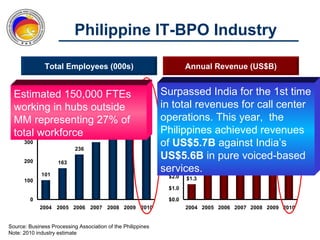
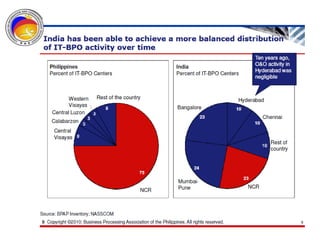
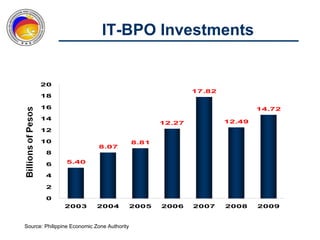
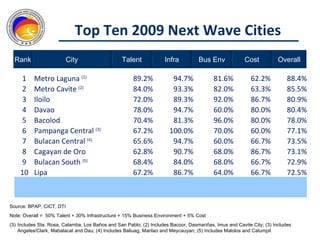
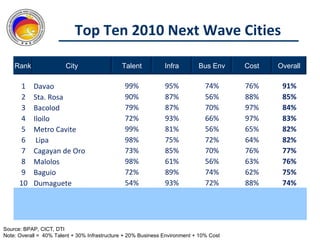
The Commission on Information and Communications Technology (CICT) aims to develop the Philippines into a digitally-enabled society through initiatives focused on e-government, cyberservices, human capital development, and information infrastructure. Key priorities include expanding IT-BPO industries, developing next wave cities, promoting service science management education, and drafting a Philippine Digital Strategy to guide ICT development from 2011-2016. The CICT works closely with industry groups and aims to provide talent, infrastructure, and a business environment conducive to the growth of the digital economy.