Embed presentation
Download to read offline

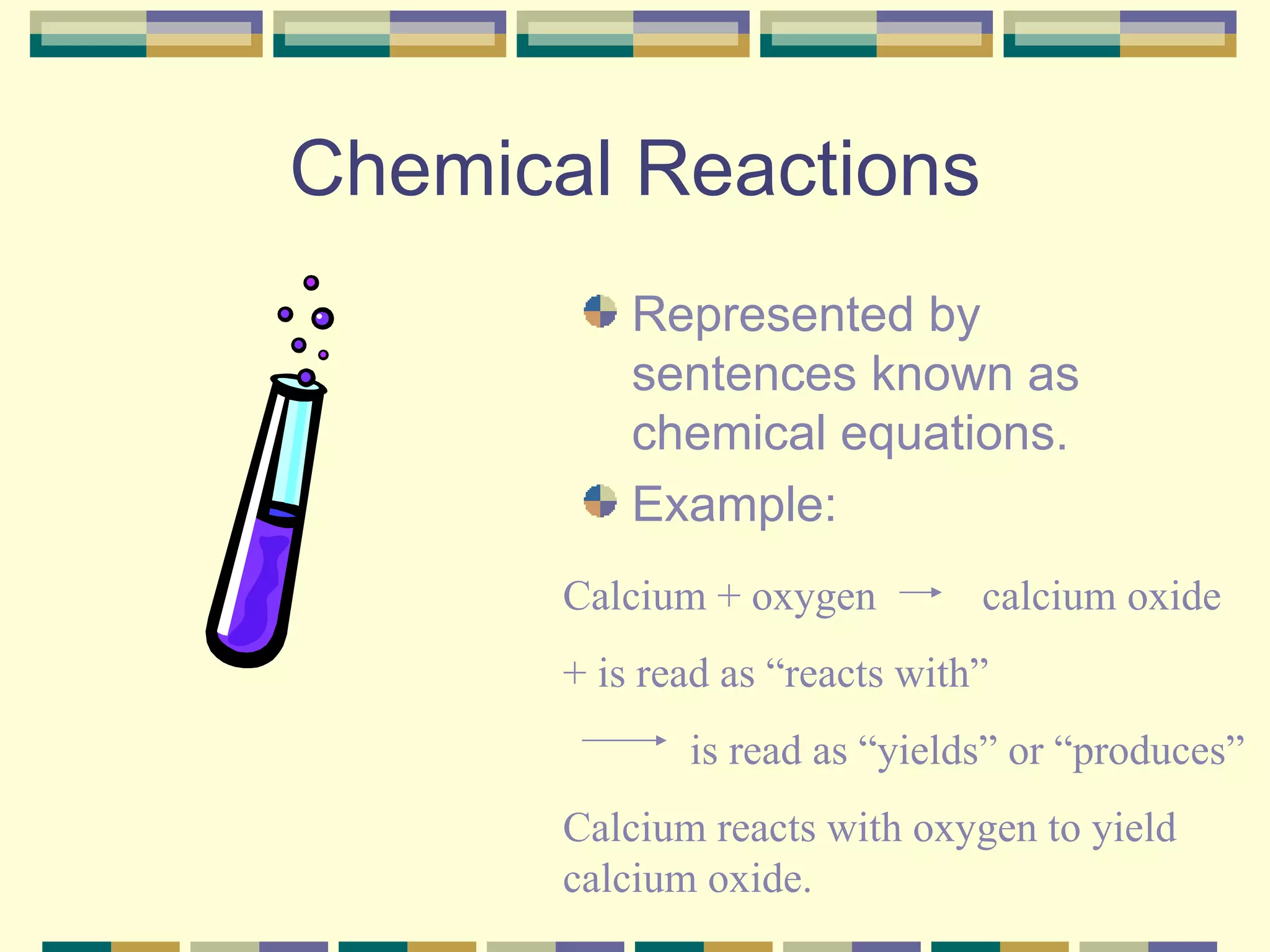


A chemical reaction is a process where reactants are converted into different products, represented by chemical equations. Chemical equations must be balanced to show mass is conserved, with the same number of atoms before and after the reaction, using coefficients as needed. There are several types of chemical reactions including synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement.




