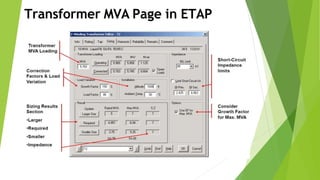
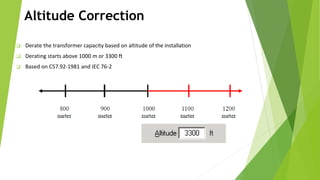
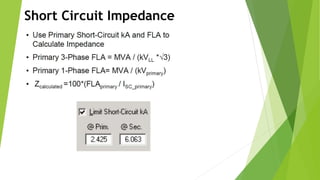
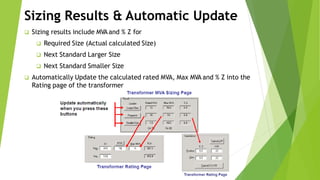
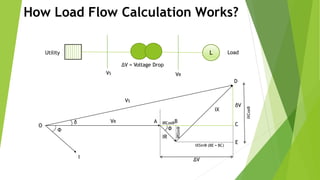
The document discusses load flow analysis calculations and transformer parameters. It explains how to calculate the X/R ratio of a transformer using nameplate data like impedance and losses. It also describes how to size transformers based on standards by considering cooling type, altitude, temperature, load variation, and short-circuit requirements. The document shows the load flow calculation process using vector diagrams and equations, comparing hand calculations to results from the ETAP software.











![O
VS
I
VR
IR
IX
δ
Ф Ф
A
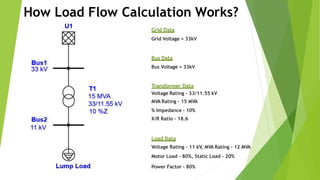
How Load Flow Calculation Works?
D
C
E
∆V
δV
IRCosФB
OD = VS, OA = VR
OD2 = OC2 + CD2
OD2 = (OA+AB+BC)2 + (DE-CE)2
AB = IR COSФ, BC = IX SINФ
DE = IX COSФ, CE = IR SINФ
VS2 = (VR + IR COSФ + IXSINФ)2 + (IX COSФ – IR SINФ)2
= (VR + (R*P + X*Q)/VR)2 + (X*P – R*Q)/VR)2
= √{(VR + (R*P + X*Q)/VR)2 + (X*P – R*Q)/VR)2}
= CD / OC = (DE – CE) / (OA + AB + BC)
= (IX COSФ - IR SINФ) / (VR + IR COSФ + IX SINФ)
= ((X*P – R*Q)/VR) / (VR + (R*P + X*Q)/VR)
= ATAN [((X*P – R*Q)/VR) / (VR + (R*P + X*Q)/VR)] Radian
VS
T
ANδ
δ
IRSinФ
IXSinФ (BE = BC)
IXCosФ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chaptertwoparttwo-230704170738-b64e7af7/85/Chapter-two-Part-two-pptx-18-320.jpg)