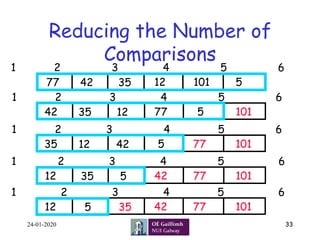
The document provides an overview of different sorting algorithms, including selection sort, insertion sort, bubble sort, and others. It discusses the basic approach for each algorithm through examples and pseudocode. Selection sort finds the minimum value and swaps it into the first position on each pass. Insertion sort inserts each element into the sorted portion of the array. Bubble sort compares adjacent elements and swaps them if out of order, bubbling the largest value to the end.











![Selection Sort Pseudocode
procedure selection sort
list : array of items
n : size of list
for i = 1 to n - 1
/* set current element as minimum*/
min = i
/* check the element to be minimum */
for j = i+1 to n
if list[j] < list[min] then
min = j;
end if
end for
/* swap the minimum element with the current element*/
if indexMin != i then
swap list[min] and list[i]
end if
end for
end procedure
24-01-2020 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-14-ct1120-200228020736/85/L-14-ct1120-12-320.jpg)


![Insertion Sort
• That is, array[0] and array[1] are in order
with respect to each other.
• Then the value in array[2] is put into its
proper place, so array [0]…. array[2] is sorted
and so on.
36
24
10
6
12
36
24
10
6
12
10
24
36
6
12
6
10
24
36
12
6
10
12
24
36
24
36
10
6
12
24-01-2020 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-14-ct1120-200228020736/85/L-14-ct1120-15-320.jpg)
![Insertion Sort
• Our strategy is to search for insertion
point from the beginning of the array and
shift the element down to make room for
new element
• We compare the item at array[current] to
one before it, and swap if it is less.
• We then compare array[current-1] to one
before it and swap if necessary.
24-01-2020 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-14-ct1120-200228020736/85/L-14-ct1120-16-320.jpg)


![Insertion Sort Pseudocode
procedure insertionSort( A : array of items )
int holePosition
int valueToInsert
for i = 1 to length(A) inclusive do:
/* select value to be inserted */
valueToInsert = A[i]
holePosition = i
/*locate hole position for the element to be inserted */
while holePosition > 0 and A[holePosition-1] > valueToInsert do:
A[holePosition] = A[holePosition-1]
holePosition = holePosition -1
end while
/* insert the number at hole position */
A[holePosition] = valueToInsert
end for
end procedure
24-01-2020 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-14-ct1120-200228020736/85/L-14-ct1120-19-320.jpg)















![Bubble Sort Algorithm
begin BubbleSort(list)
for all elements of list
if list[i] > list[i+1]
swap(list[i], list[i+1])
end if
end for
return list
end BubbleSort
24-01-2020 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-14-ct1120-200228020736/85/L-14-ct1120-36-320.jpg)
![Bubble Sort Pseudocode
procedure bubbleSort( list : array of items )
loop = list.count;
for i = 0 to loop-1 do:
swapped = false
for j = 0 to loop-1 do:
/* compare the adjacent elements */
if list[j] > list[j+1] then
/* swap them */
swap( list[j], list[j+1] )
swapped = true
end if
end for
24-01-2020 37
/*if no number was swapped that means
array is sorted now, break the loop.*/
if(not swapped) then
break
end if
end for
end procedure return list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-14-ct1120-200228020736/85/L-14-ct1120-37-320.jpg)


