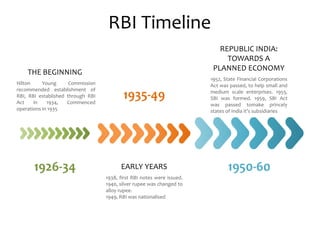
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was established in 1935 as the central bank of India. It regulates banking, money supply and interest rates in India. Some key roles of RBI include acting as a monetary authority, regulator of the financial system, manager of foreign exchange, issuer of currency and banking licenses. RBI also plays an important developmental role in promoting banking, industrial finance and exports. Recently, RBI has mandated online filing of FDI forms and capacity building certification for banks in areas like treasury operations, risk management and credit management.