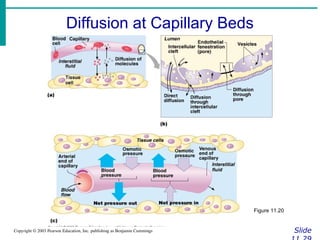
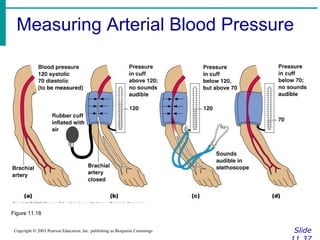
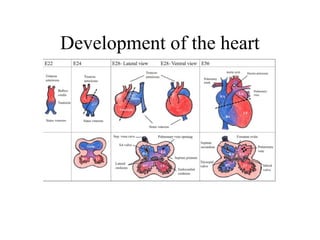
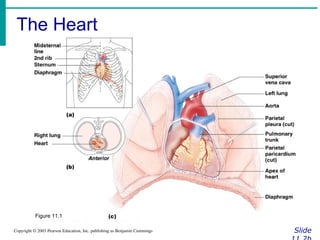
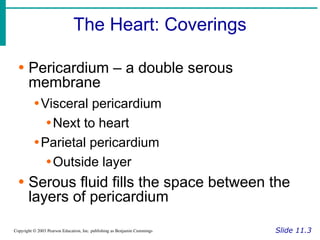
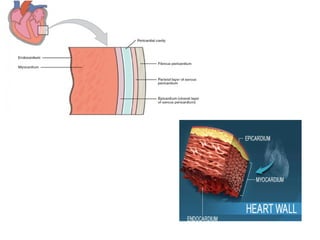
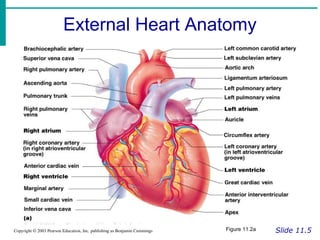
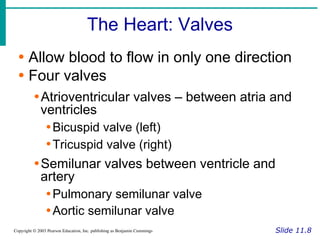
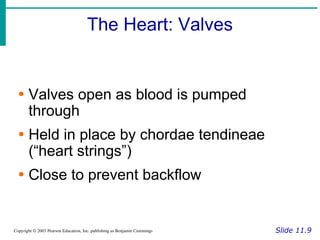
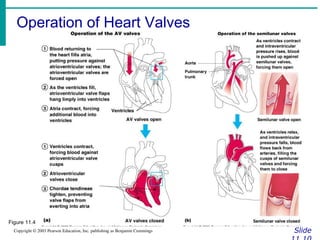
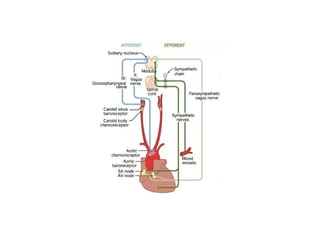
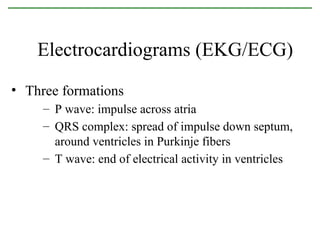
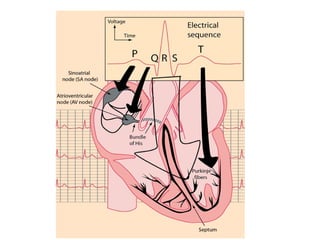
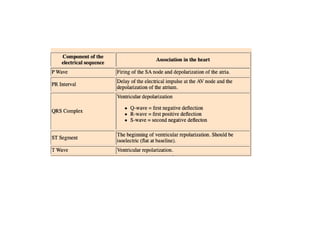
The document provides an overview of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and blood vessels. It discusses the heart's anatomy, chambers, valves, conduction system, cardiac cycle, and regulation. It describes the layers of blood vessels and differences between artery, vein, and capillary structure and function. Key terms explained include cardiac output, blood pressure, pulse, and factors that influence circulation. The summary focuses on essential information about heart and blood vessel structure and function.













![The Heart: Cardiac Output
Slide
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
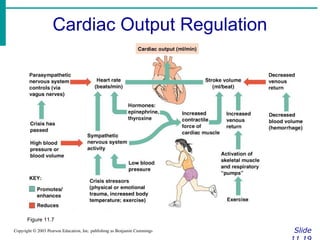
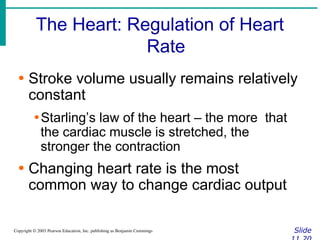
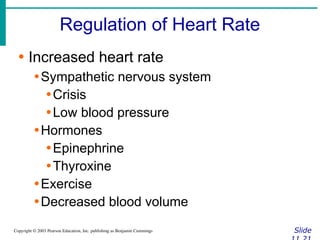
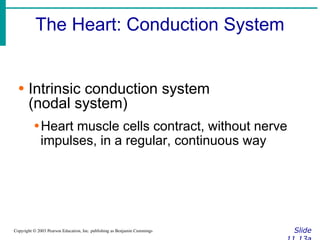
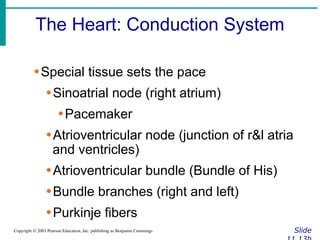
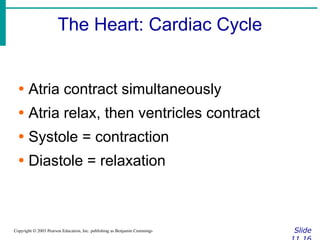
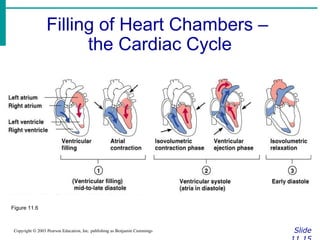
∙ Cardiac output (CO)
∙Amount of blood pumped by each side of
the heart in one minute
∙CO = (heart rate [HR]) x (stroke volume
[SV])
∙ Stroke volume
∙Volume of blood pumped by each ventricle
in one contraction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circulatorysystem-230407091632-4d3e0f4f/85/CIRCULATORY-SYSTEM-pptx-2-pdf-52-320.jpg)