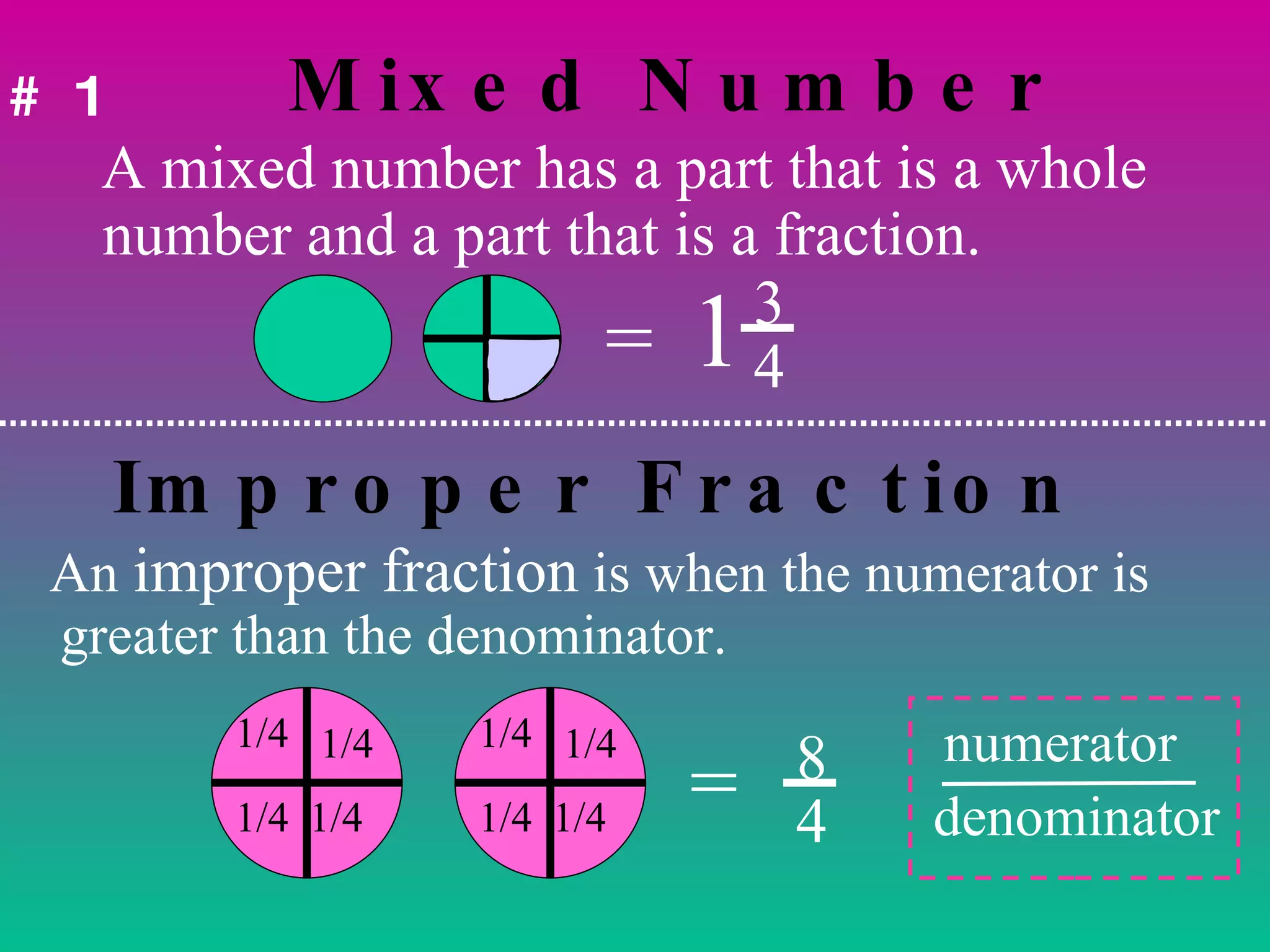
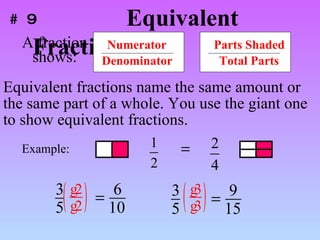
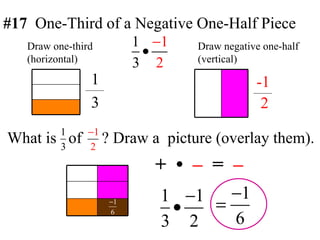
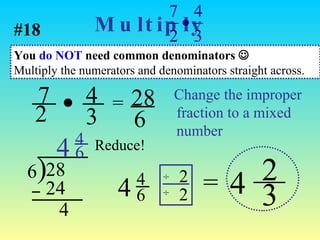
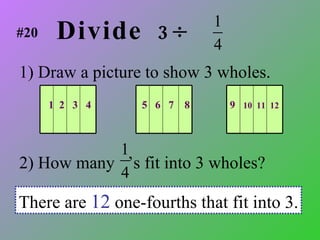
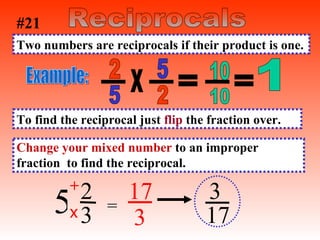
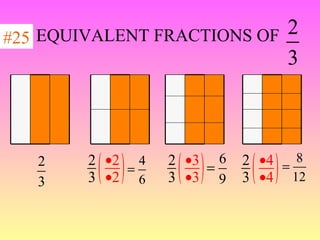
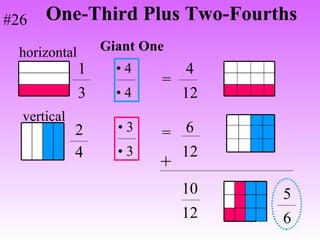
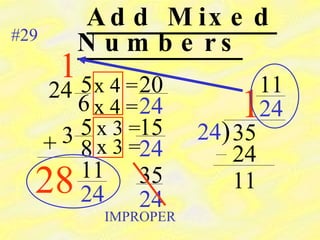
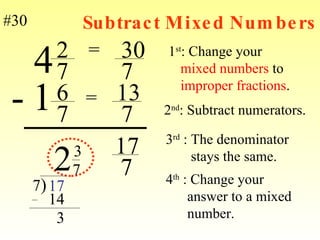
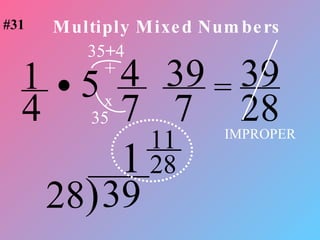1) A mixed number has a whole number part and a fractional part, while an improper fraction has a numerator larger than the denominator.
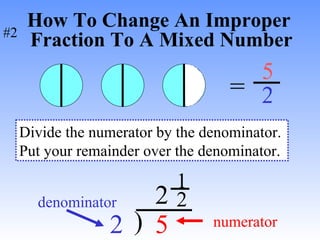
2) To change between mixed numbers and improper fractions, you can multiply or divide the whole number by the denominator and add or subtract the numerator.
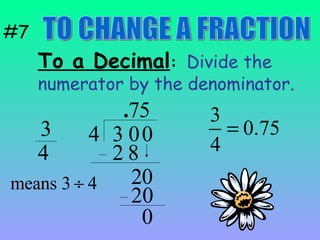
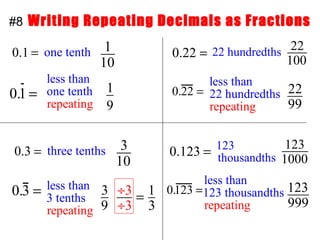
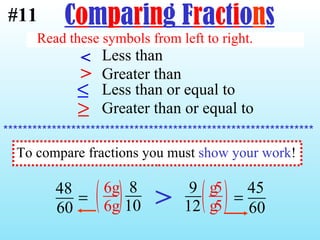
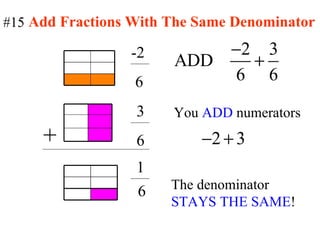
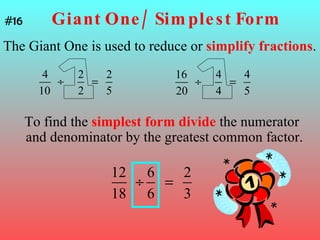
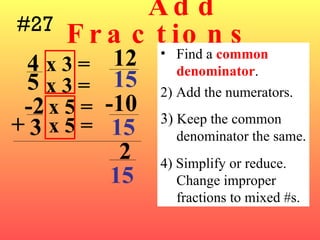
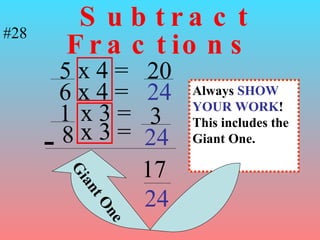
3) When adding, subtracting, multiplying or dividing fractions, you often need a common denominator or need to use reciprocals.