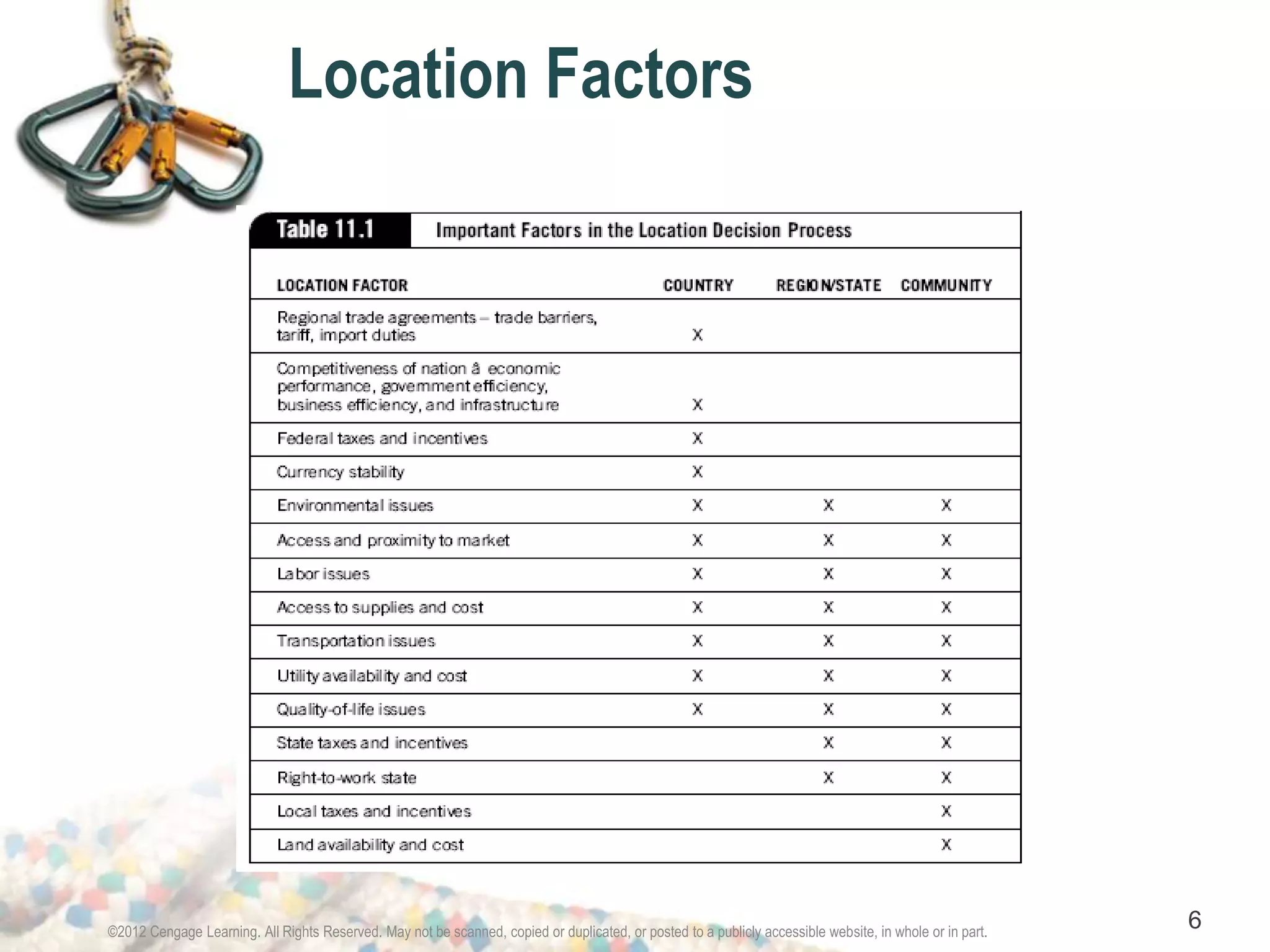
This chapter discusses factors that influence location decisions for supply chain facilities. It identifies critical location factors such as access to markets and suppliers, labor and transportation costs, tax rates and incentives. It also presents techniques for evaluating potential locations, including weighted factor models and break-even analysis. Additionally, it covers the importance of business clusters and sustainable development considerations in global location strategies.





![Location Factors (Continued)
RTA & the WTO (Continued)
European Union (EU): [1950] Set up after the WWII, the
EU consists of 27 members
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA):
[1994] among the U.S., Canada, & Mexico
Southern Common Market (MERCOSUR): [1991]
among Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, & Uruguay
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
[1967] in SE Asia
Common Market of Eastern and Southern Africa
(COMESA)
©2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter113rded-141119092300-conversion-gate02/75/Chapter-11-3rd-edition-8-2048.jpg)