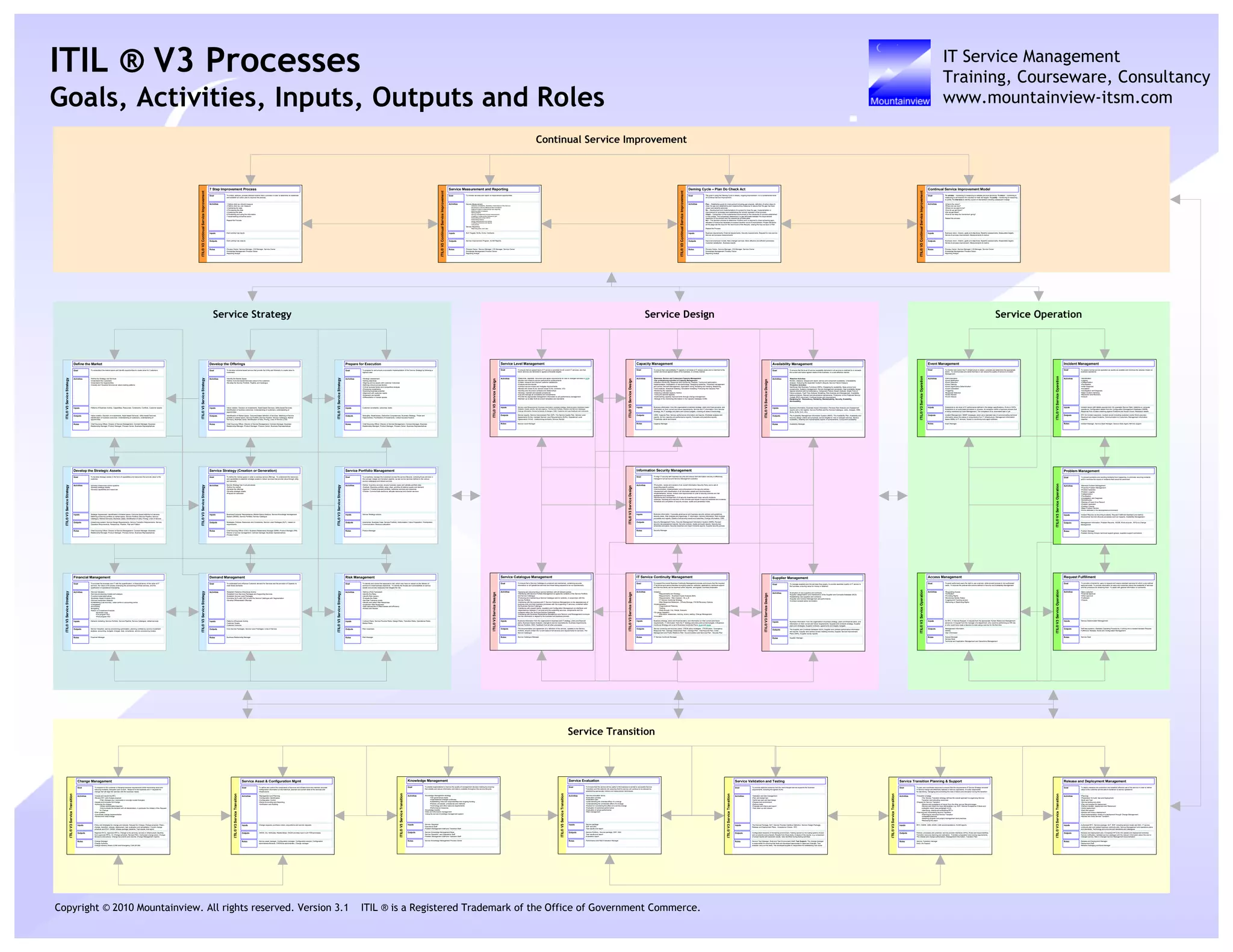
The document discusses several ITIL processes including Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement.
For each process, it provides the goal, key activities, inputs, outputs, and roles. Some of the processes covered in detail include Service Portfolio Management, Service Catalog Management, Availability Management, Capacity Management, IT Service Continuity Management, and Request Fulfillment.