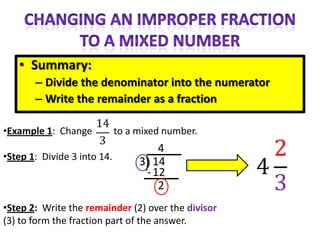
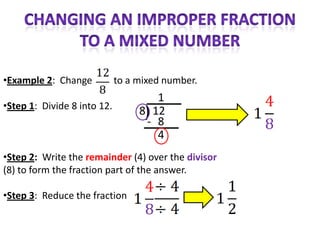
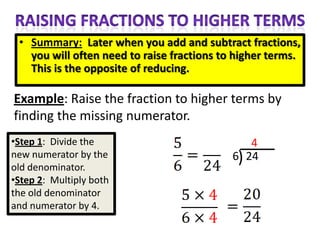
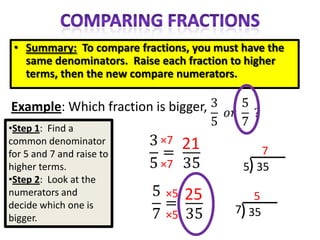
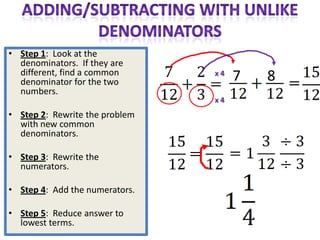
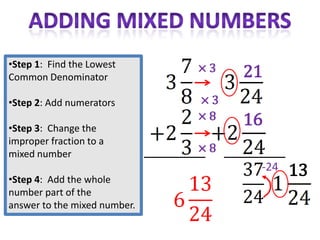
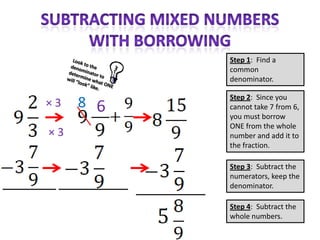
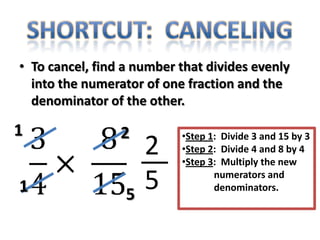
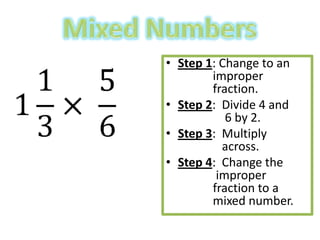
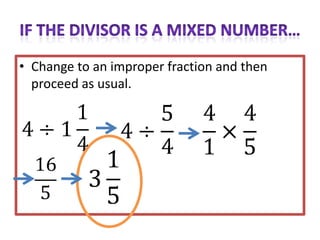
The document provides instructions and examples for performing various fraction operations, such as changing fractions to mixed numbers and improper fractions, reducing fractions, adding and subtracting fractions, multiplying and dividing fractions, and canceling common factors. Key steps are outlined for each type of fraction problem to demonstrate the procedure. Examples are included to illustrate how to apply the steps to calculate fraction problems.