This document discusses solving linear equations in one unknown. It provides definitions of key terms like linear equation, solution/root of an equation. It explains that a linear equation in one unknown has only one solution/root. Various forms of linear equations are presented along with the steps to solve each type. Examples are worked through to demonstrate the solving process and common errors are identified. The document also contains sample past year PMR exam questions testing the solving of linear equations.




![Module PMR
PMR past year questions
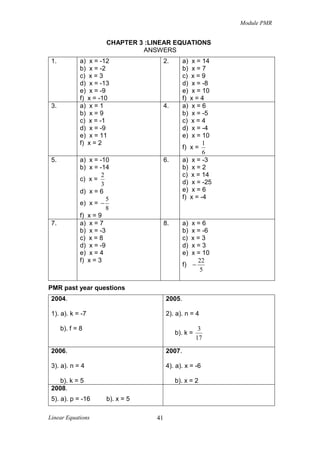
2004
1). Solve each of the following equations.
a) k = −14 − k
3
b) f + (6 − 4 f ) = −31
2
[3 marks]
2005
2). Solve each of the following equations.
a) 2n = 3n − 4
b) 2k =
3 − 7k
5
[3 marks]
2006
3). Solve each of the following equations.
a)
12
=3
n
b) 2(k − 1) = k + 3
[3 marks]
Linear Equations
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3linearequations-131209230019-phpapp02/85/Chapter-3-linear-equations-8-320.jpg)
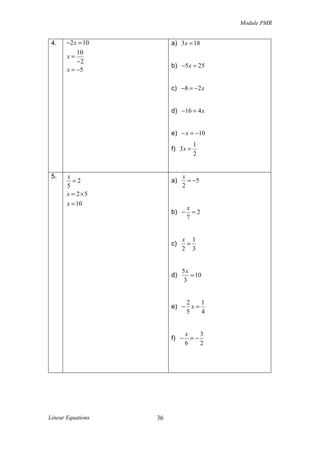
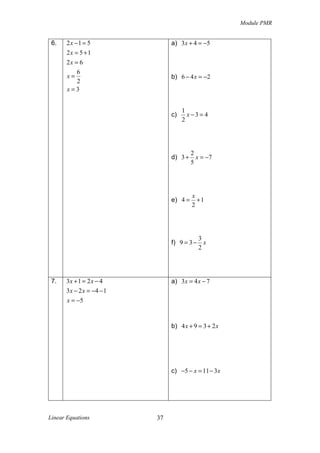
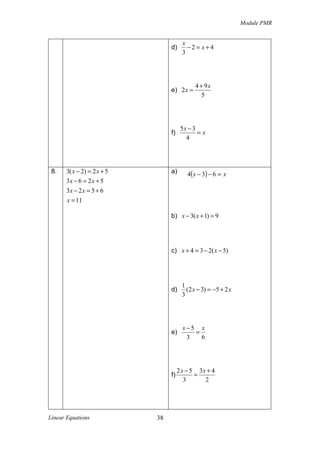
![Module PMR
2007
4). Solve each of the following equations.
a) x + 10 = 4
b)
5x − 4
=x
3
[3 marks]
2008
5). Solve each of the following equations.
a) p + 5 = −11
b) x − 1 =
x+3
2
[3 marks]
Linear Equations
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3linearequations-131209230019-phpapp02/85/Chapter-3-linear-equations-9-320.jpg)