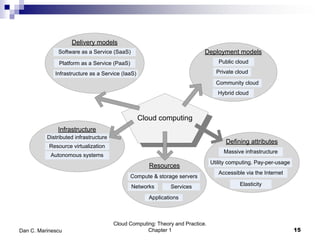
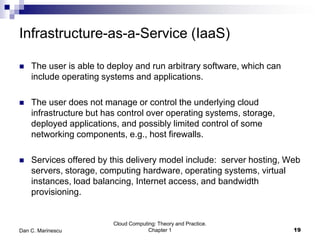
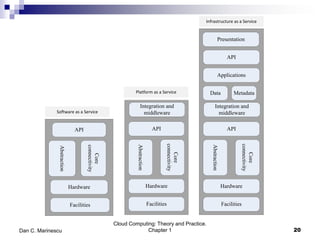
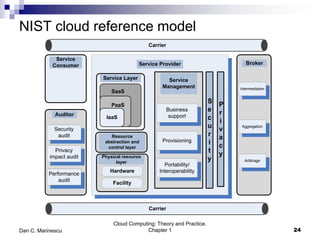
This chapter introduces cloud computing and discusses its key concepts. It describes cloud computing as a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. It discusses the delivery models of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). The chapter also outlines some of the benefits of cloud computing as well as challenges and ethical issues that need to be addressed for its successful adoption.