- The document discusses work-related attitudes like job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and organizational citizenship behavior. It explains that these attitudes influence an organization's priorities and outcomes.
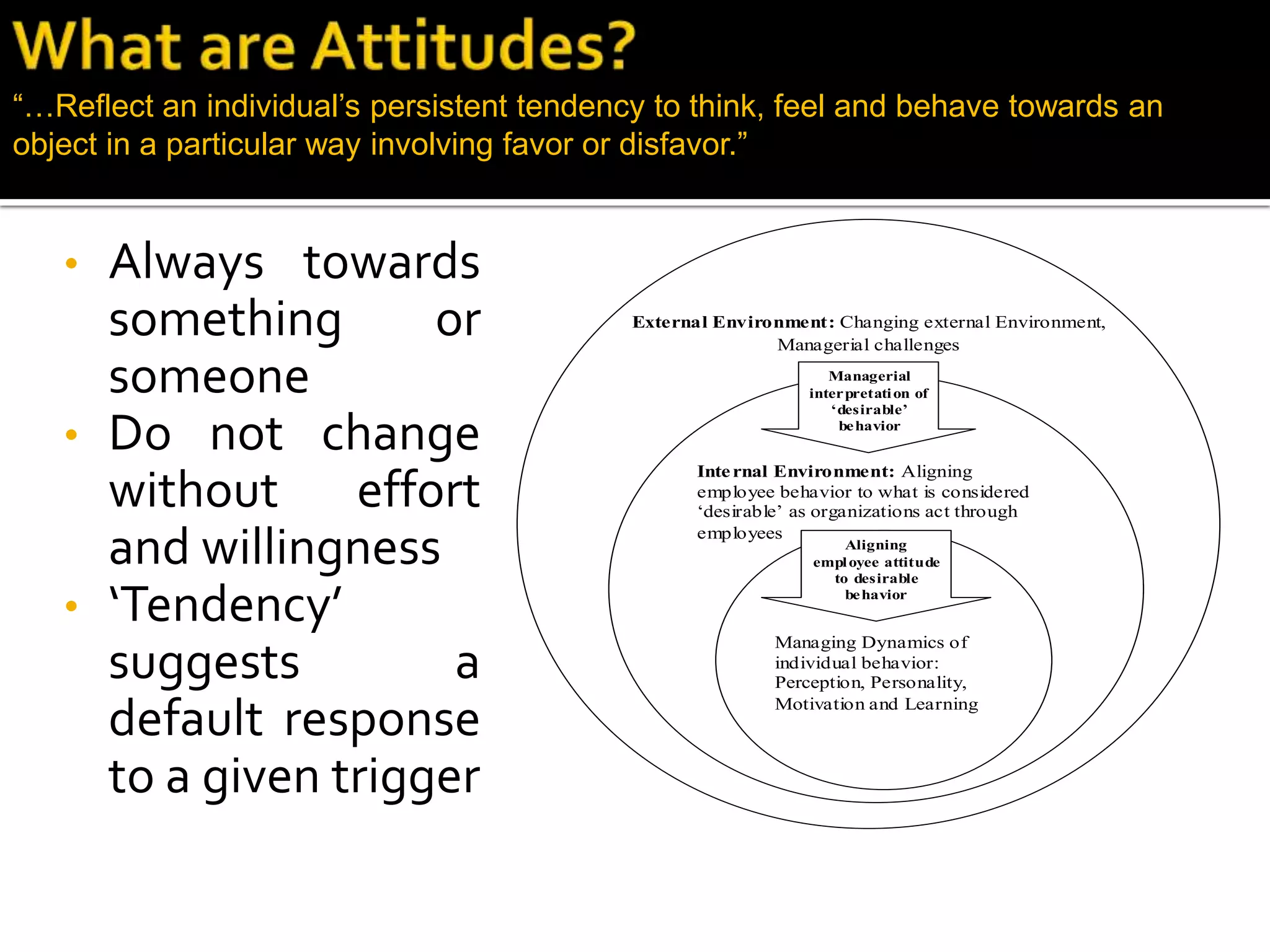
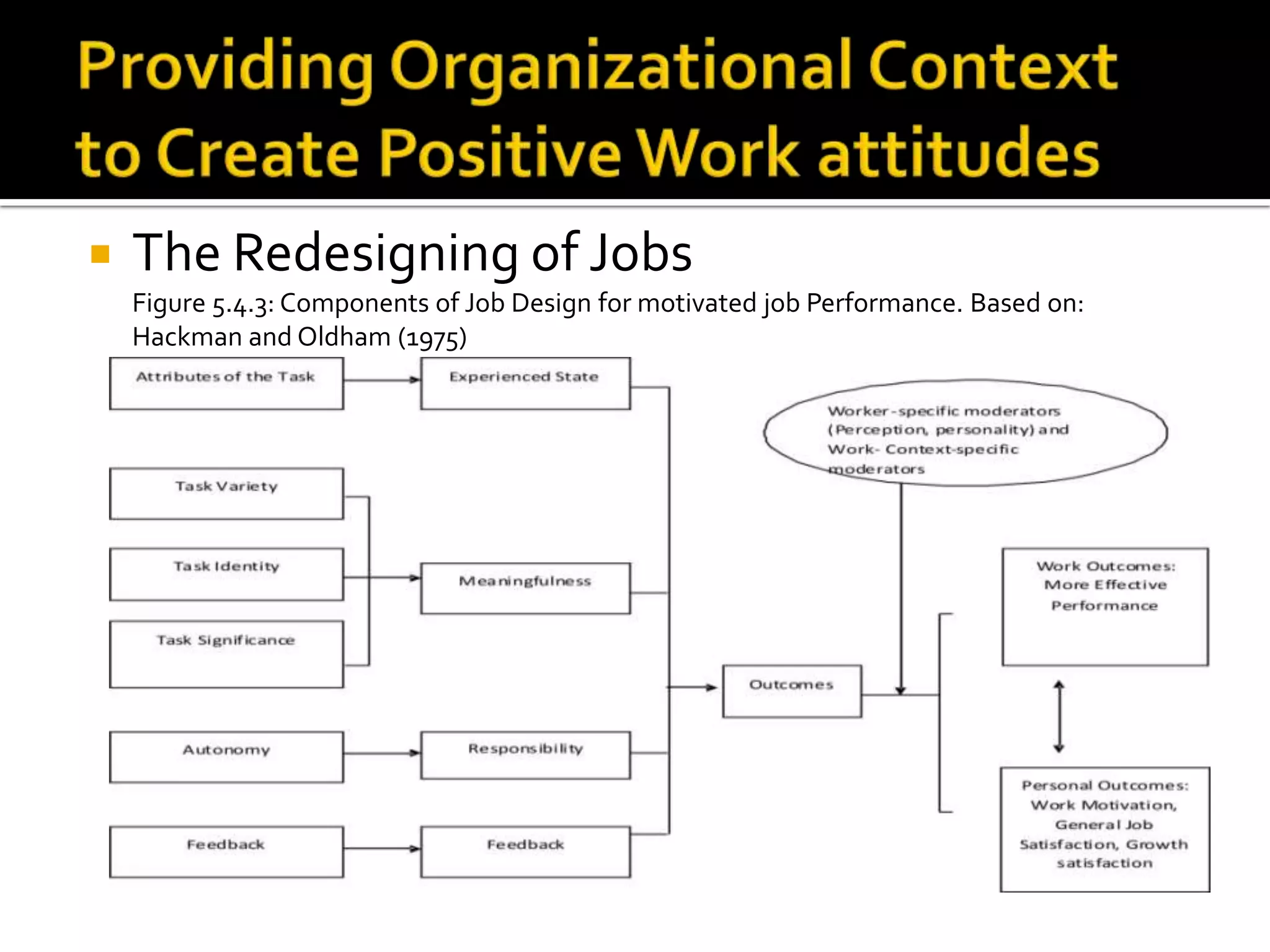
- Organizations can shape favorable attitudes at work by realigning employee behavior to what is considered desirable, managing individual perceptions and motivations, and adopting measures like job redesign, incentives, and feedback.
- Measures include reinforcing desired behaviors, punishing undesirable ones, using individual and group incentives, setting goals and providing feedback, ensuring pay equity, and offering stock ownership plans to increase employee commitment.