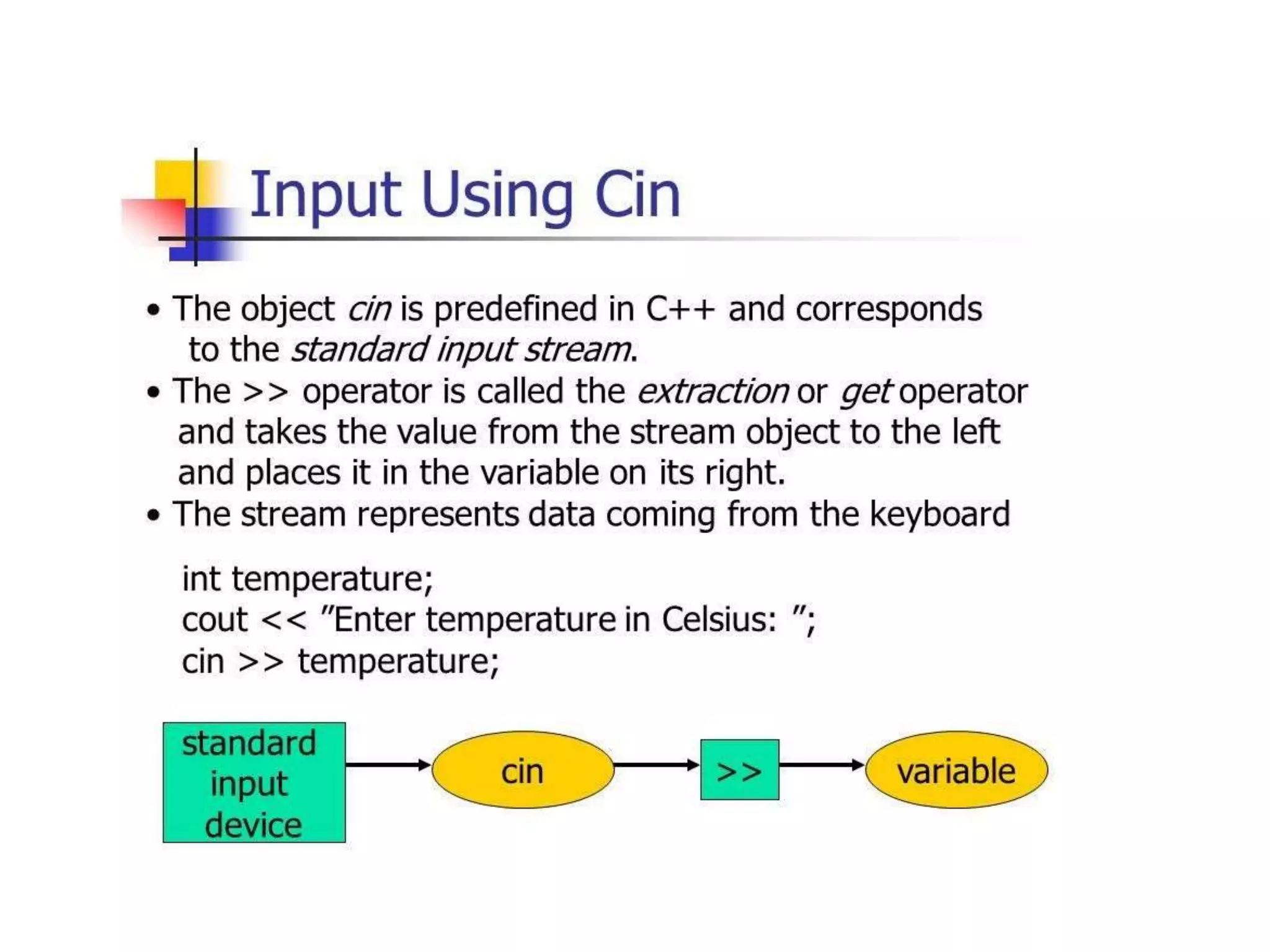
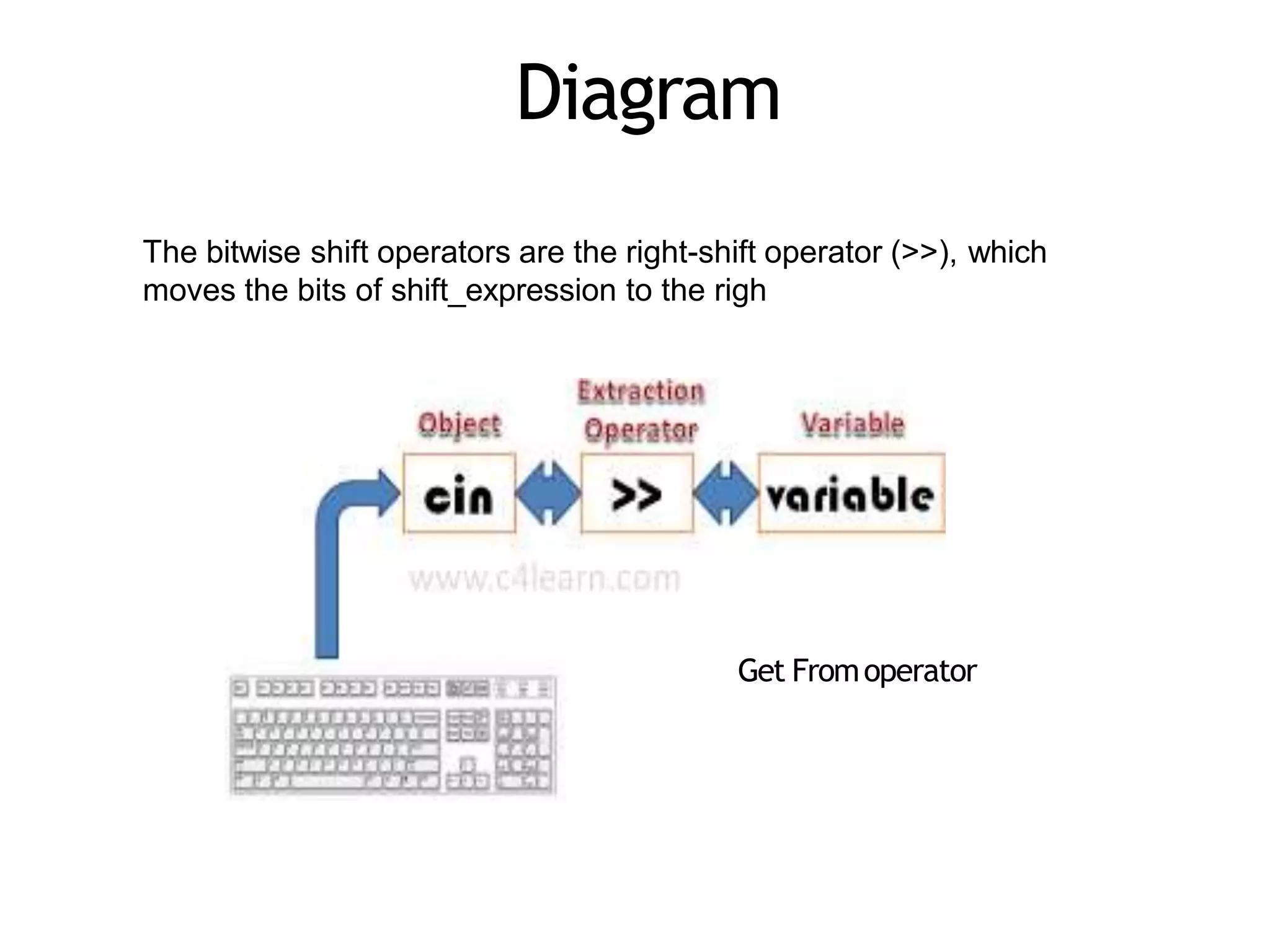
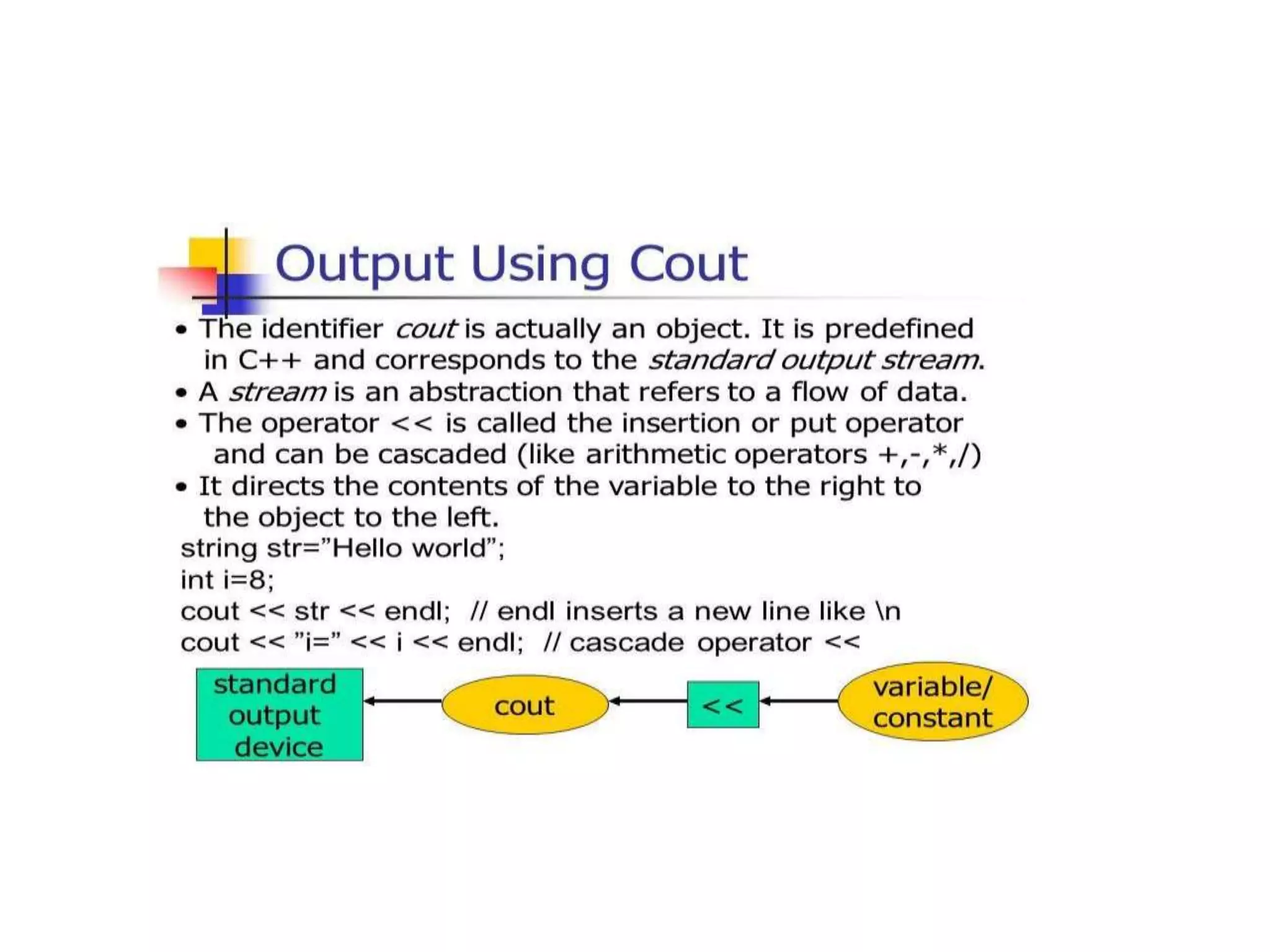
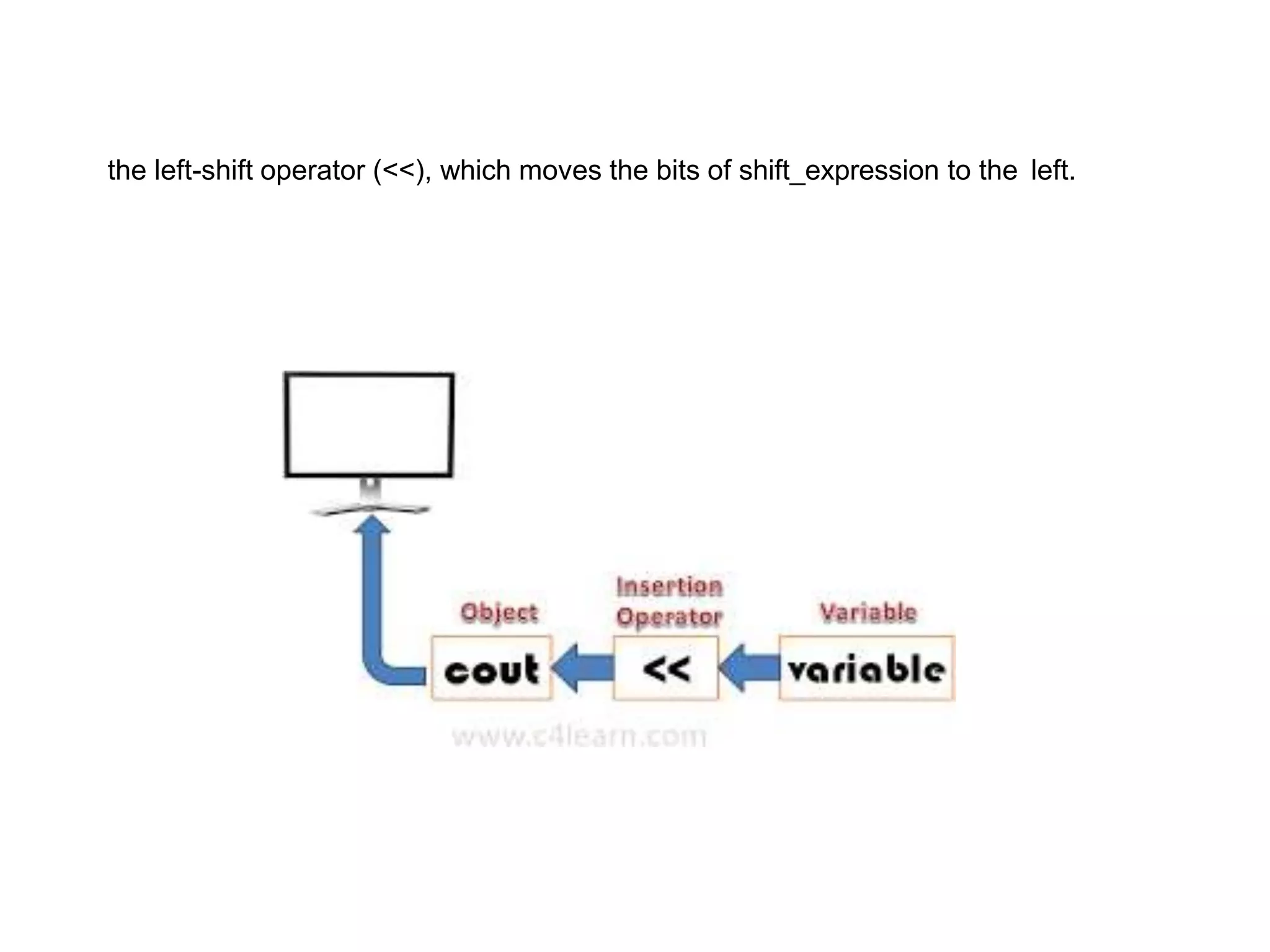
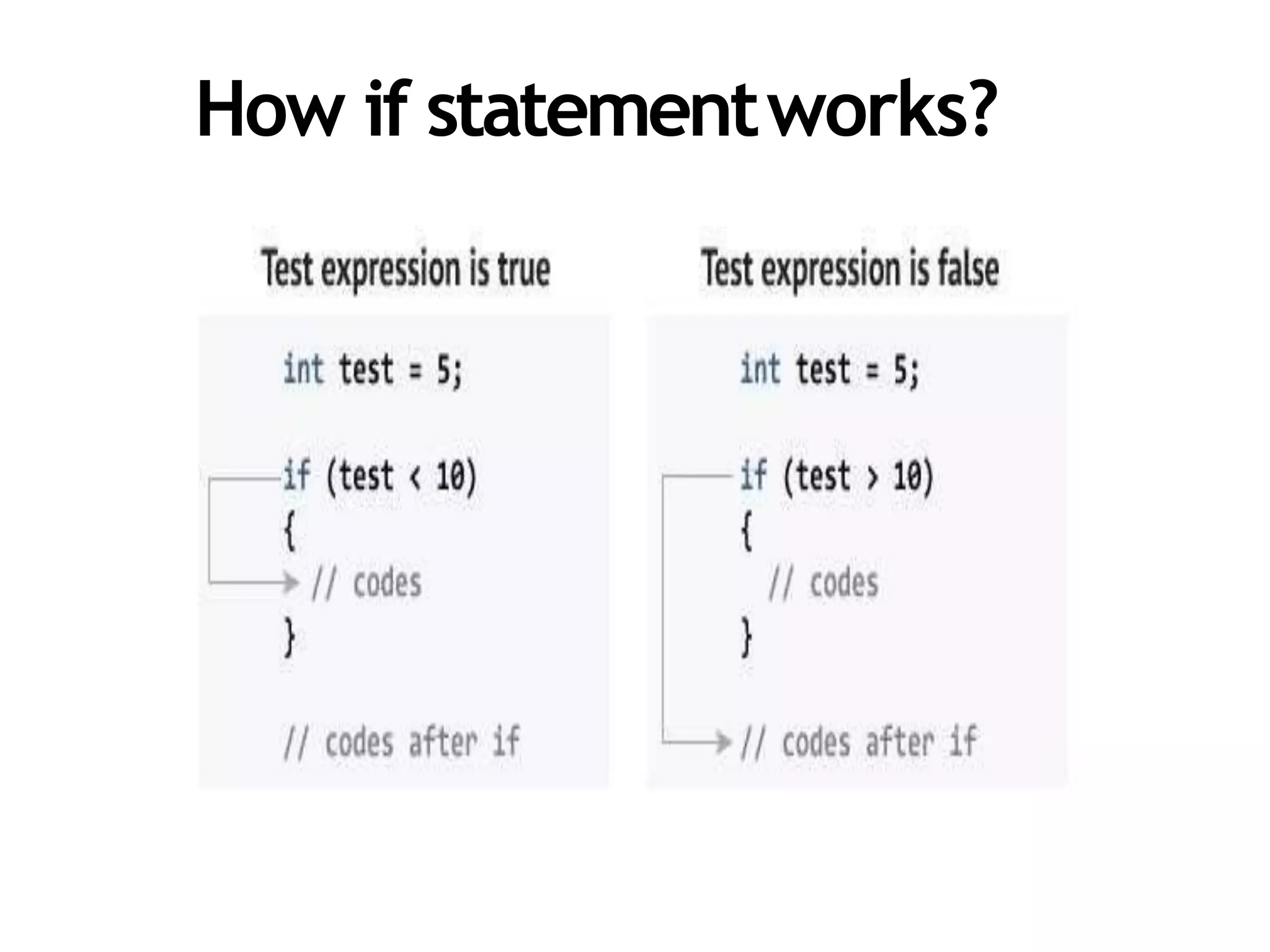
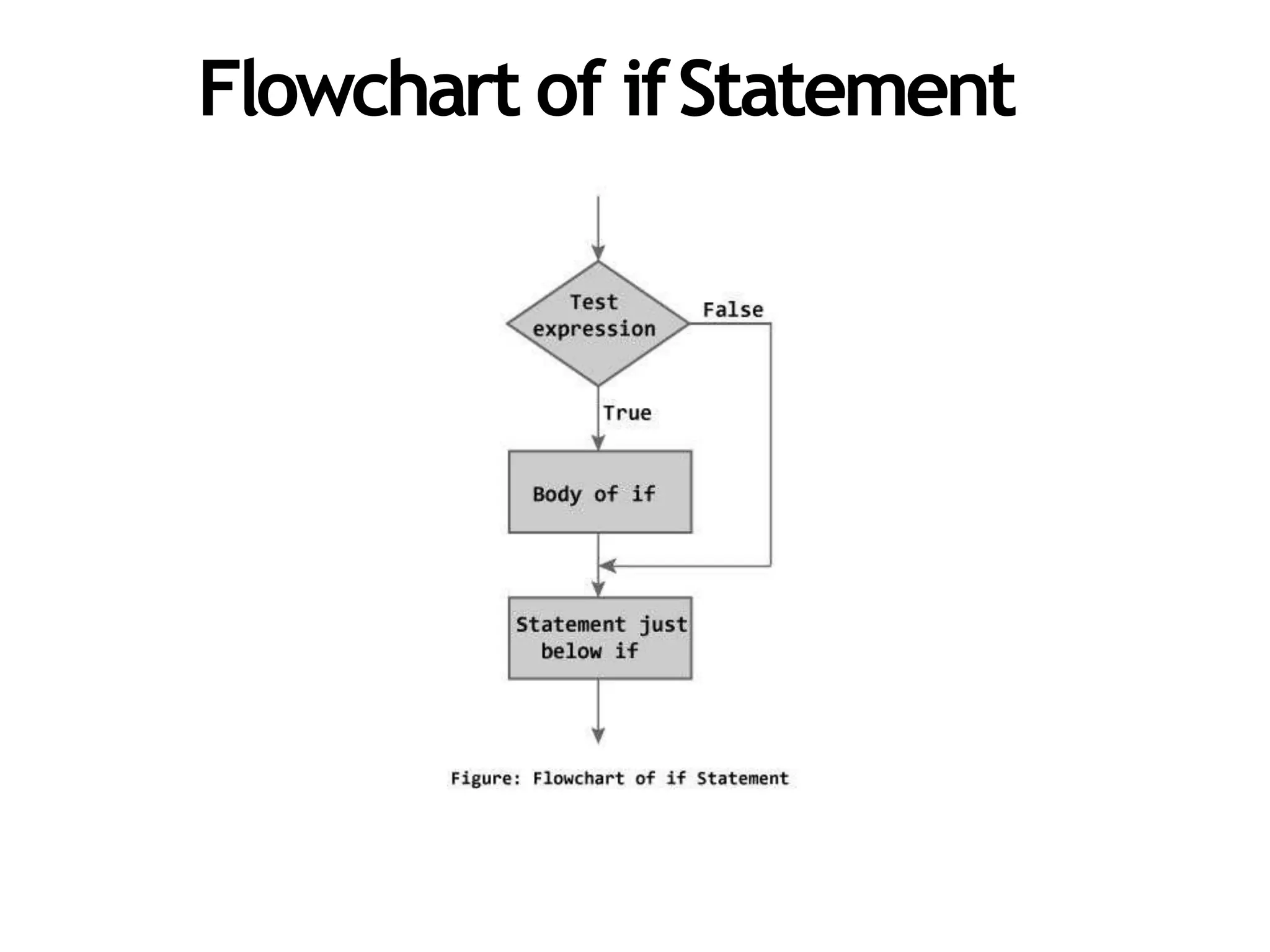
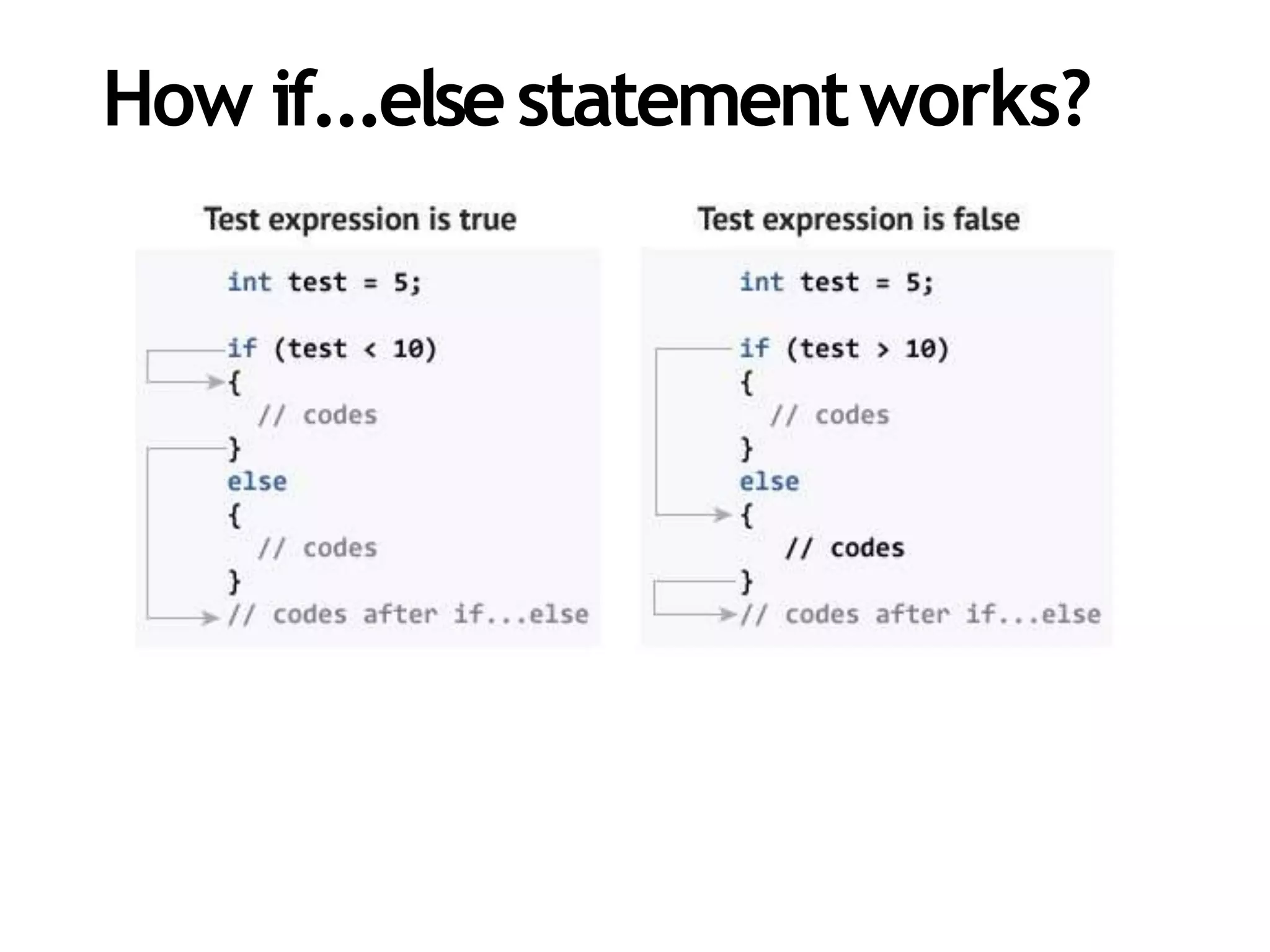
The document discusses different types of conditional statements in C++ including if, if/else, nested if/else, and else if statements. It provides the syntax for each statement, examples of code using them, and flowcharts illustrating how they work. The key conditional statements covered are:
- if statement which executes code if a test expression is true
- if/else statement which executes one code block if the test is true and another if it's false
- nested if/else statements which allow multiple levels of conditional logic
- else if ladder which chains multiple conditions together