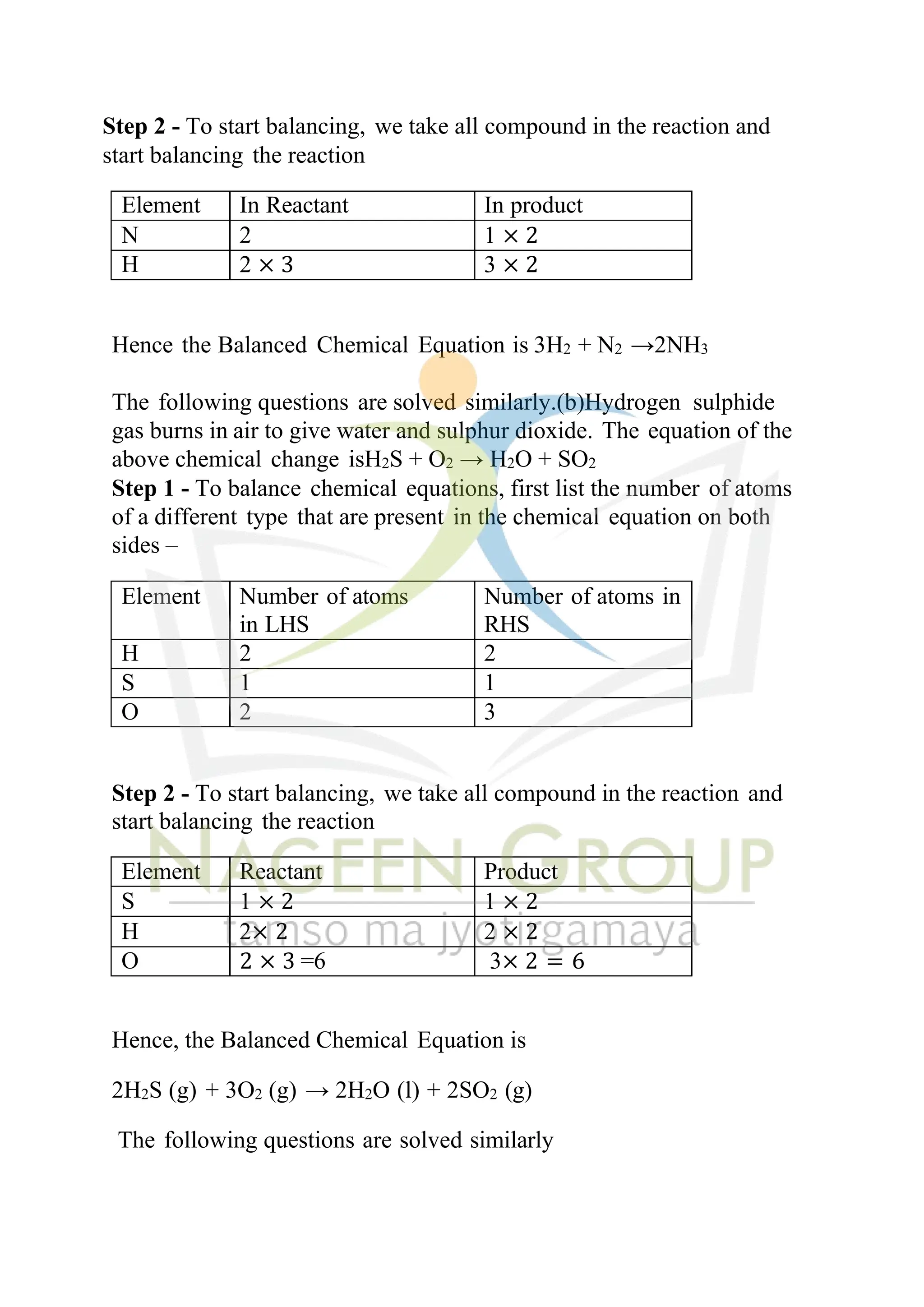
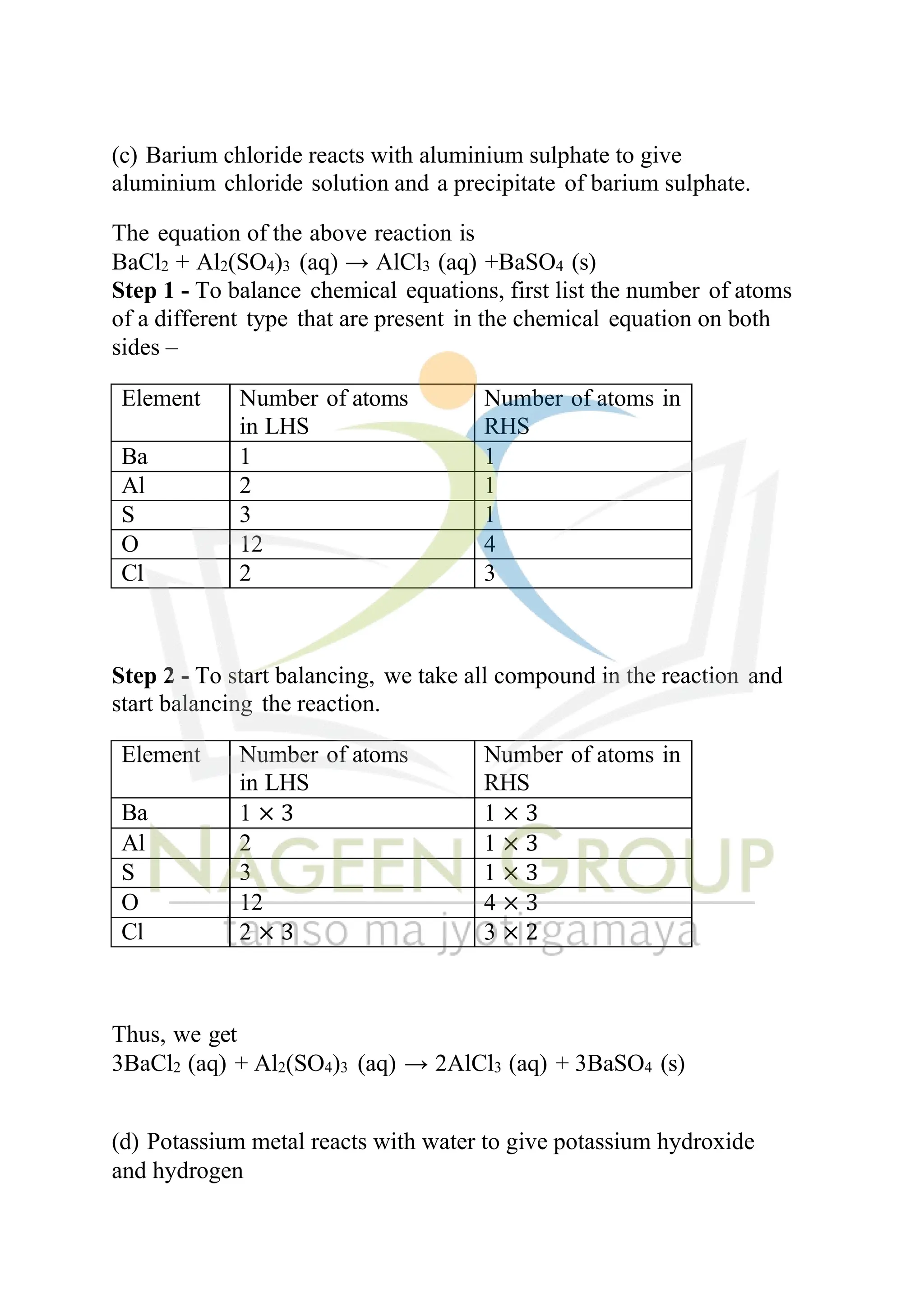
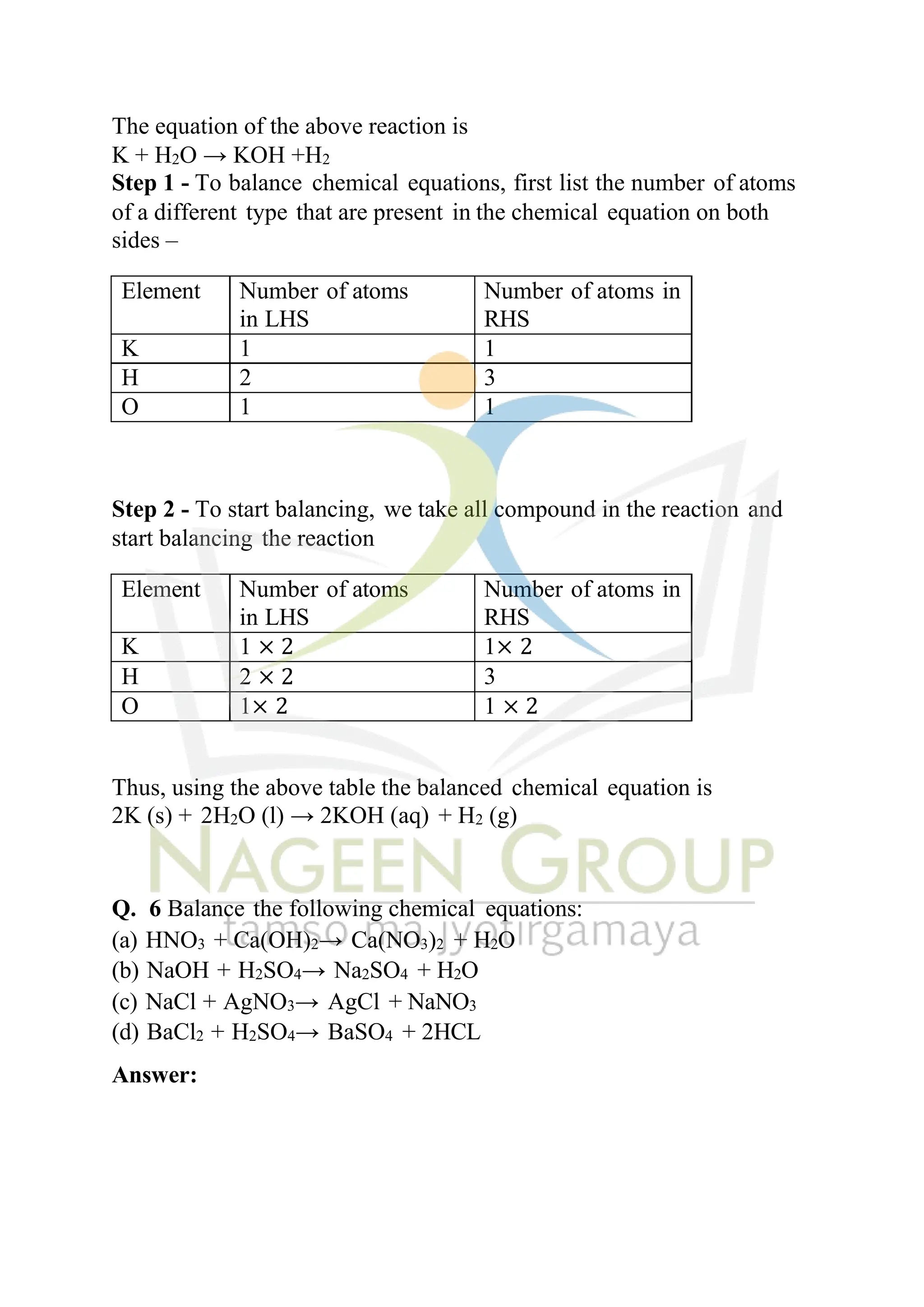
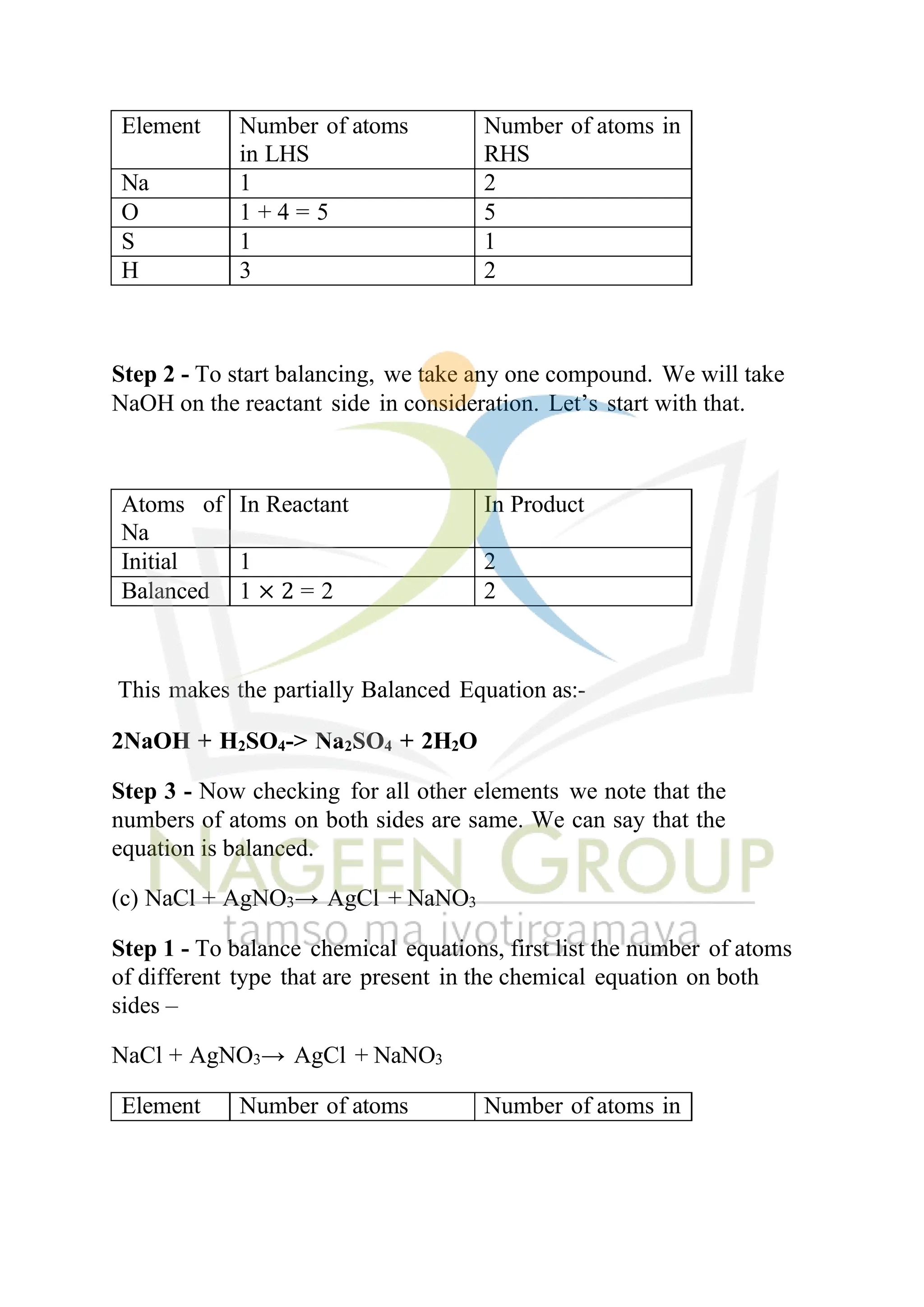
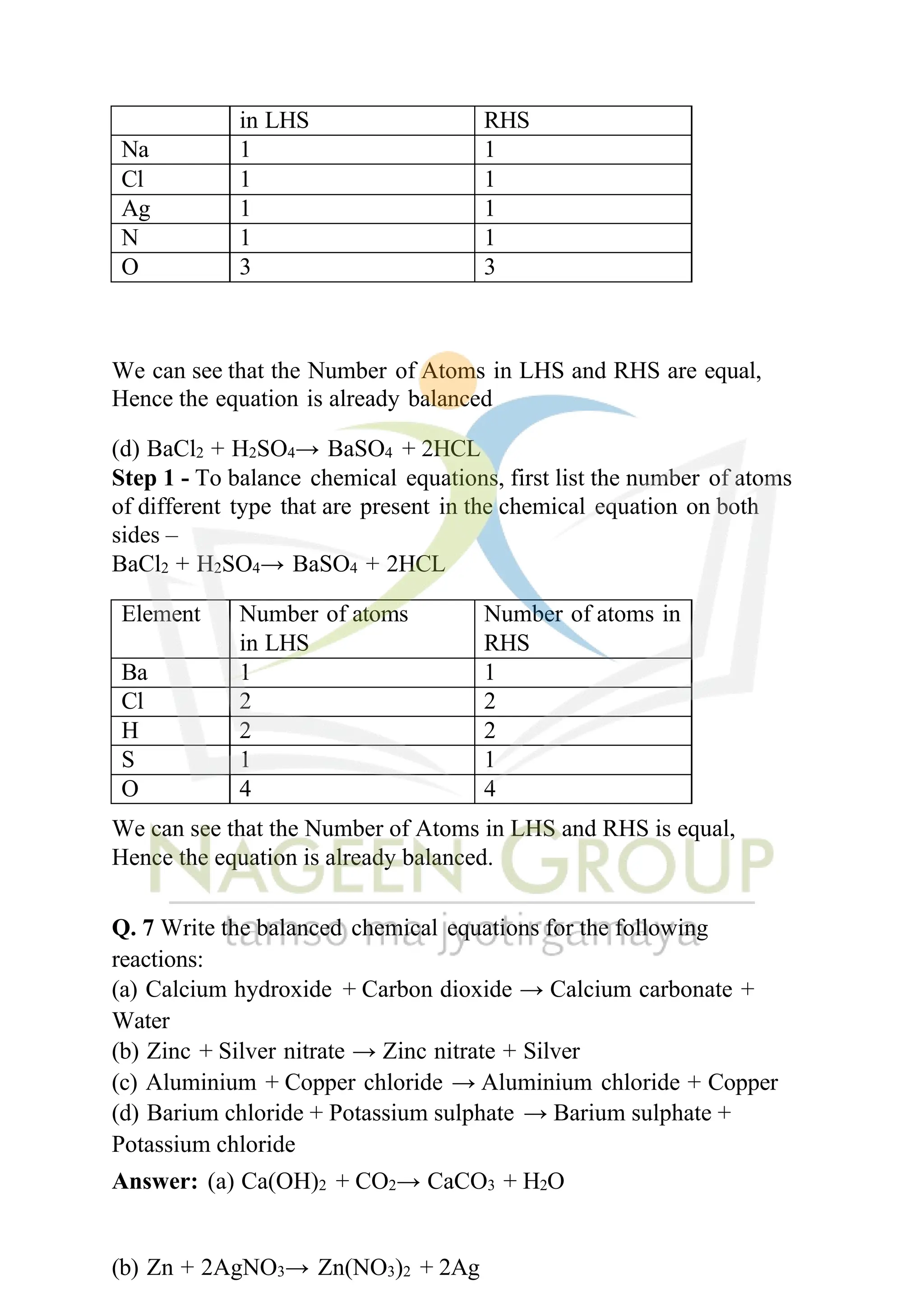
The document contains NCERT solutions for chemistry focusing on chemical reactions and equations relevant for the 2024-25 syllabus. It covers various types of chemical reactions, including displacement and double displacement, as well as the necessity of balancing chemical equations to adhere to the law of conservation of mass. The document also provides examples of balanced equations and exercises for practice.