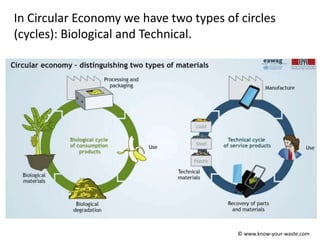
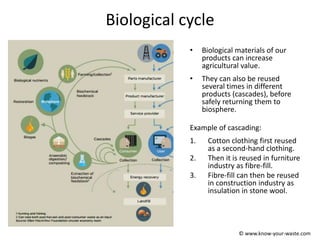
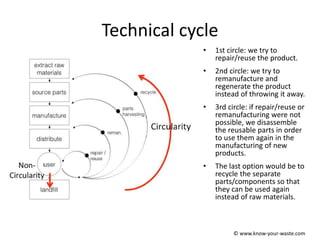
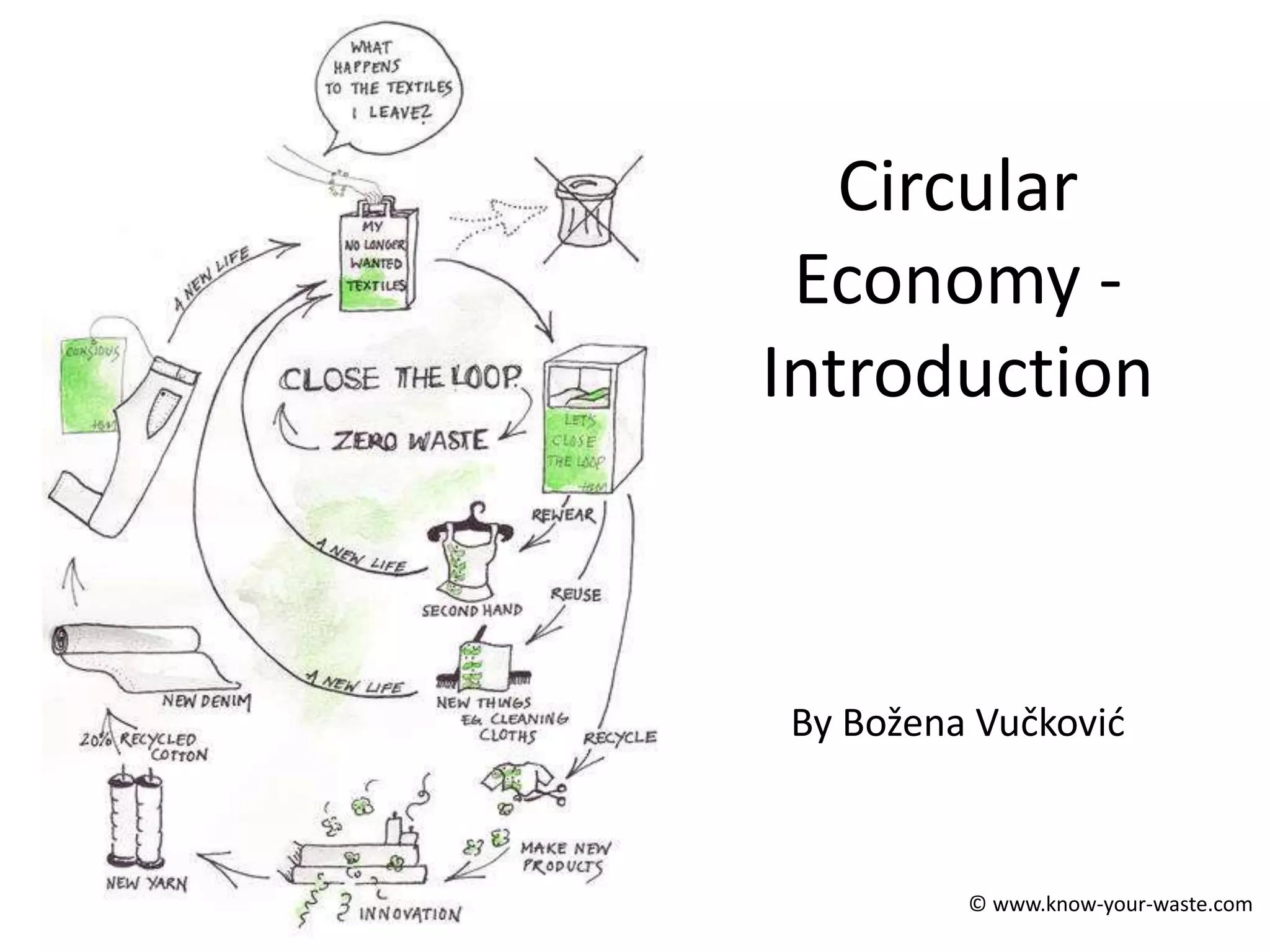
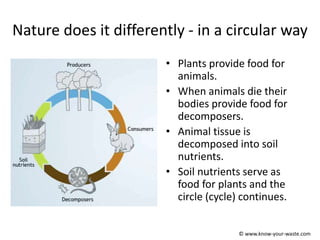
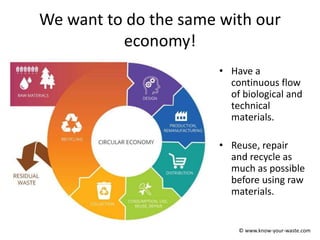
The document introduces the concept of a circular economy as an alternative to the current linear economy model of "take, make, use, dispose". It describes how economies were more circular historically through practices like repairing items, composting food waste, and using parts from broken items to fix others. However, modern economies became more linear as repairing items became more expensive and consumers preferred quick replacements. The circular economy aims to mimic natural resource cycles by reusing, repairing and recycling materials as much as possible before using new raw materials. It discusses the biological and technical material cycles and how innovation can help transition to a more circular system through improved design, business models, recycling technology and collaboration.


![Waste is not waste, it is a resource!
• Did you know that in 1 ton of old cell phones there is 324
times more gold than in 1 ton of ore from Yanacocha, one
of the biggest gold mines in the world. [12]
• All that gold is goint to waste instead of being reused.
1t ore = 0.85 g (0.03 oz.) of gold 1t phones = 275 g (9.72 oz.) of gold
© www.know-your-waste.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circulareconomyintroduction-160411225950/85/Circular-Economy-Introduction-7-320.jpg)