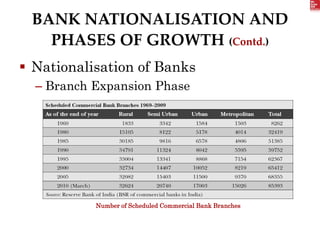
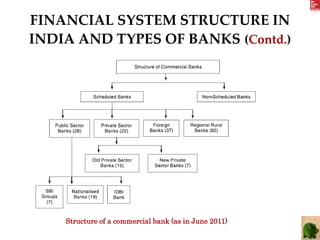
The document summarizes the evolution of banking in India from 1786 to the present. It discusses 3 phases: (1) Early Indian banks from 1786-1969 prior to reforms, which saw the establishment of colonial banks and slow growth. (2) Nationalization of banks from 1969-1991 for social benefits and rural credit. (3) Post-1991 reforms introducing privatization, competition and new technologies. Key events included the nationalization of SBI in 1955 and major commercial banks in 1969/1980, establishing RRBs in 1975, and liberalization reforms starting in 1992.