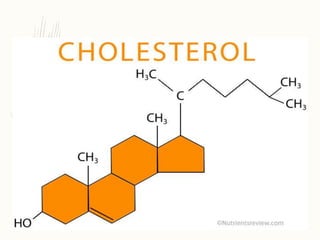
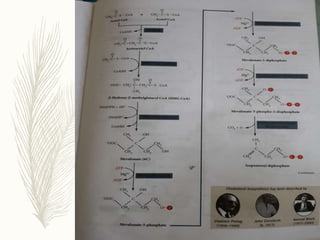
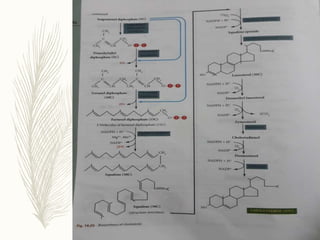
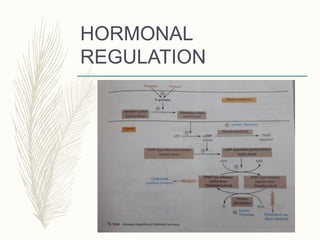
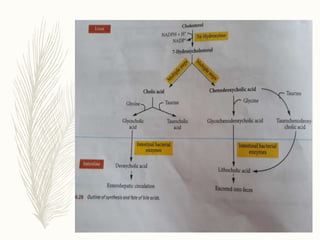
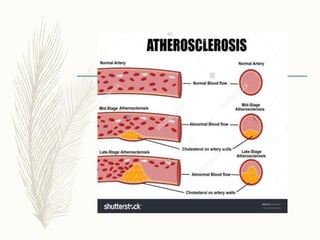
Cholesterol is a lipid that is essential for cell membrane structure and hormone production. It is synthesized through a metabolic pathway and regulated at the rate-limiting step by HMG-CoA reductase. High cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, a hardening of the arteries due to plaque buildup. Plaque forms when cholesterol builds up in artery walls as macrophages take up cholesterol and become foam cells. Over time, plaque can narrow arteries and risk blockages leading to heart attacks and other problems. Risk factors for high cholesterol and atherosclerosis include diet, obesity, smoking, and other lifestyle and genetic factors.