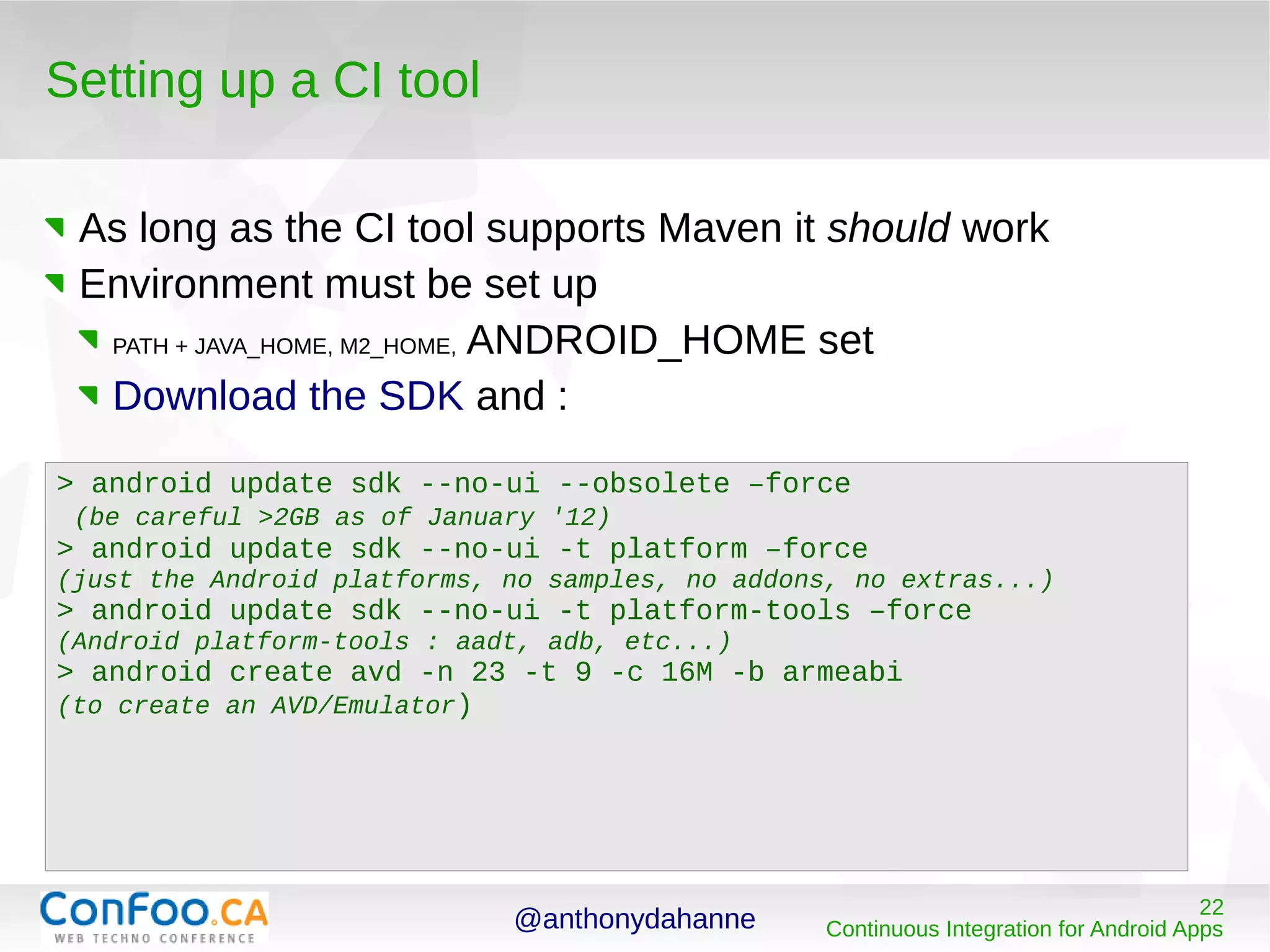
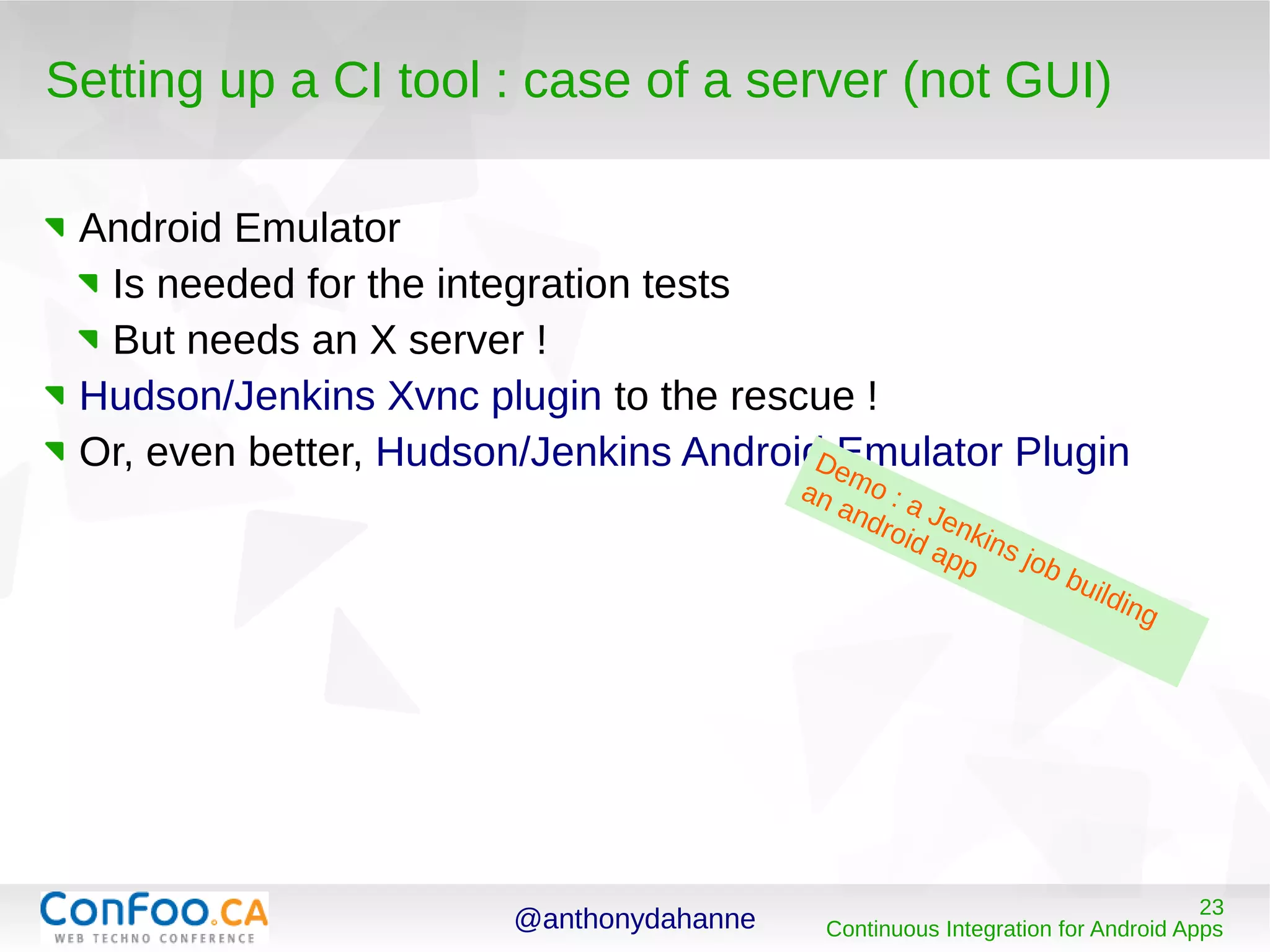
The document provides an overview of continuous integration (CI) for Android apps, explaining its importance, benefits, and how to implement it using tools like Ant and Maven. It covers steps for building and testing an Android app, including recommendations for setting up a CI environment and integrating testing practices. Additionally, it discusses advancing beyond CI to include continuous quality control and deployment practices.






![@anthonydahanne 12
Continuous Integration for Android Apps
Building an Android app : with Ant
Ant is the official building tool chosen by the ADT team
The Ant script can be generated and used easily from an
Android project :
> android update project --path ./
Updated local.properties
Added file ./build.xml
Updated file ./proguard.cfg
> ant debug install
[…]
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
Demo : generate an ant script
to build your project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ci-for-android-apps-120301111320-phpapp02/75/Ci-for-android-apps-12-2048.jpg)