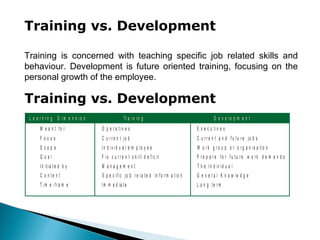
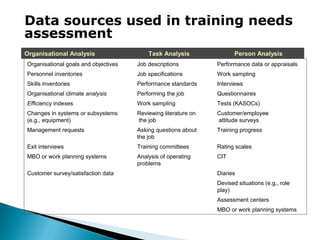
This document discusses various topics related to employee training and development. It defines training and development, outlines the need for training due to changing technology, quality customers, and other factors. It also distinguishes between training and development, noting that training focuses on current job skills while development prepares employees for future roles. A systematic approach to training is described, including assessing training needs through organizational, task, and personal analyses. Different training methods like on-the-job and off-the-job training are also mentioned.