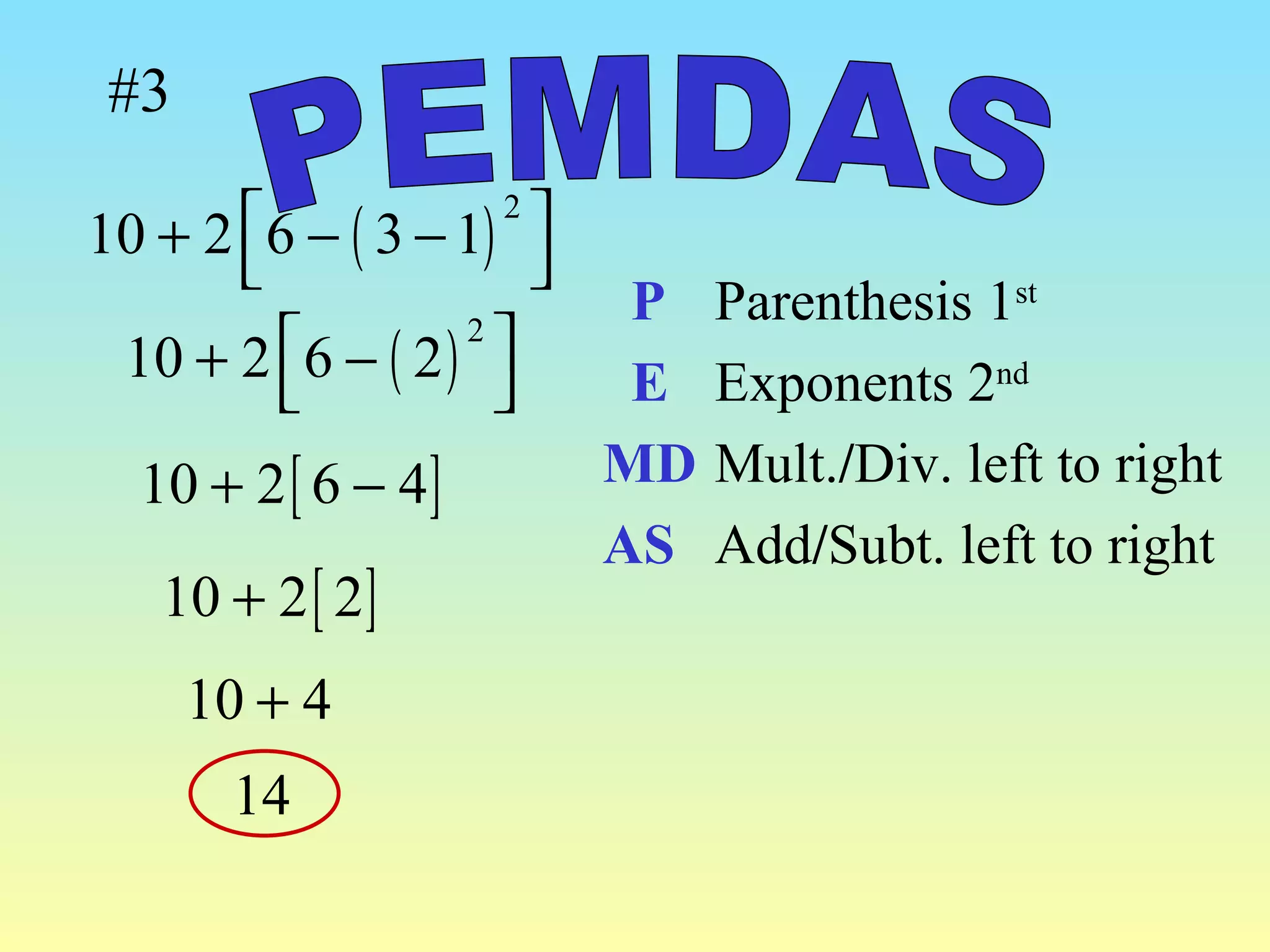
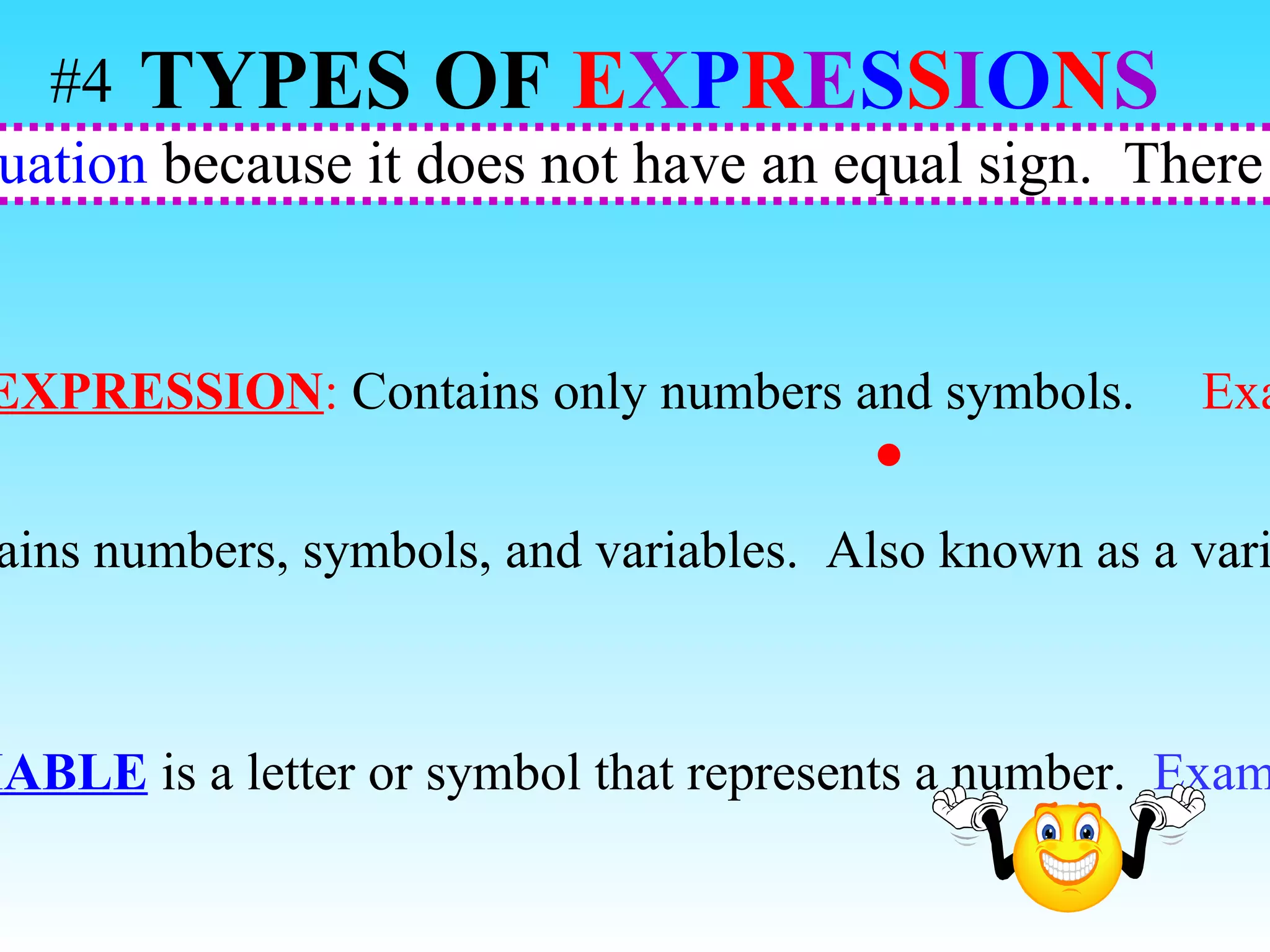
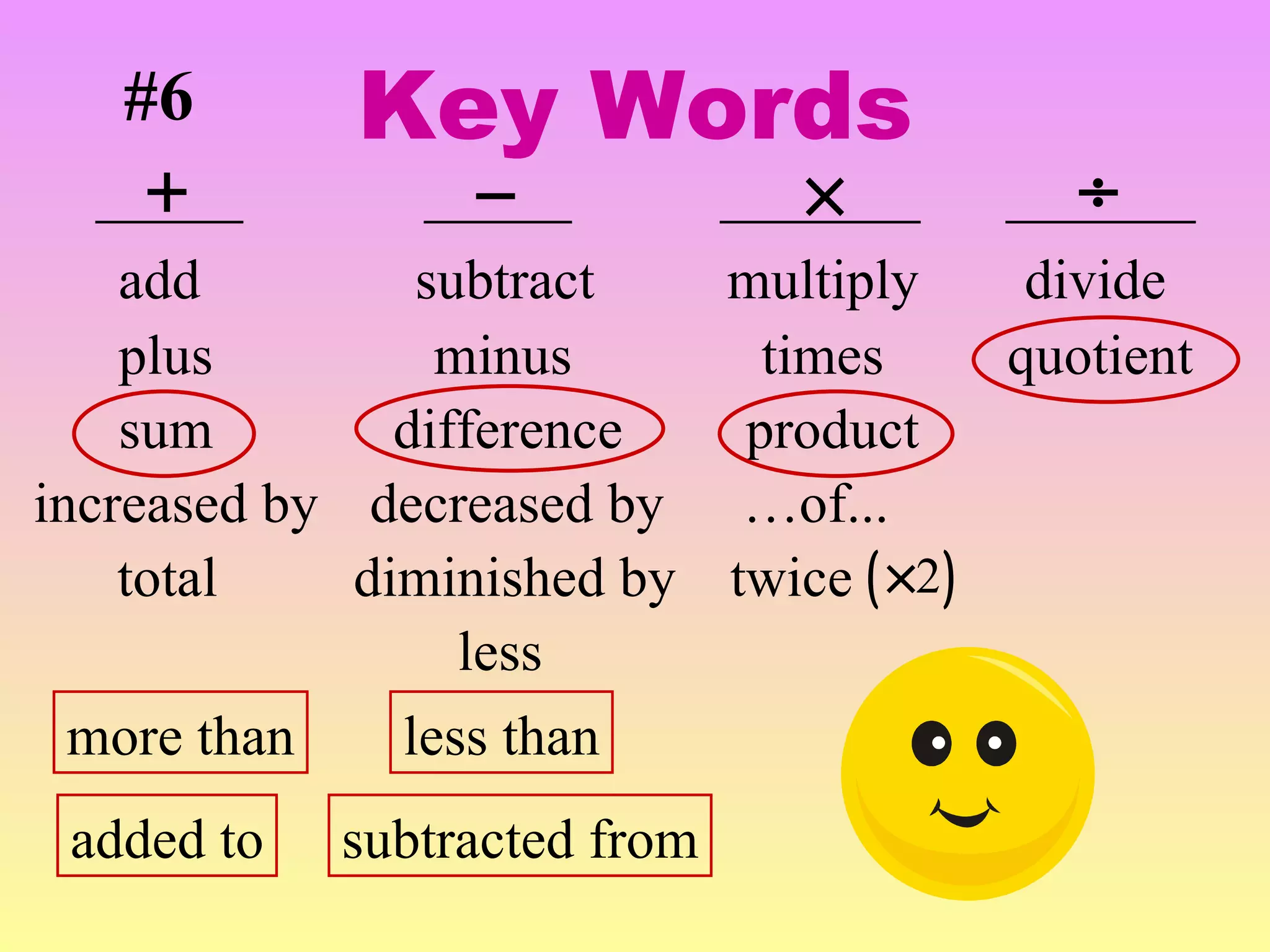
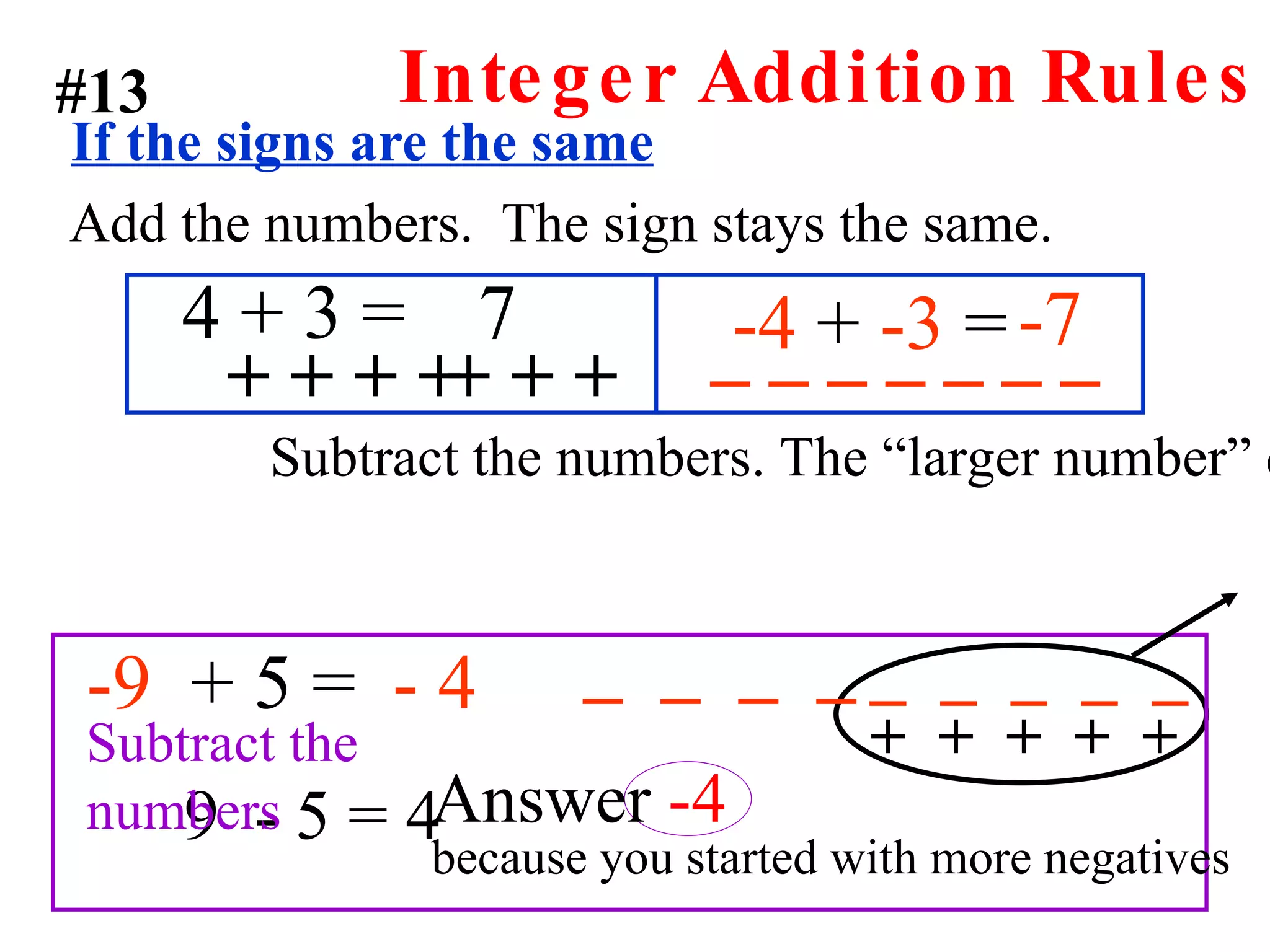
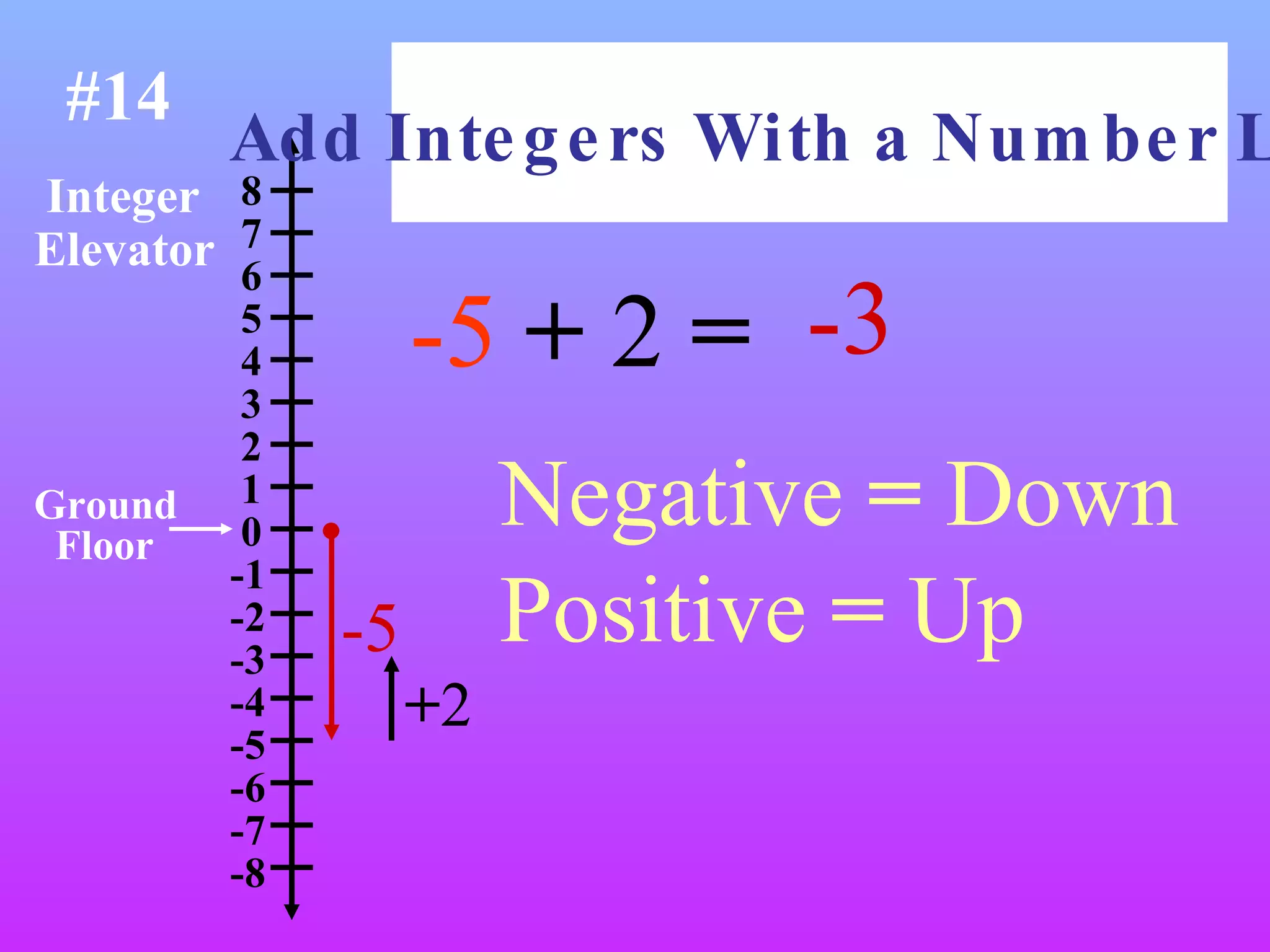
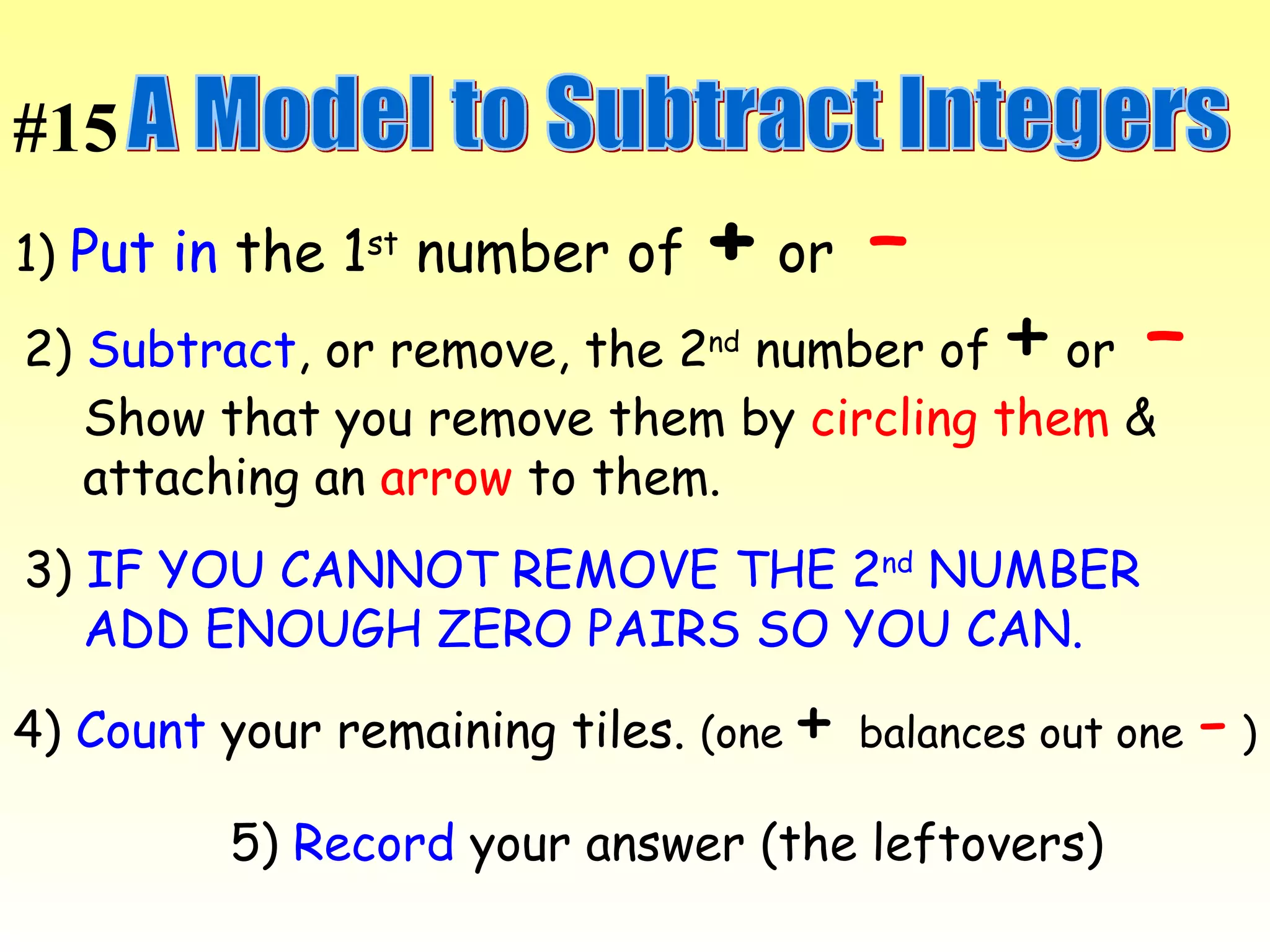
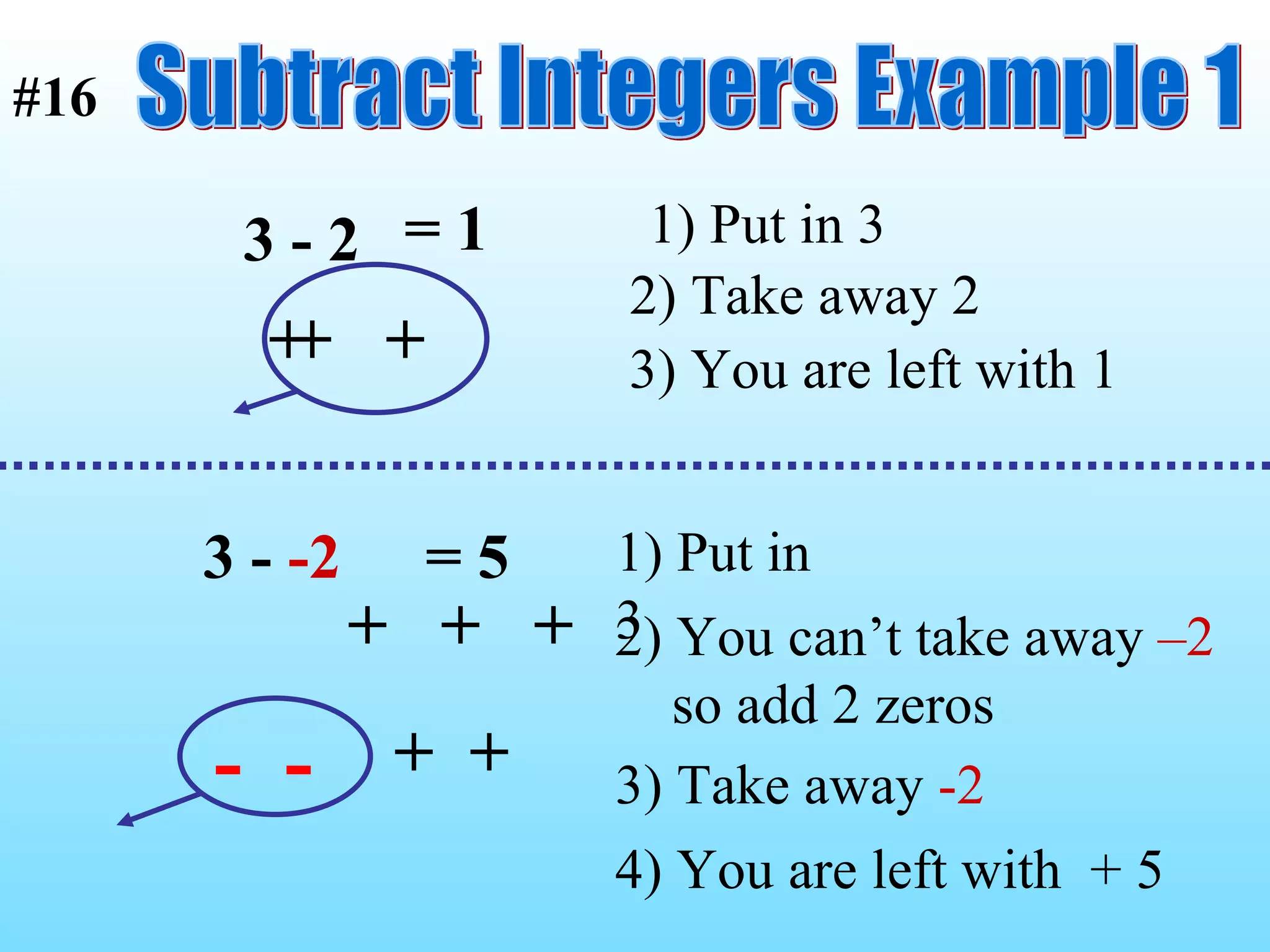
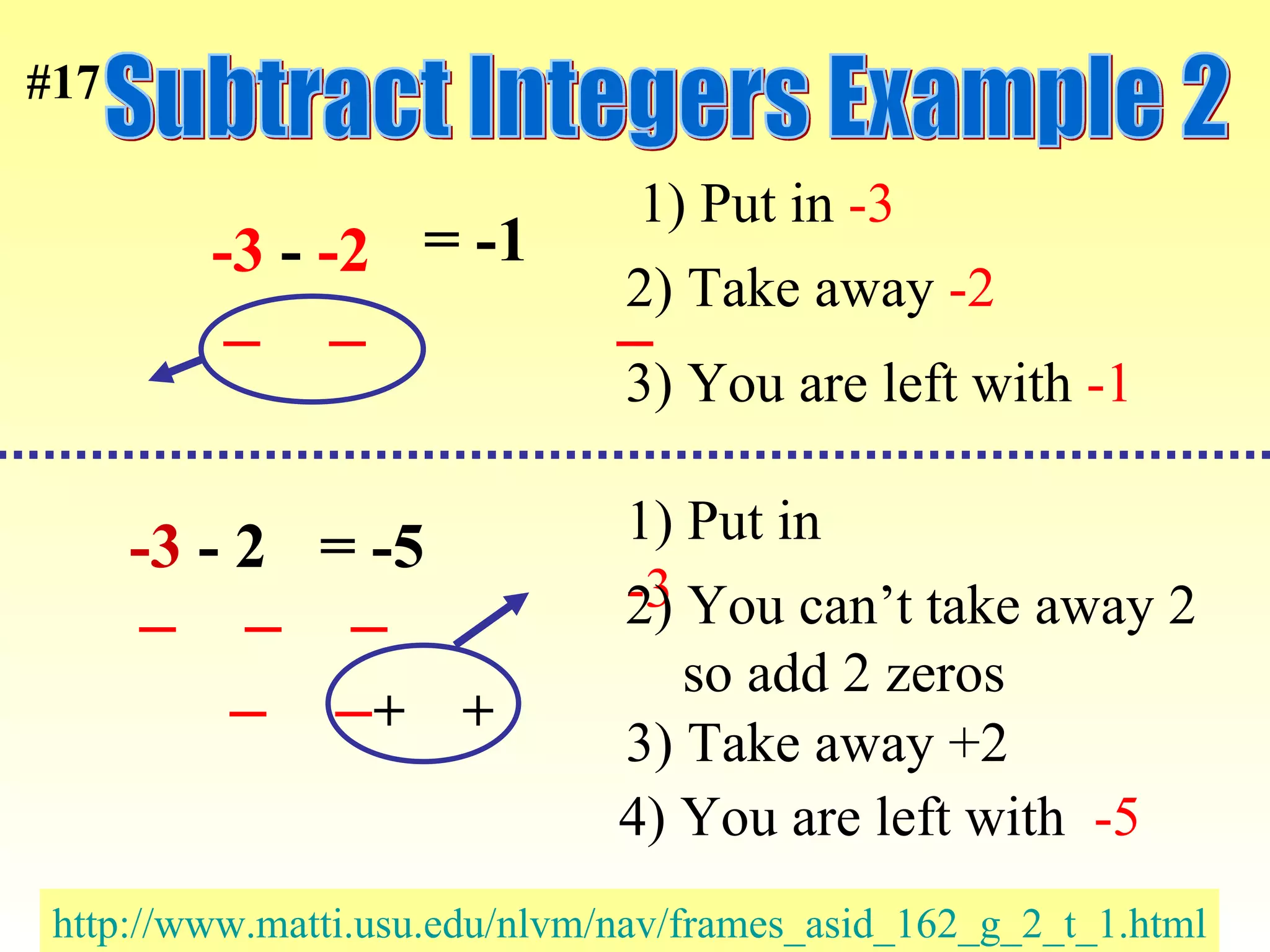
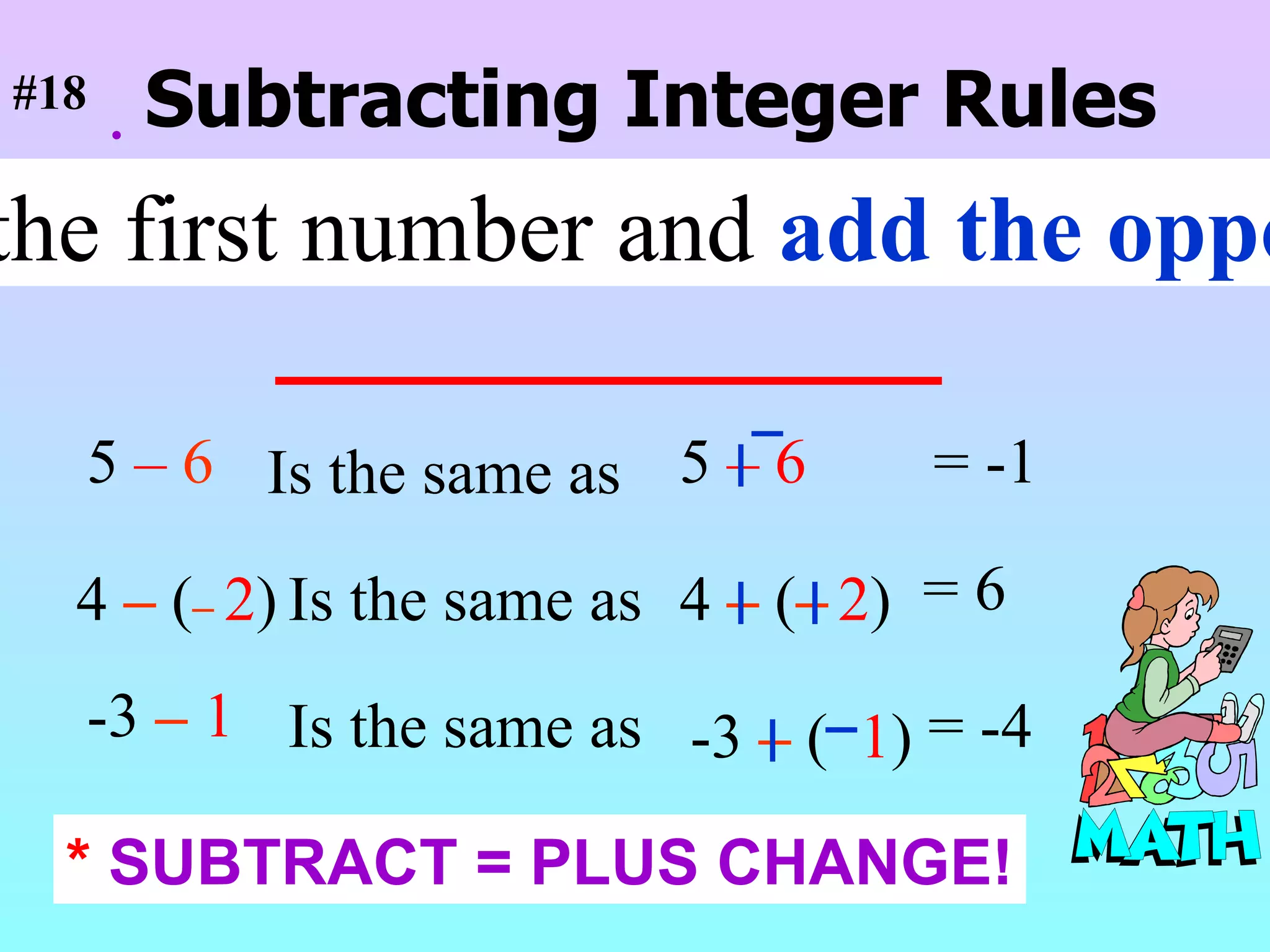
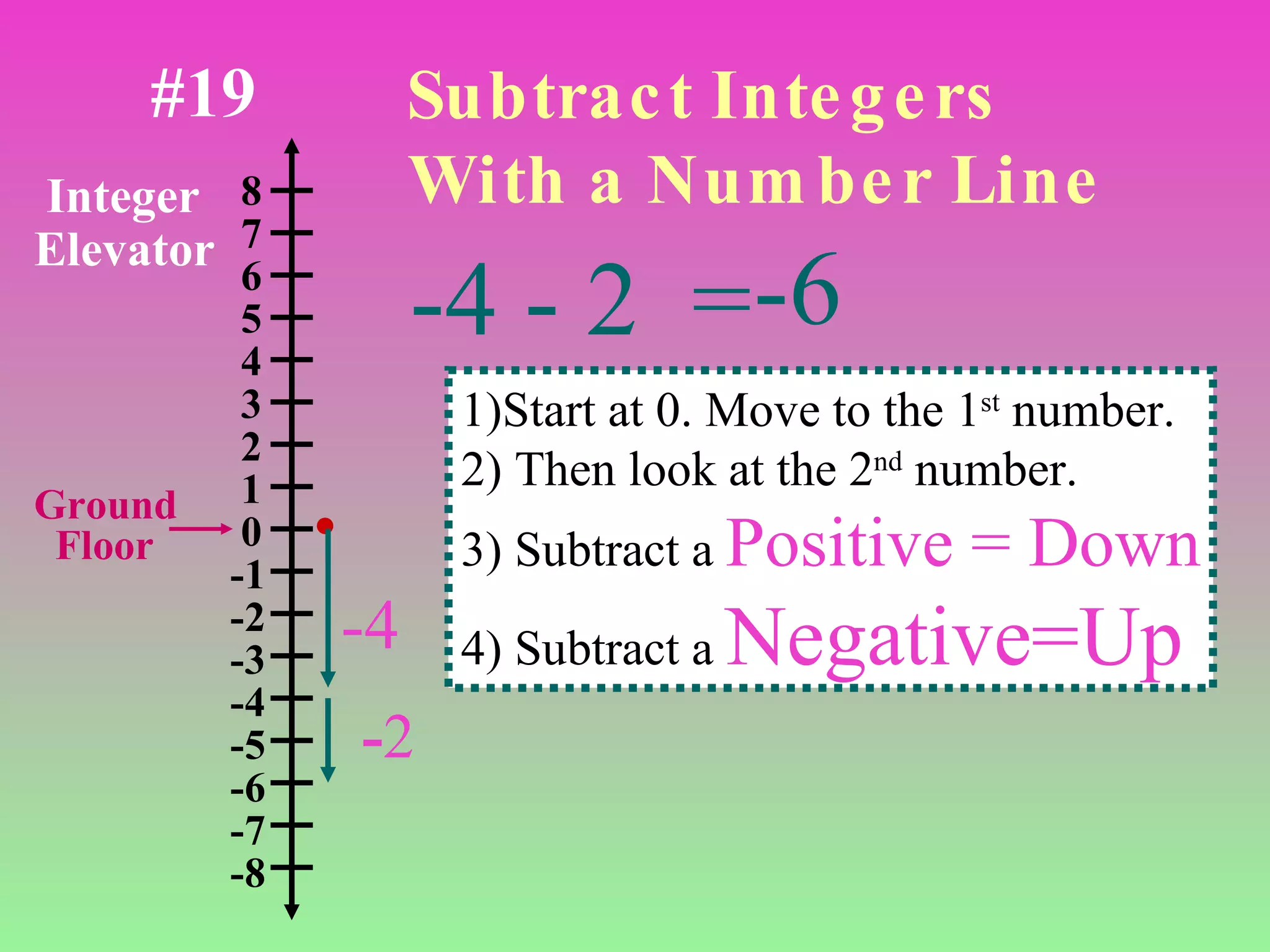
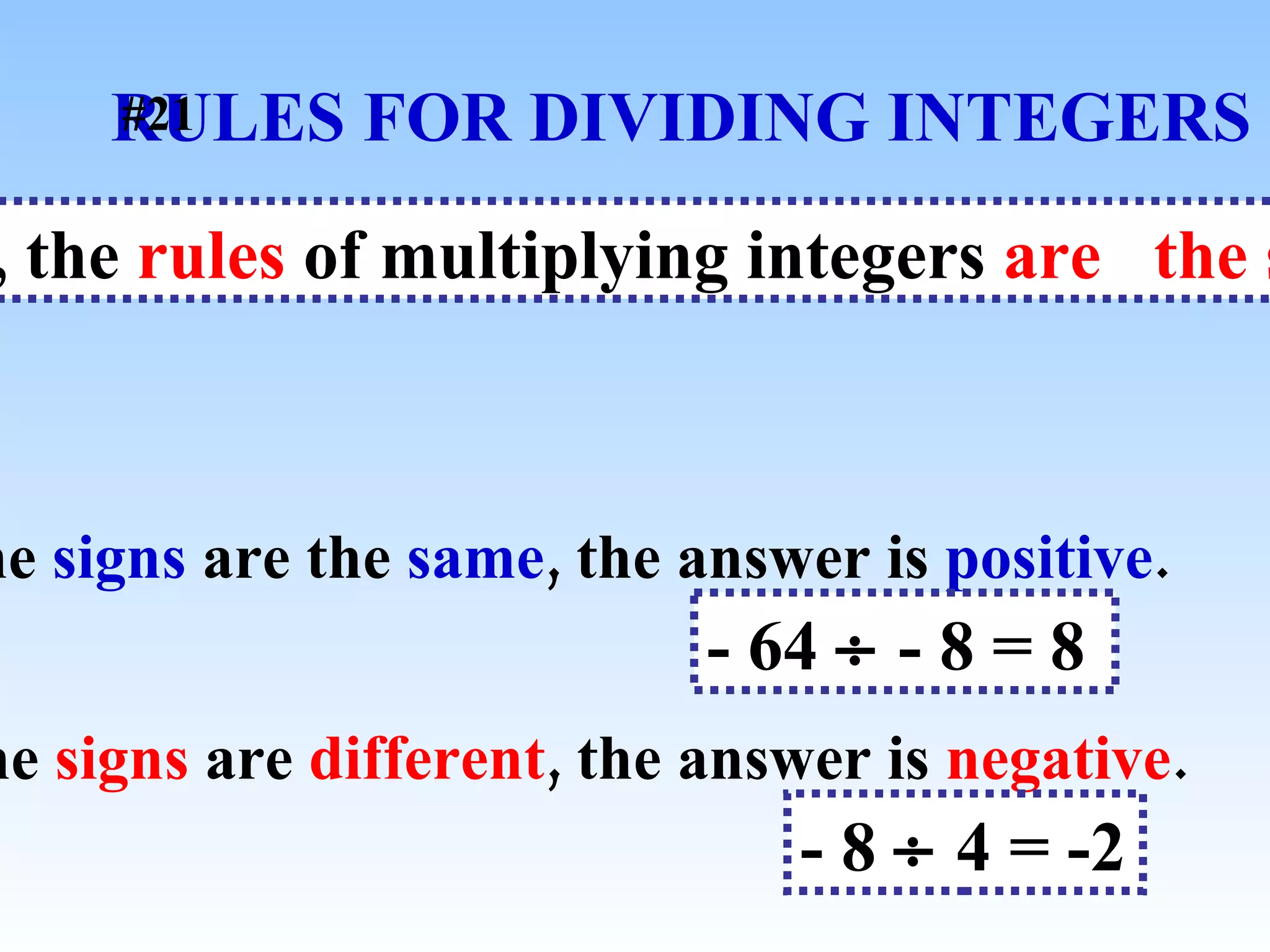
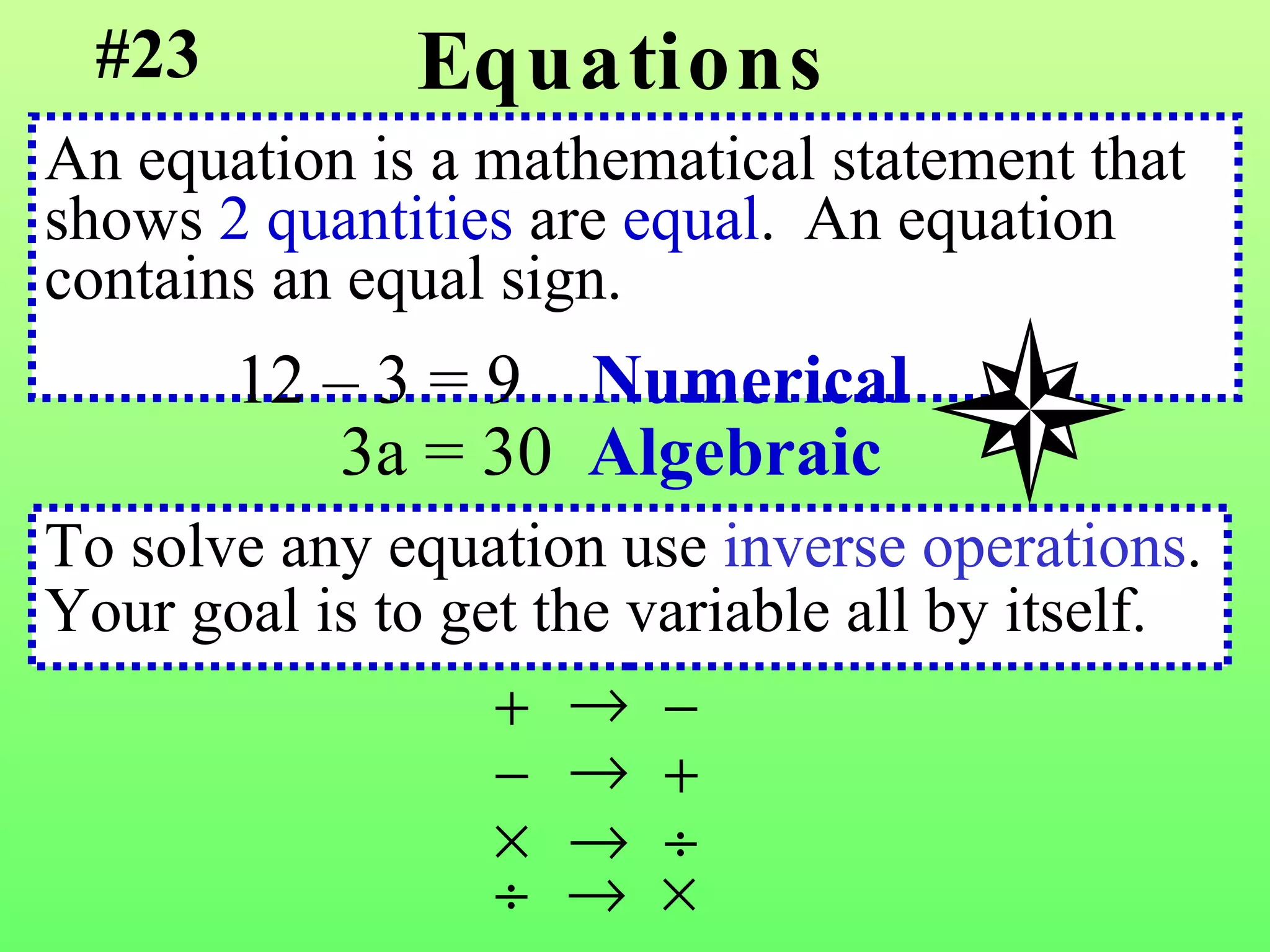
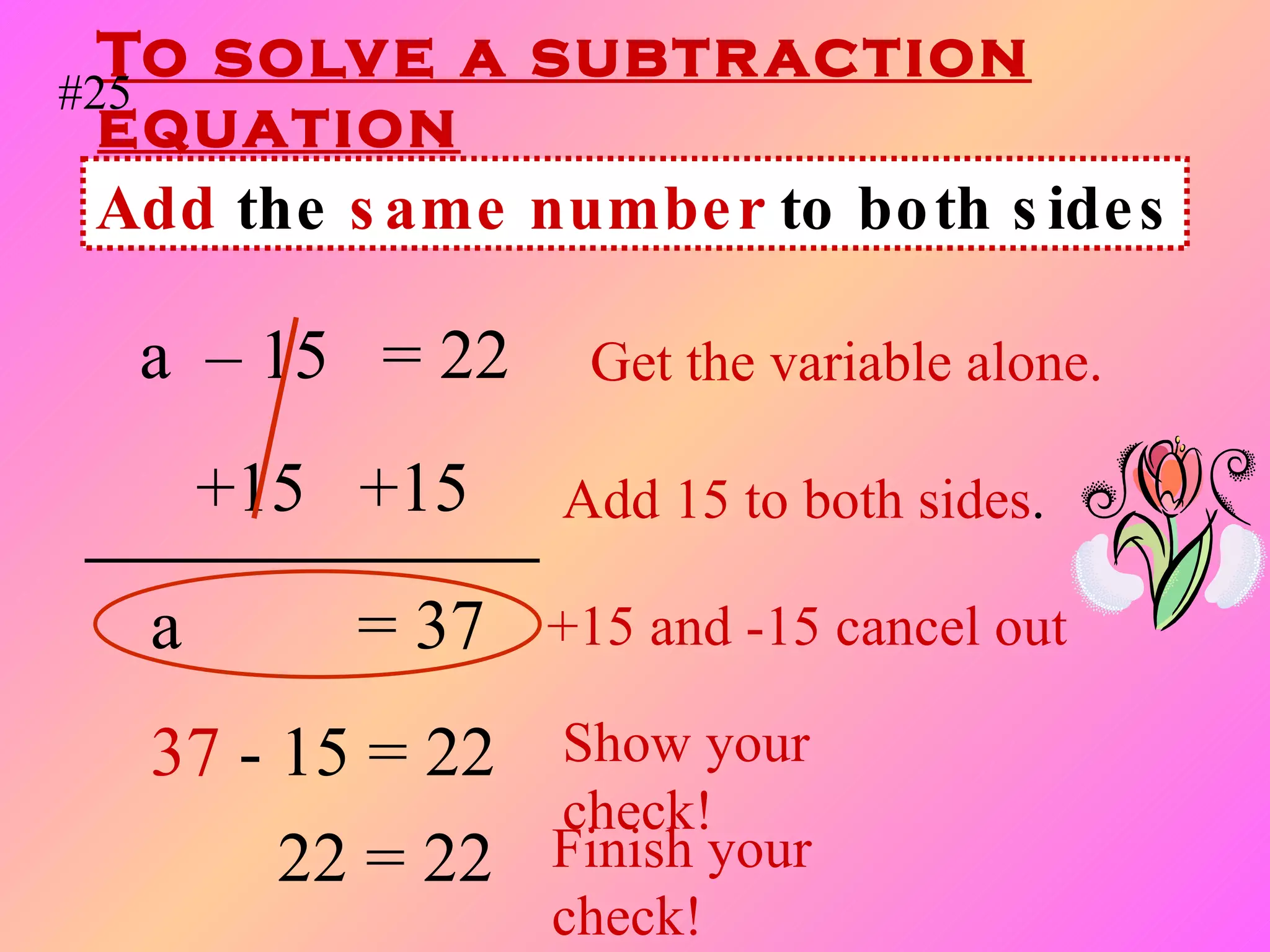
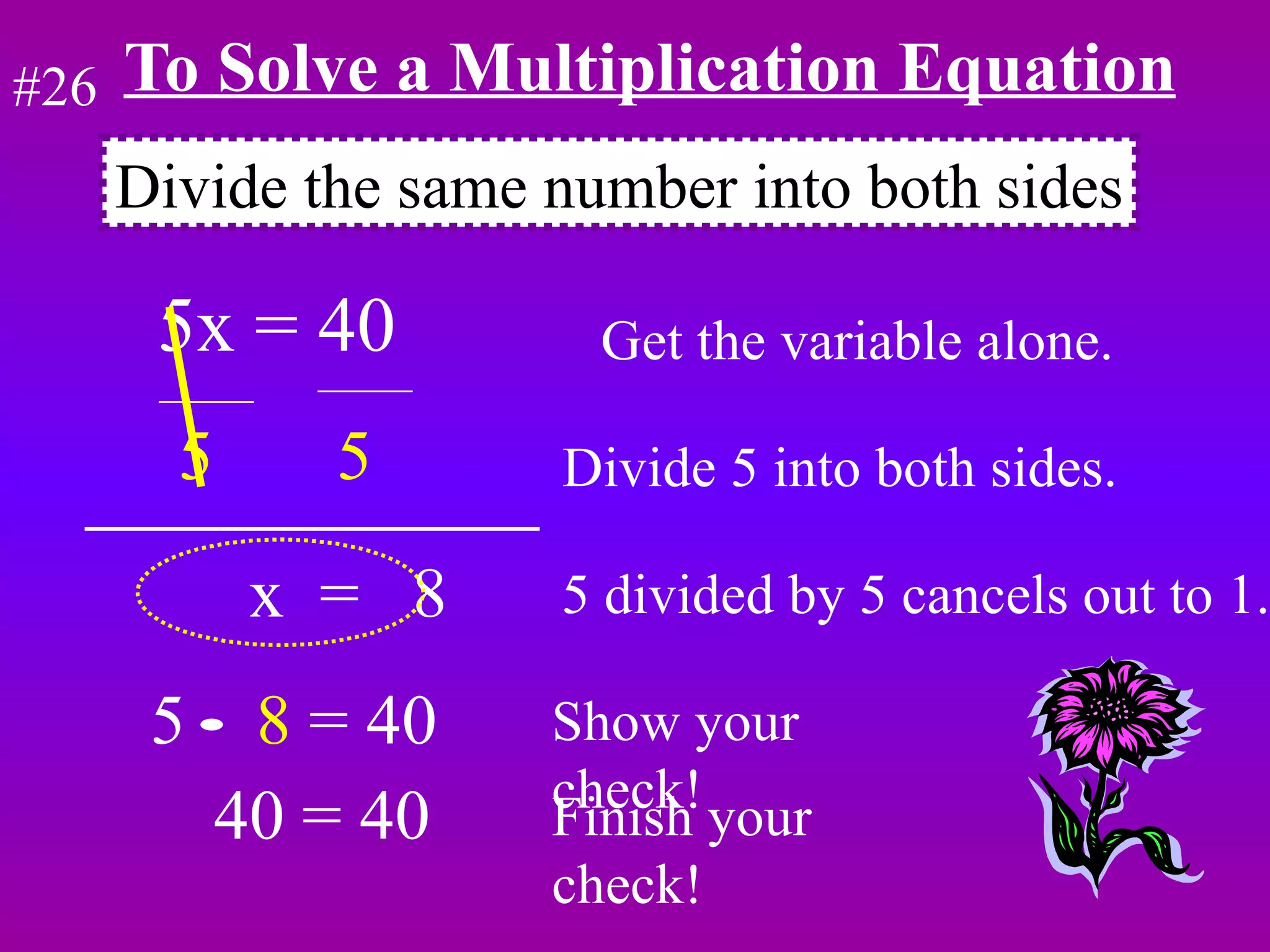
The document discusses the order of operations (PEMDAS) and provides examples of how to evaluate expressions and solve equations. It explains that parentheses, exponents, multiplication/division from left to right, and addition/subtraction from left to right have priority in calculations. Algebraic expressions and equations are introduced along with rules for manipulating integers and solving different types of equations.