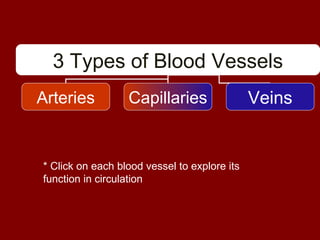
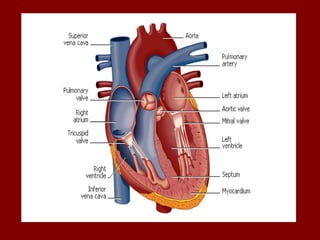
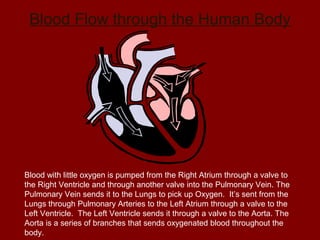
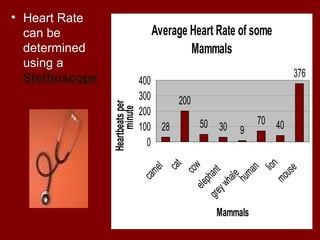
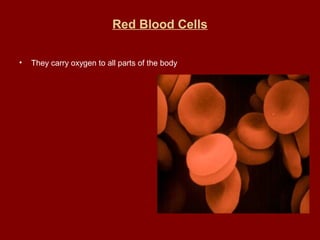
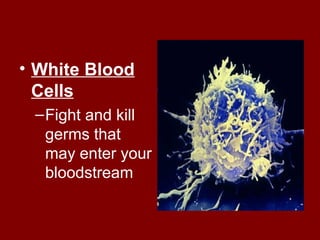
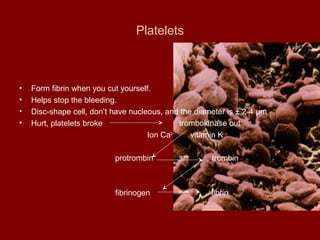
The document summarizes the circulatory system and its major components. It discusses how blood vessels transport blood throughout the body, the heart pumps blood through four chambers, and blood carries oxygen, food, and waste. It describes the three main types of blood vessels - arteries, capillaries, and veins - and explains how blood flows from the heart through the lungs to pick up oxygen before being pumped throughout the body. The document also provides details on the composition of blood and the four main blood types.