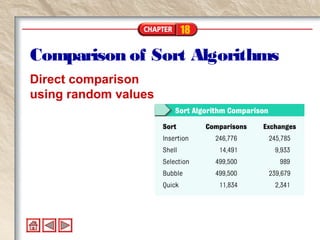
The document discusses different sorting algorithms and methods. It introduces the concept of sortable objects that implement the Comparable interface and defines sorting algorithms like insertion sort, shell sort, selection sort, bubble sort, and quicksort. It also describes how sorting is implemented for arrays and collections in Java and the classes and methods involved in the sorting process.