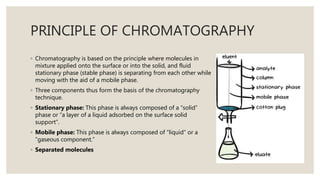
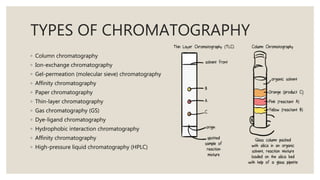
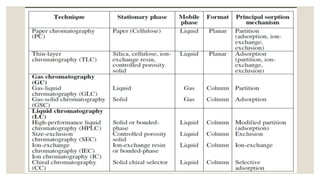
Chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate mixtures into individual components. It works by distributing components between two phases - a stationary phase and a mobile phase. There are several types of chromatography that differ based on the stationary and mobile phases used, including column chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, gas chromatography, and high-pressure liquid chromatography. Chromatography has many applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food testing, forensics, and molecular biology to analyze samples, detect unknown compounds, and determine purity.