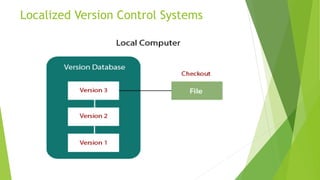
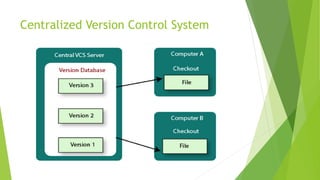
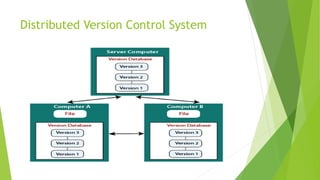
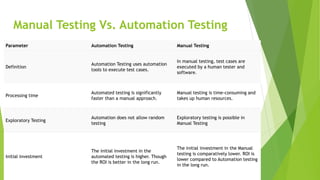
Version control systems track and manage changes to code and files. Centralized systems store code in a single central repository, while distributed systems allow each user to have their own local repository. Automated testing executes test cases using tools to validate software functionality faster than manual testing. Different types of automated tests include unit, integration, smoke, and regression testing.