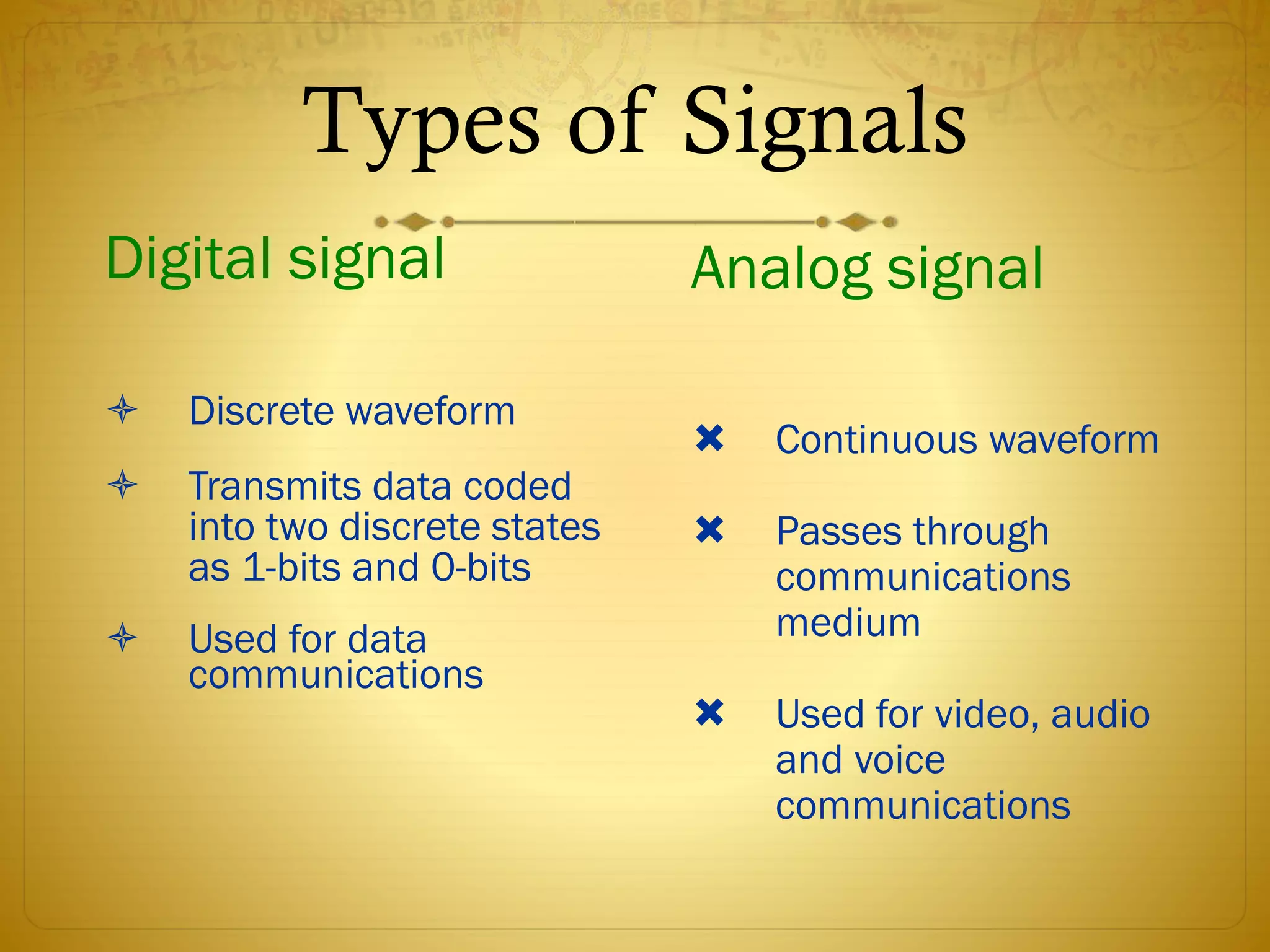
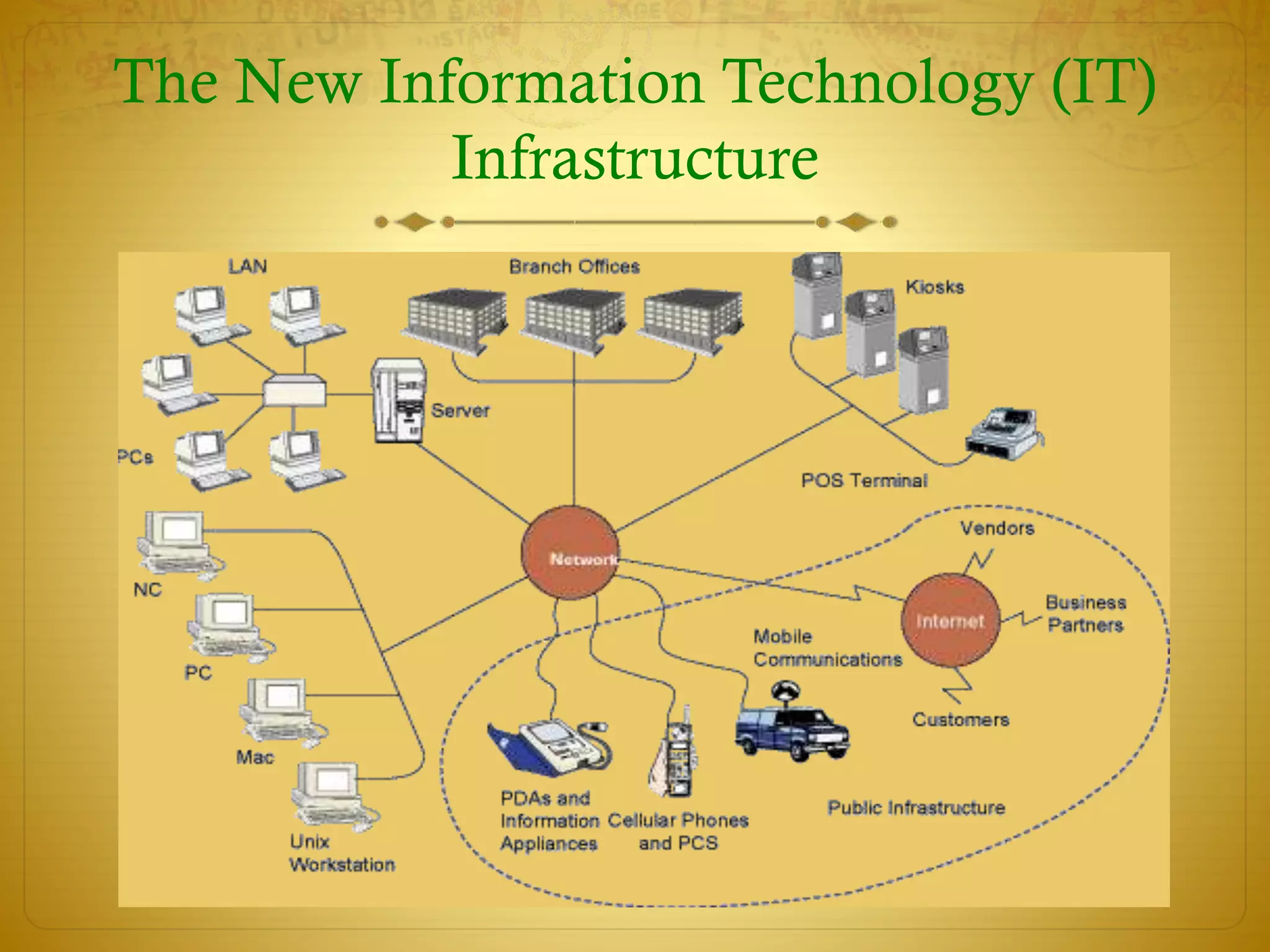
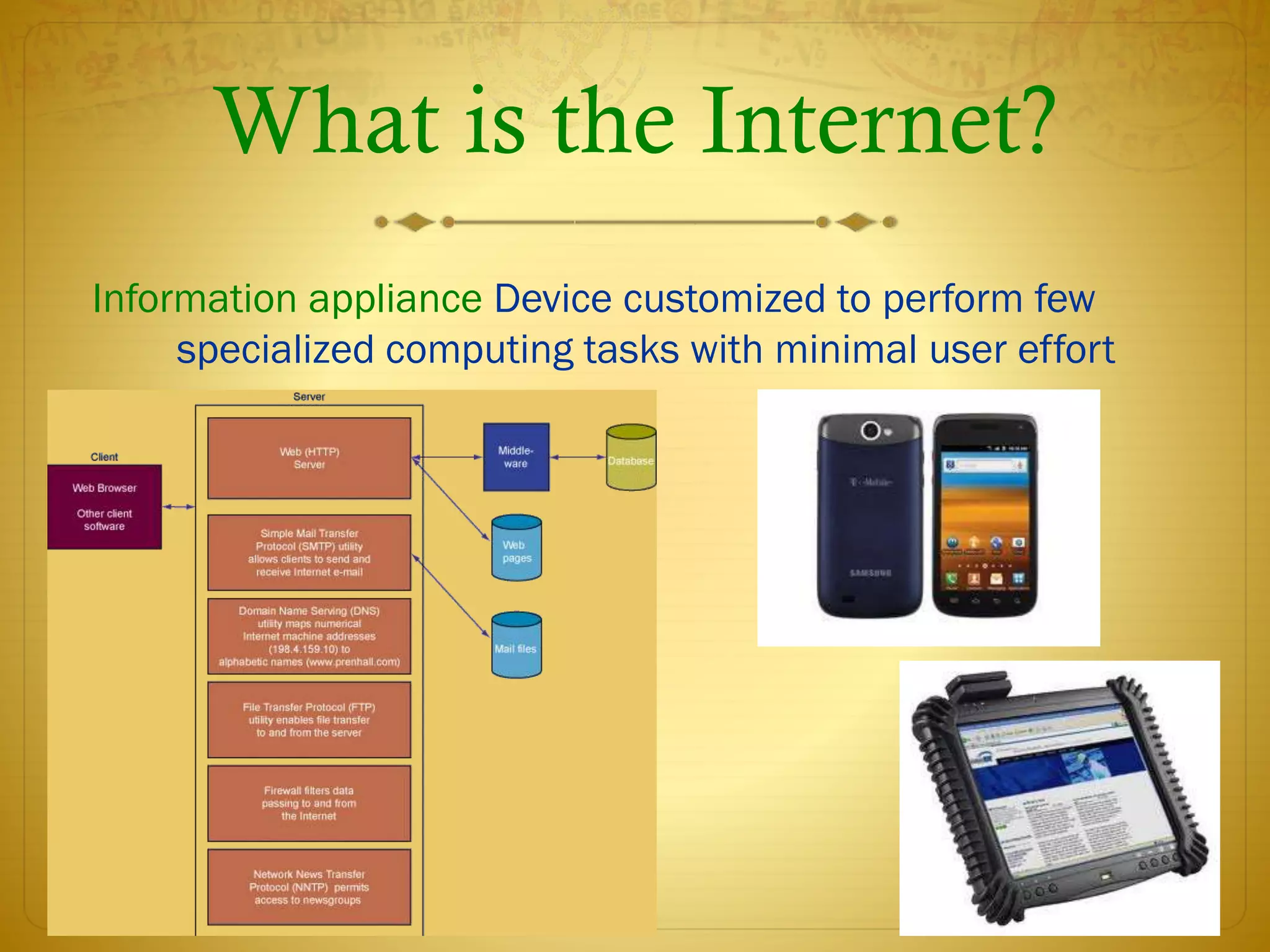
This document discusses telecommunications, the internet, and wireless technology. It covers telecommunication system components and functions like computers, terminals, communication processors, and software. It describes digital and analog signals and different types of communication networks like star, bus, and ring networks. The document also discusses electronic commerce technologies, the new IT infrastructure, internet tools, the wireless web, and challenges of managing the new IT infrastructure.