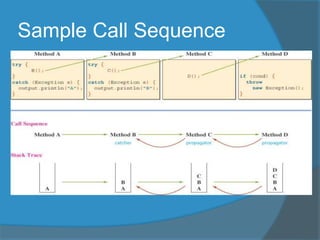
A method can propagate an exception back to its caller by including the thrown exception type in its method header. When a method directly throws an exception using the throw keyword, it is the origin of the exception. A method that may throw an exception either directly or indirectly is called an exception thrower, which can be either a catcher that includes a catch block or a propagator that does not contain a catch block.