Banking originated in India in the late 18th century with the Bank of Hindustan and General Bank of India. The oldest and largest bank still in existence is the State Bank of India, which originated from the Bank of Calcutta in 1806. The three presidency banks of Bengal, Bombay and Madras merged in 1921 to form the Imperial Bank of India, which became the State Bank of India after independence. Banking reforms since the early 1990s have led to increased competition and participation of private banks in India's banking sector.





![Public sector banks
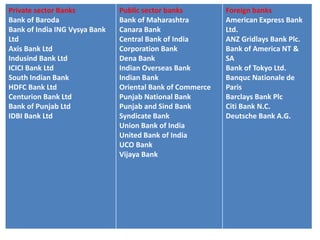
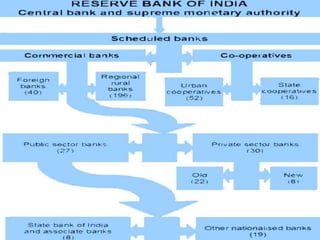
• Public Sector Banks (PSBs) are banks where a
majority stake (i.e. more than 50%) is held by
a government. The shares of these banks are
listed on stock exchanges. There are a total of
27 PSBs in India [19 Nationalised banks + 6
State bank group (SBI + 5 associates) + 1 IDBI
bank (Other Public Sector-Indian Bank) = 26
PSBs + 1 recent Bhartiya Mahila Bank].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankingsector-170419090407/85/Banking-sector-8-320.jpg)














