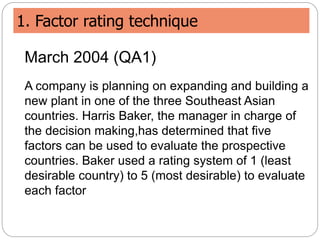
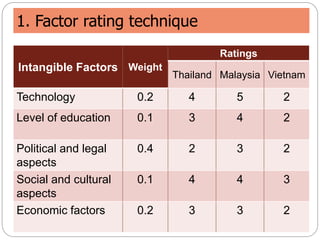
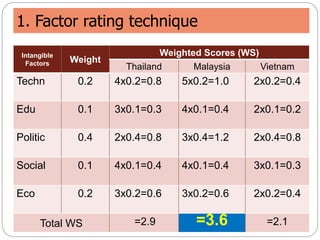
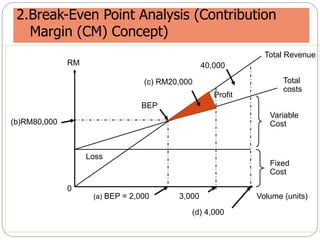
This document discusses facility location analysis and provides examples of location decision methods. It defines facility location as determining a geographic site for a firm's operations. Key factors influencing location decisions are discussed as tangible/quantitative and intangible factors. Methods covered include the factor rating technique, break-even point analysis, and location break-even analysis. Examples of each method are provided to illustrate how they are used to evaluate potential locations.