This document discusses chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a myeloproliferative disorder originating from stem cells characterized by the Philadelphia chromosome. The key points are:
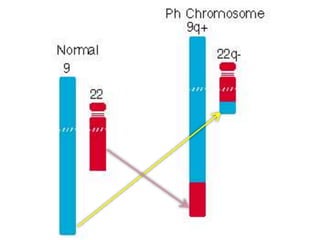
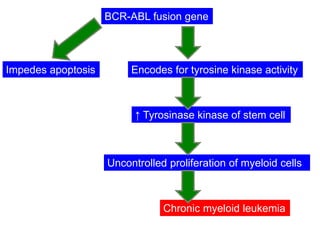
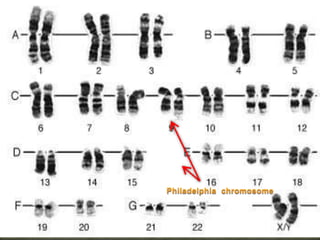
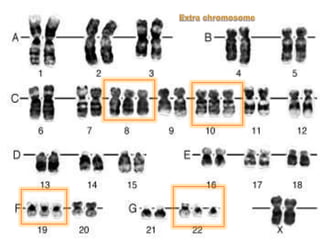
CML is caused by the BCR-ABL fusion gene resulting from a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, which encodes for uncontrolled tyrosine kinase activity. This leads to increased proliferation of myeloid cells.
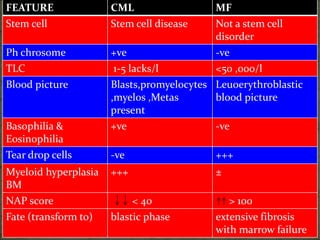
CML progresses through three phases: chronic, accelerated, and blastic (acute) phases as the disease becomes more aggressive and chemotherapy-resistant over time.
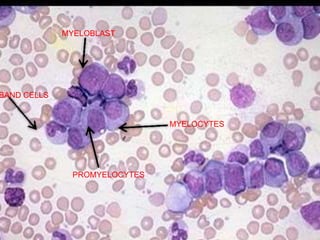
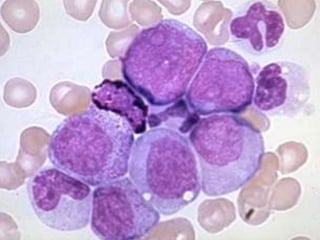
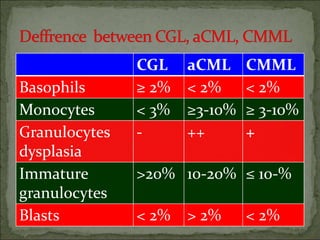
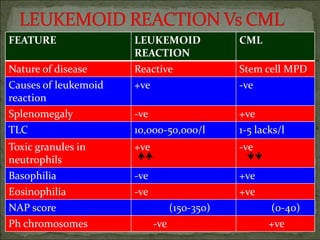
Diagnosis involves blood tests showing leukocytosis with immature cells, elevated LDH and basophils, and bone marrow biopsy demonstrating hypercellularity and myeloid hyper