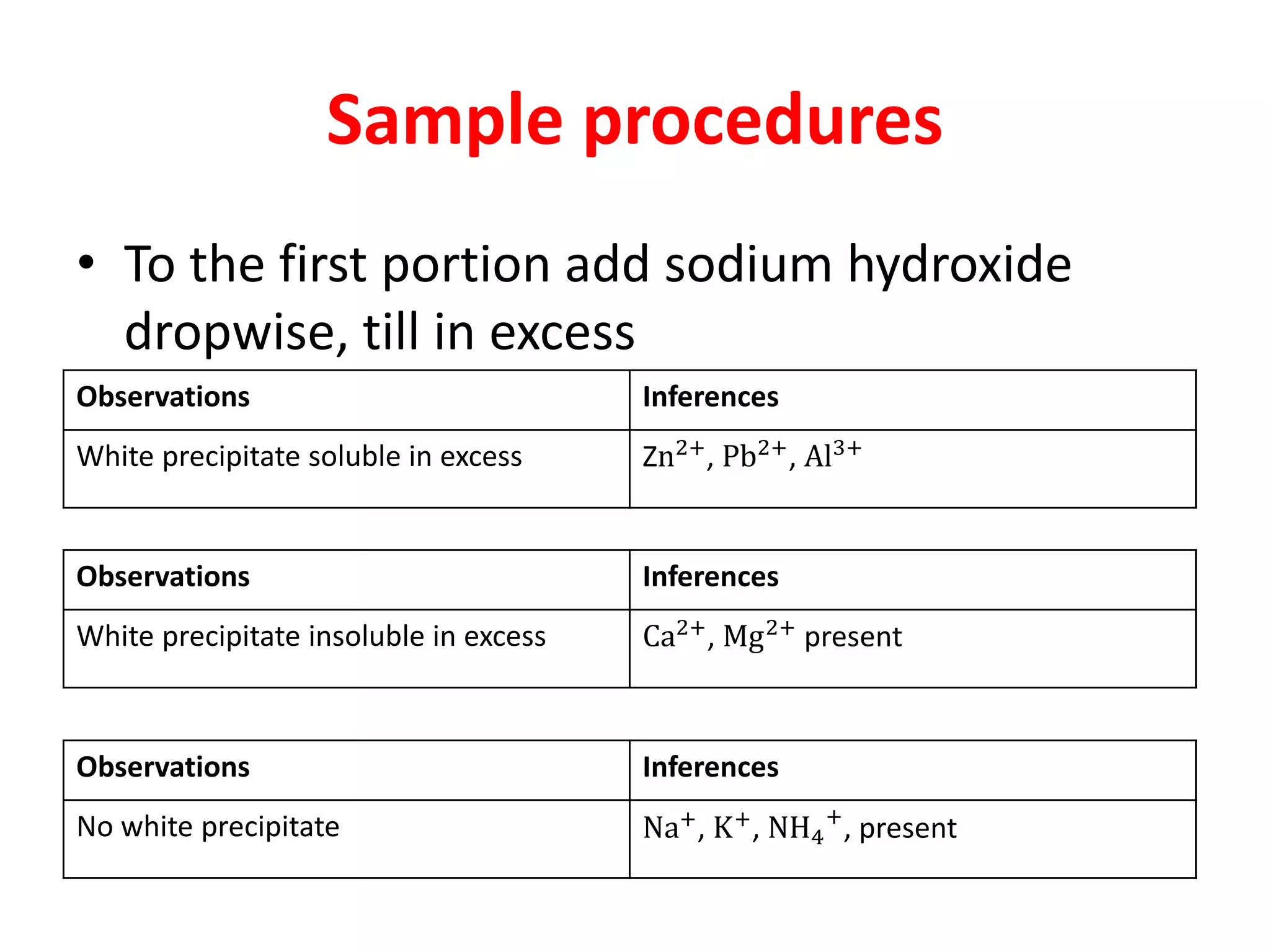
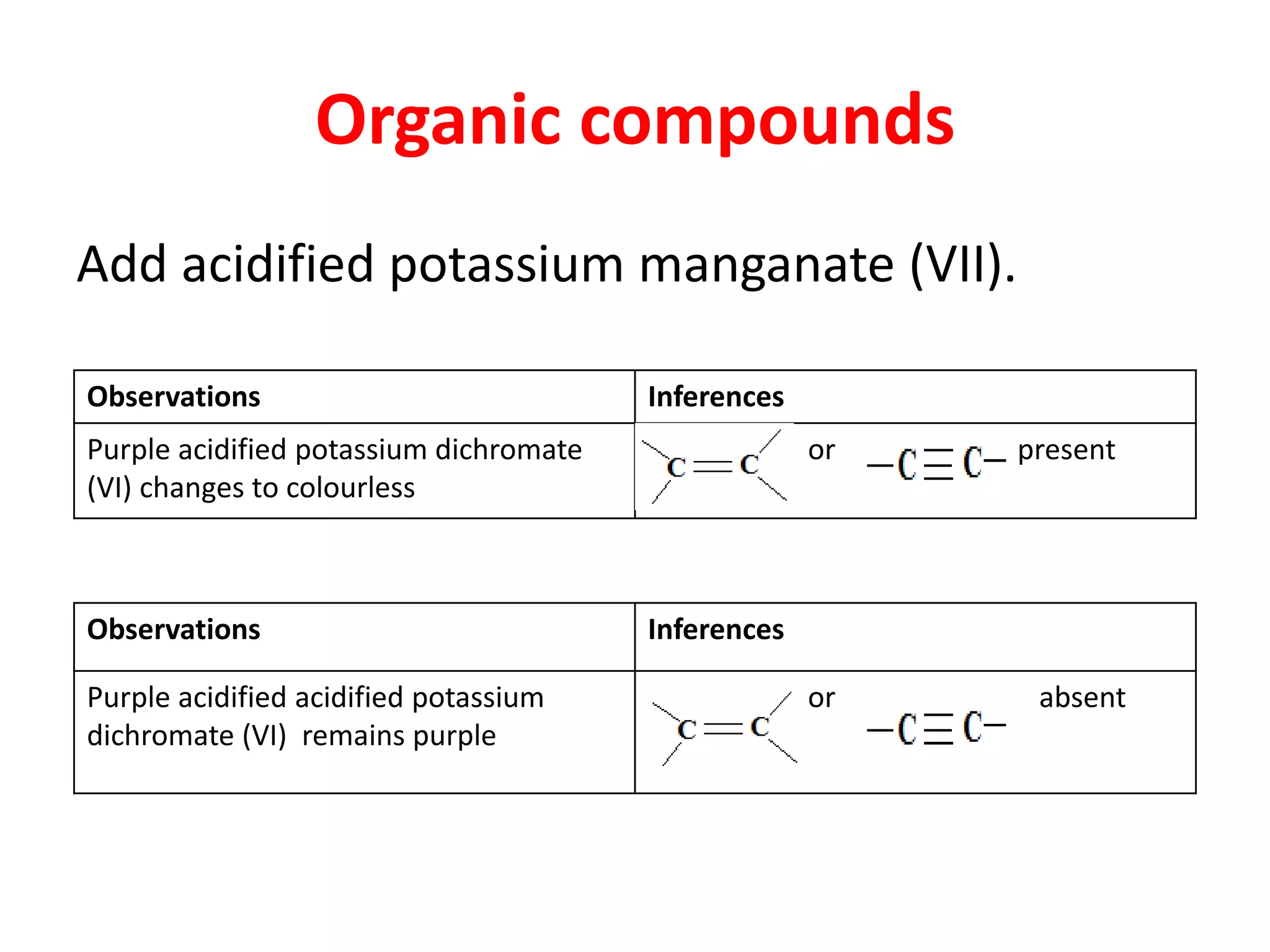
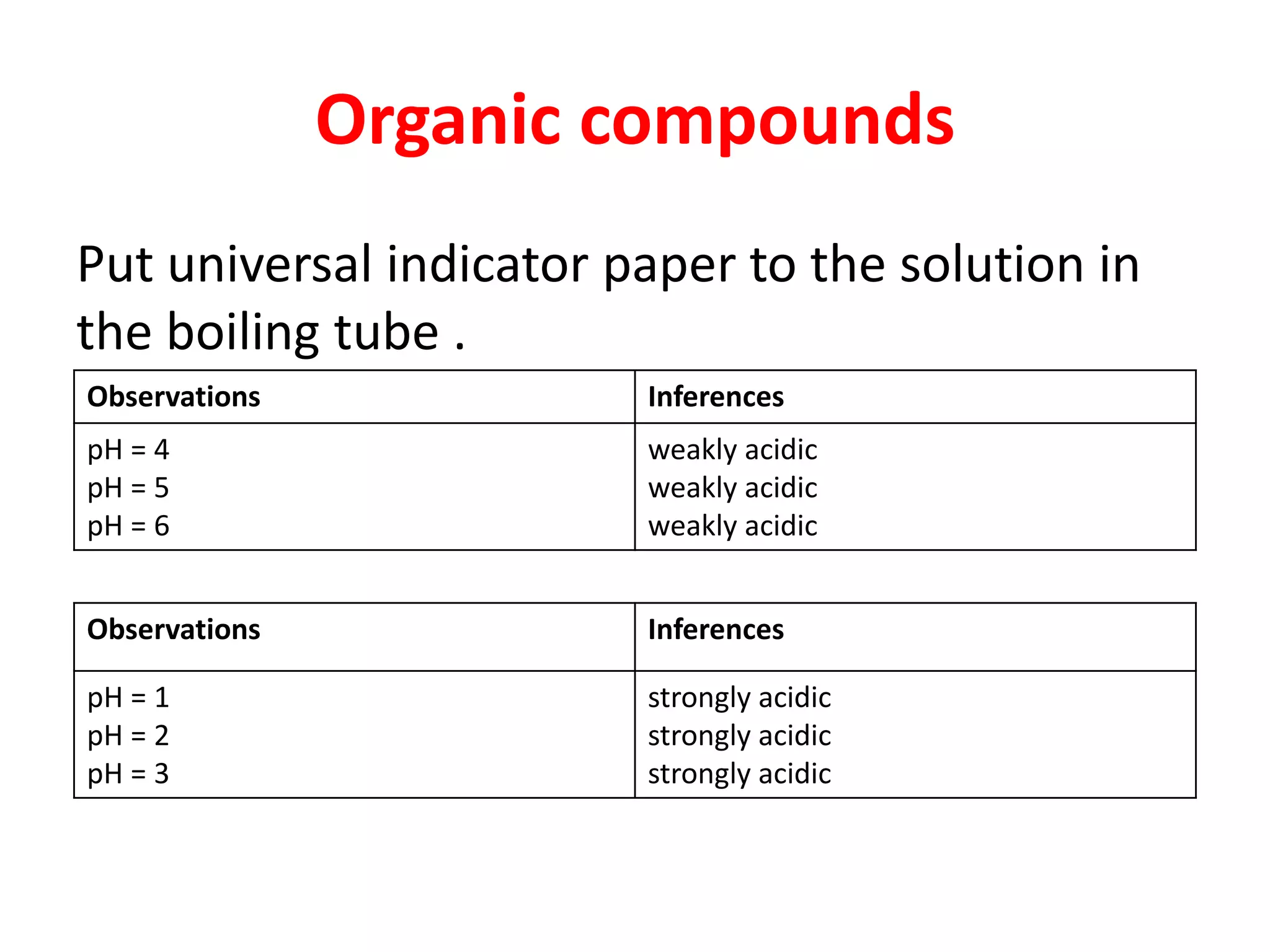
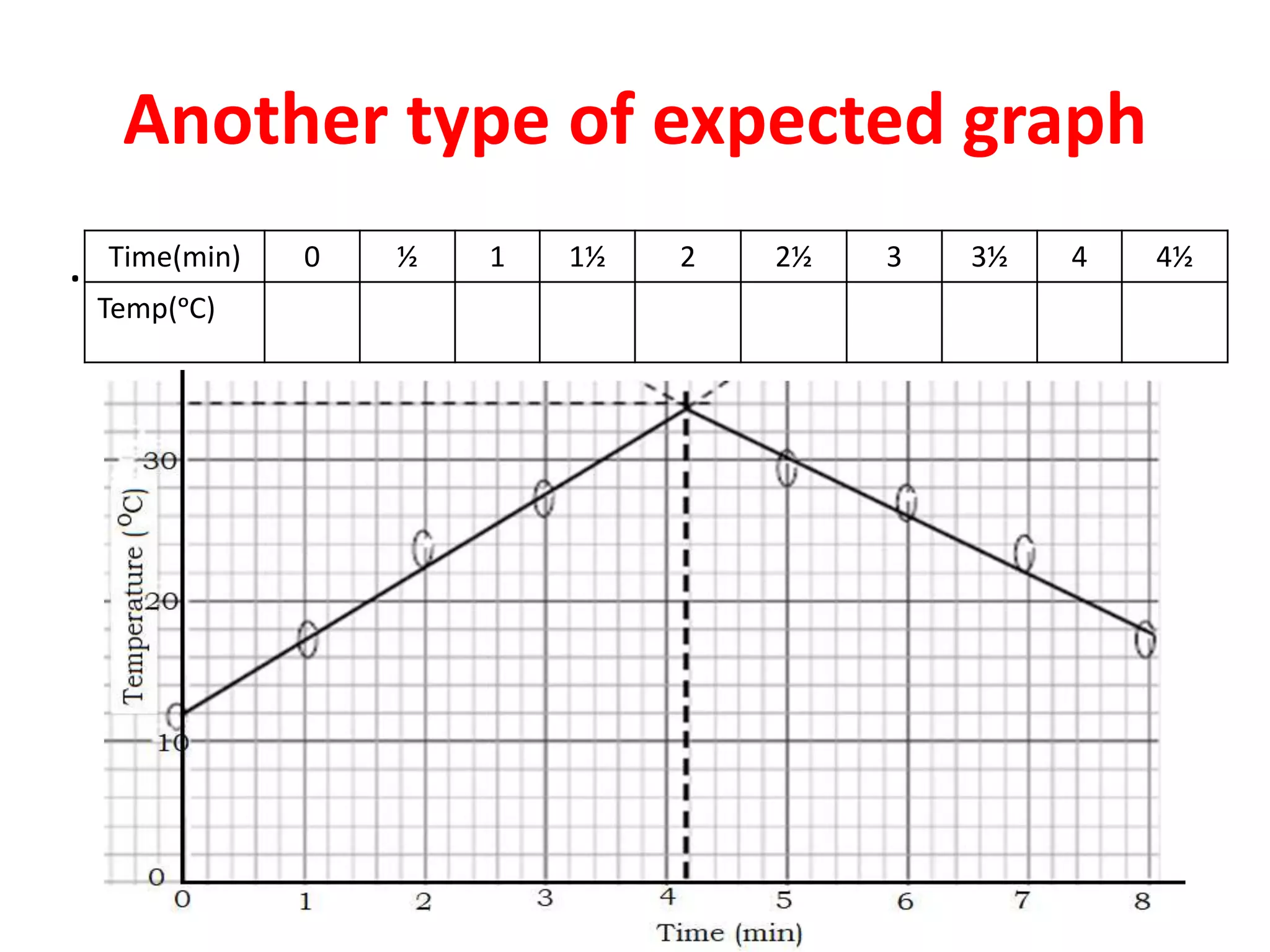
This document provides guidance on qualitative analysis techniques for KCSE chemistry practical exams. It outlines common reagents used to test for various cations and anions, including sodium hydroxide, ammonia, lead nitrate, sulfuric acid, potassium manganate. Sample procedures are provided for using these reagents to infer the presence of ions like sulfate, carbonate, chloride, and lead. Guidelines are also given for organic compound testing using bromine water or potassium manganate, as well as expected temperature graphs for thermochemistry questions.