This document discusses various behavior management techniques used in pediatric dentistry. It covers non-pharmacological techniques like minimizing wait times and ensuring adequate pain control. It also discusses pharmacological techniques like local anesthetics and oral/enteral medications. The main behavior management techniques discussed are communication, behavior shaping through desensitization and modeling, and behavior management through voice control, distraction, positive and negative reinforcement, and selective exclusion of parents. Specific techniques like tell-show-do, praise, and rewards are explained in detail. The goals of behavior management are also stated as gaining compliance and redirecting inappropriate behaviors while ensuring patient safety.

![3
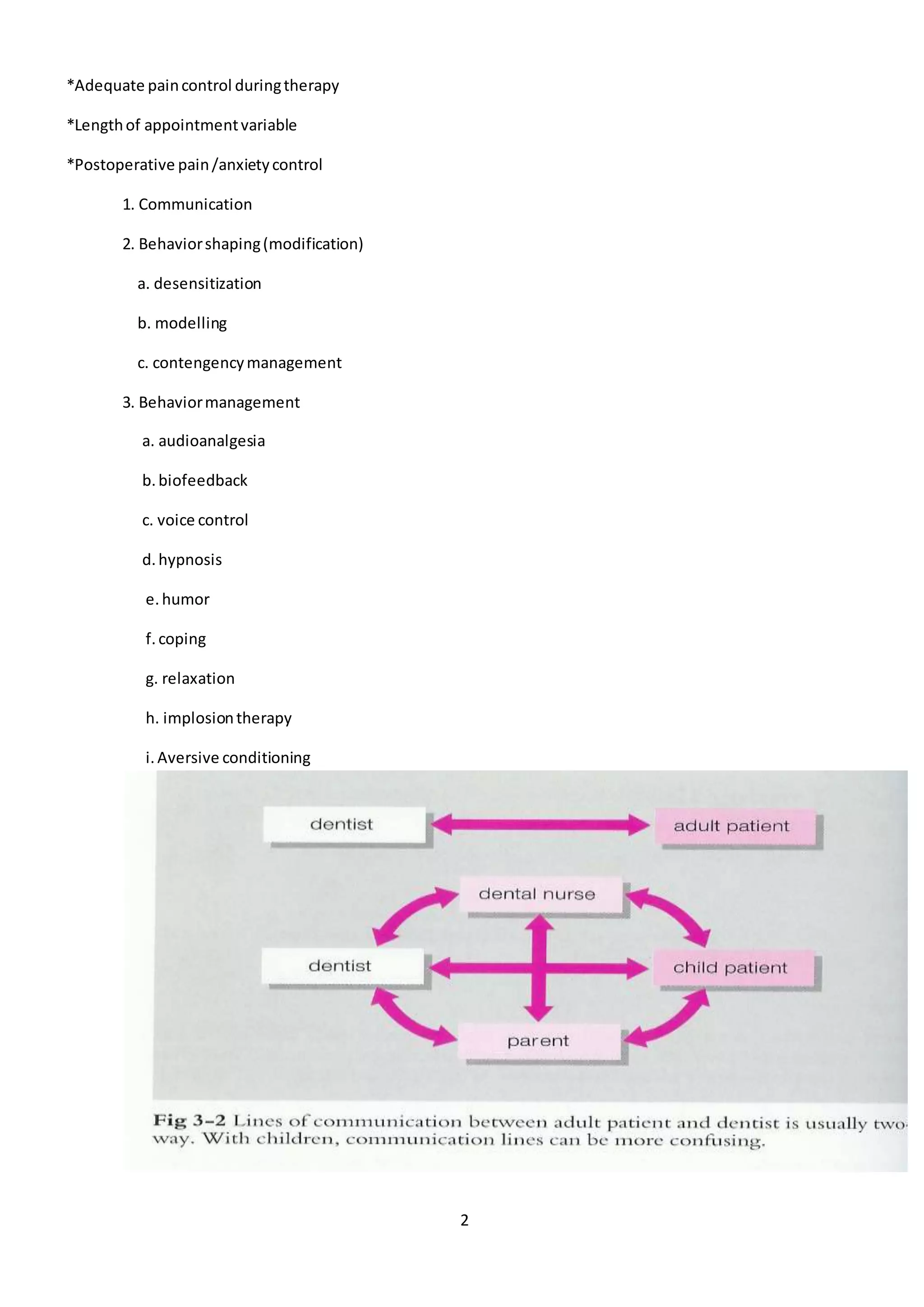
1- Communication
Verbal [establishment of communication,
establishment of communicator ,message clarity,tone]
Nonverbal [Multi sensory Communication]
NONVERBAL COMMUNICATION
Reinforcement of behavior
through provider contact,
posture and facial expression
• Enhances the effectiveness of other communicative management techniques
• Culturally sensitive
• Recognized behaviors that convey information
• Facial expression
• High Five
• Reciprocal Social Interaction
• Eye gaze
• Turn taking
• Respect personal space
• Respond to social signals
Communicating with children
Effective communication with children is critical for gaining the child’s cooperation to receive
dental care.
1. Tell Show Do
2. Reflective listening
3. Self-disclosing assertiveness
4. Descriptive praise.
Effective communication is a primary objective.
Communicate in two basic ways:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/child-behavior-lec-4-beh-161121182032/75/Child-behavior-lec-4-beh-manag-2015-3-2048.jpg)



![7
Modelling
Bandura (1969) :- Live ,Filmed ,Posters ,Audiovisuals
Allowing the patient to observe one or more individuals [models]
Patient frequently imitates the models
Distraction
Diverting the patient’s attention from what may be perceived as an unpleasant procedure.
Music , Video ,Talking ,White noise ,Hypnosis ,Breathing
Objectives of Distraction
1. decrease the perception of unpleasantness;
2. avert negative or avoidance behavior.
Indications: May be used with any patient.
Contraindications: None.
Contingency management (Reinforcement )
Positive reinforcer
Negative reinforcers :- Social ,Material ,Activity
Reinforcement :- ‘isthe strengtheningof a pattern of desired behaviour & increasing the probability of
that behaviour being displayed again in the future’
Types ofReinforcement
Positive Reinforcement
Negative reinforcement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/child-behavior-lec-4-beh-161121182032/75/Child-behavior-lec-4-beh-manag-2015-7-2048.jpg)





