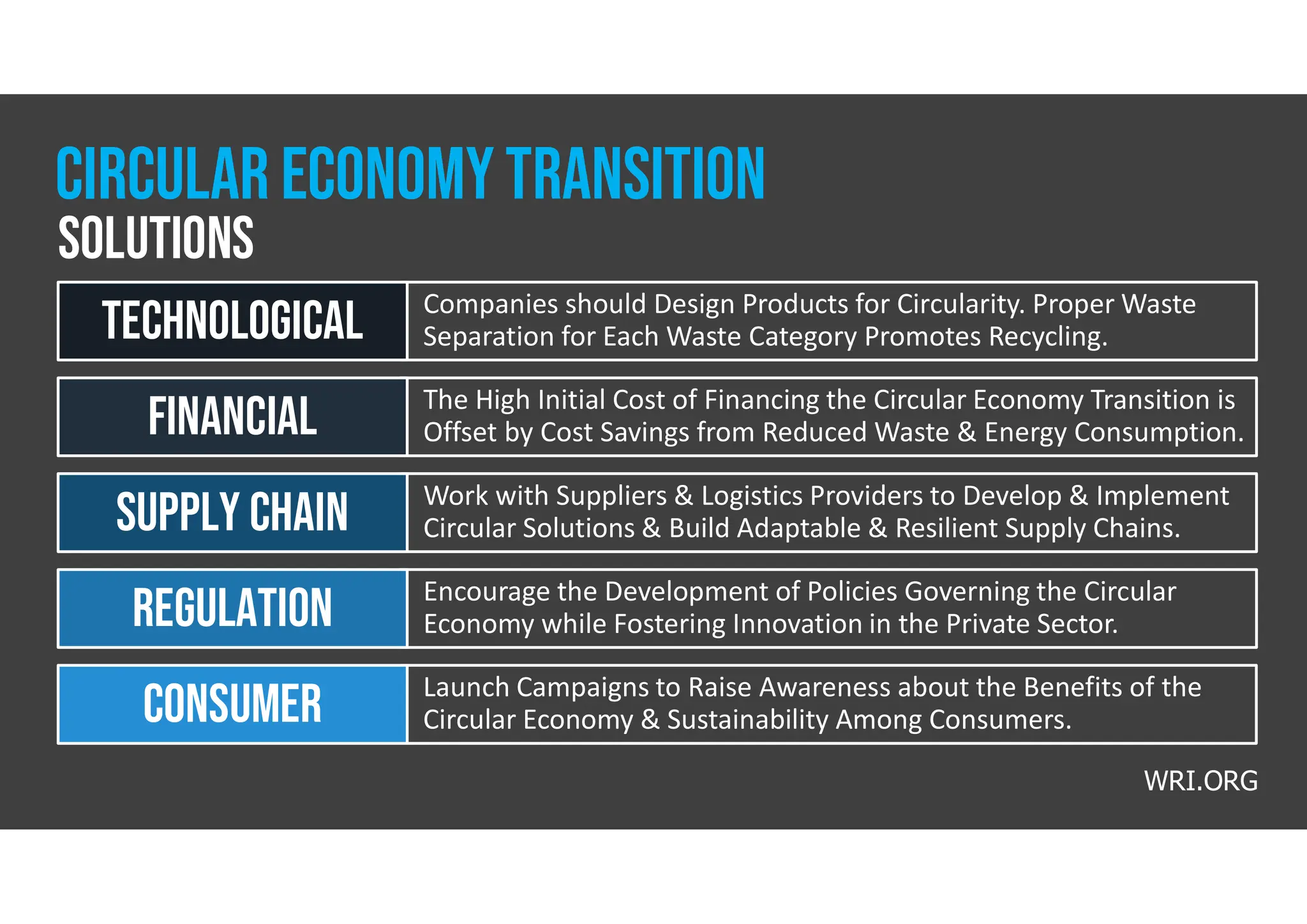
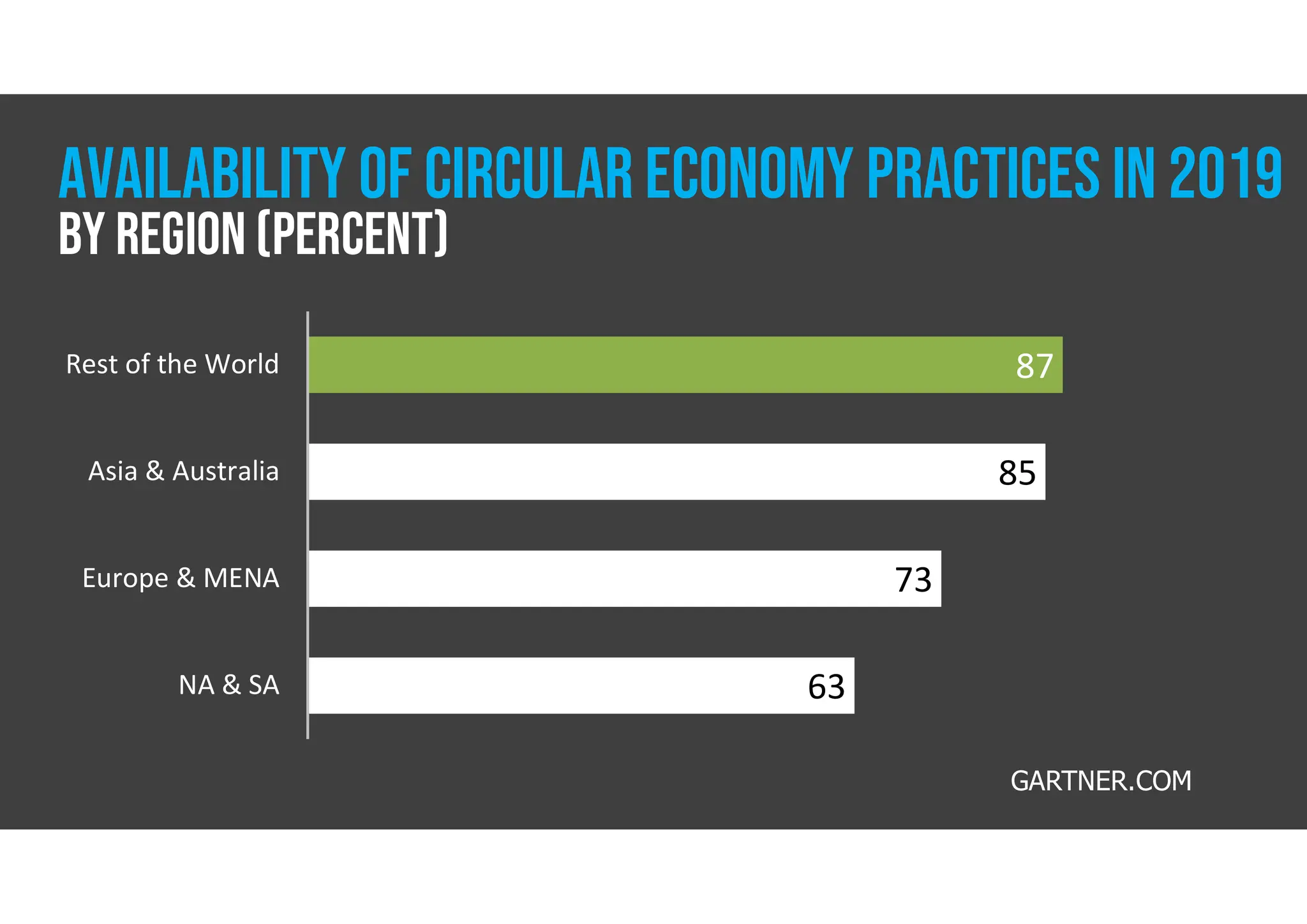
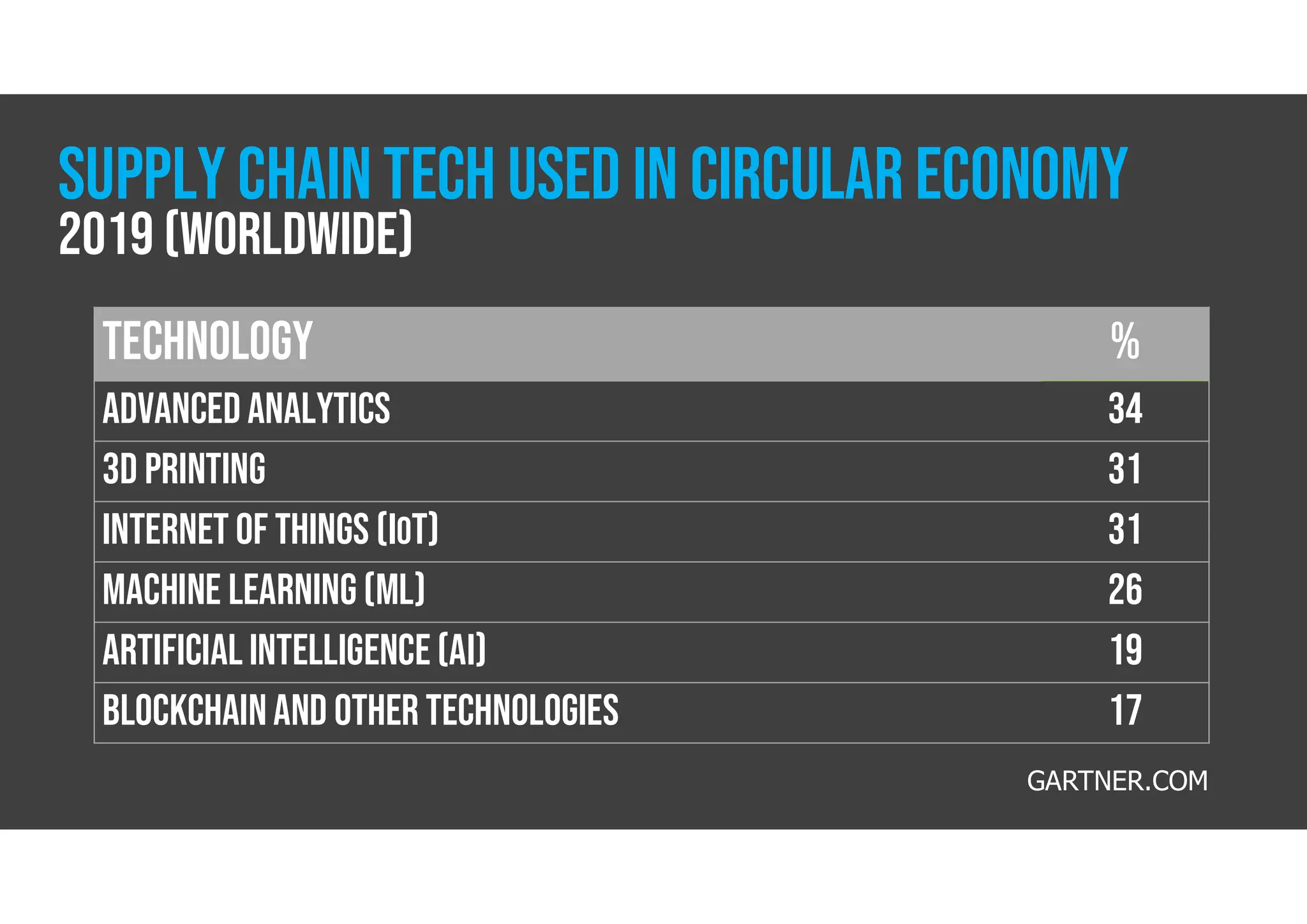
The document discusses the circular economy as a sustainable model promoting reuse and recycling to minimize waste and resource consumption, highlighting its potential to drive innovation and job creation. It identifies barriers such as consumer perceptions, regulatory challenges, and the need for technological investments while stressing the importance of new business models and policies to support its transition. Additionally, it outlines the circular economy's contribution to various sustainable development goals and provides statistics on its economic impact and consumer engagement.